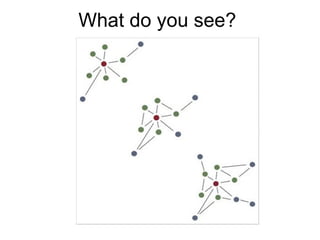
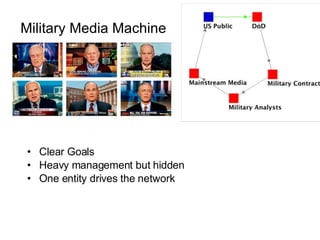
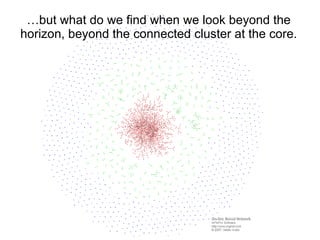
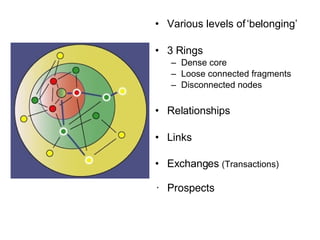
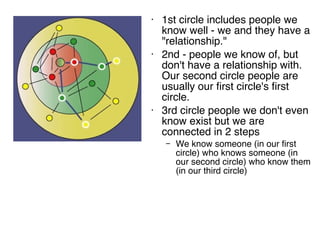
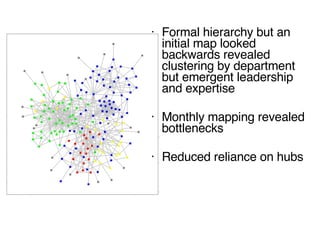
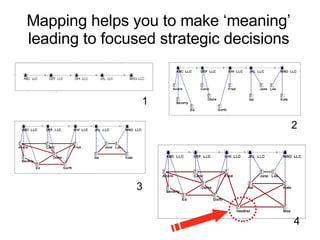
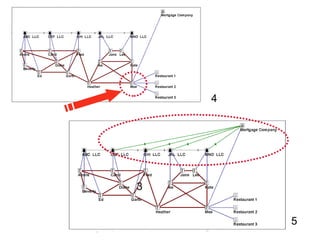
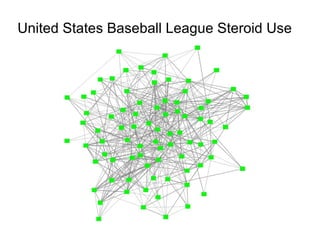
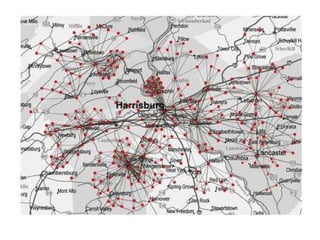
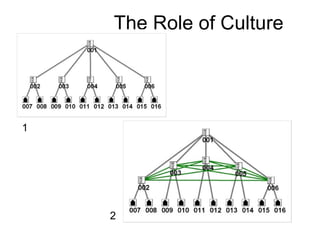
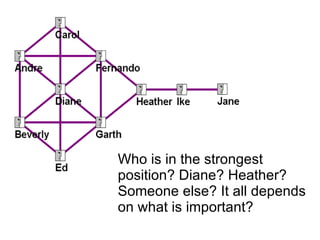
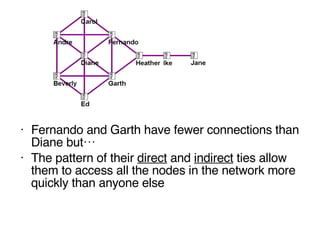
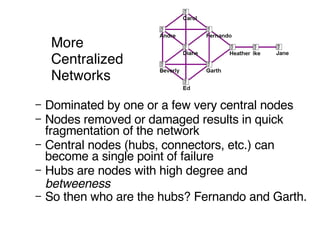
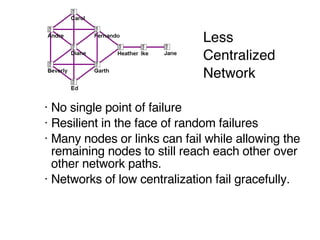
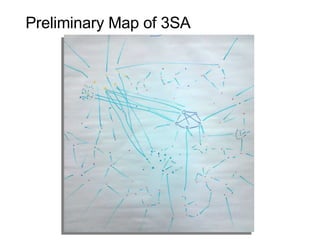
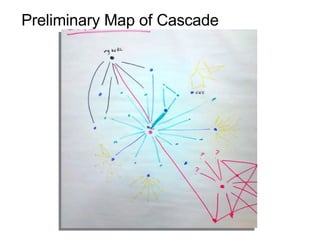
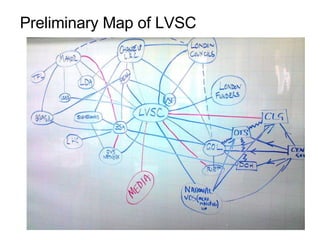
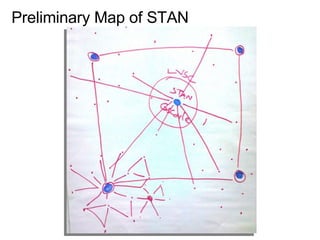
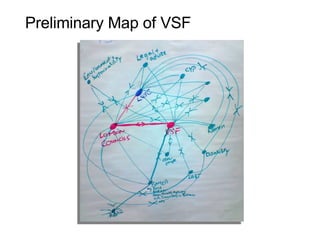
This document discusses network theory and mapping networks. It explains that mapping existing networks can reveal strengths, weaknesses, disconnects, and influential members. Regular mapping also shows how networks progress over time and can identify bottlenecks. Mapping helps strategically understand relationships and connections within an organization or community. The document also discusses different types of network structures and the roles of central and peripheral members in information spreading.