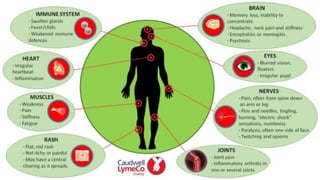
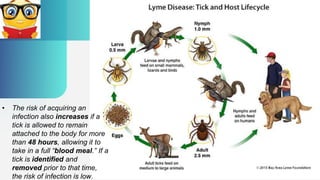
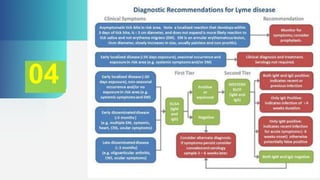
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted to humans mainly by deer ticks, and presents a variety of symptoms that develop after a tick bite. It is classified into three stages: localized, disseminated, and persistent, with the latter potentially leading to chronic conditions such as lyme arthritis. Prevention includes avoiding tick-infested areas, wearing protective clothing, and prompt tick removal to minimize infection risk.










![PREVENTION
06
• Avoid tick-infested areas, especially during summer months
• Walk on cleared or paved surfaces when available, rather
than tall grass
• Wear long pants, sleeved shirts, and close-toed shoes
• Light-colored clothing makes it easier to locate a tick
• Always check for ticks whenever coming from outdoors. The
risk of Lyme disease is minimized when the tick is removed
within 36 hours.
• Showering immediately after being outdoors reduces the risk
of tick attachment
• Wash clothing that's been outdoors (dryer kills ticks)
• Remove the tick only by using tweezers to pull the tick
directly off the skin (no twisting)
• After removal of the tick, wash site with soap and water and
then swab the area with antiseptic [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lyme-200502235937/85/Lyme-Disease-Their-outcomes-and-different-treatment-options-16-320.jpg)


