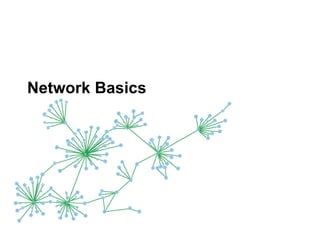
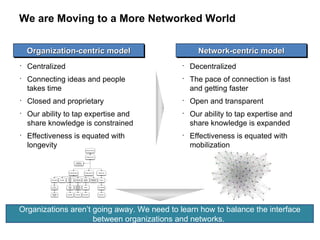
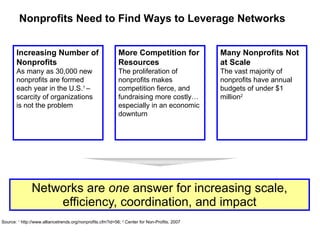
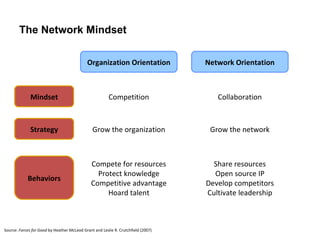
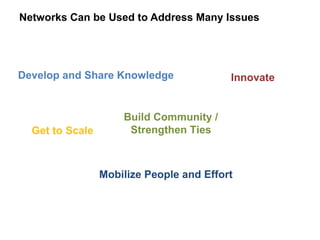
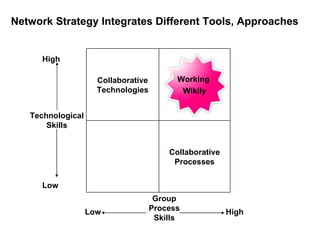
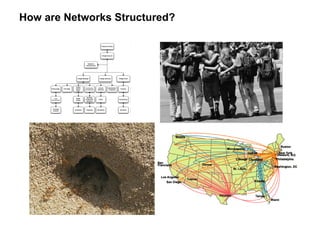
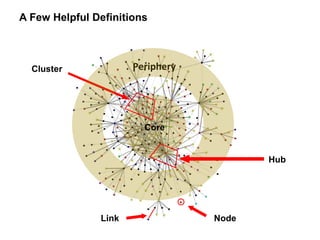
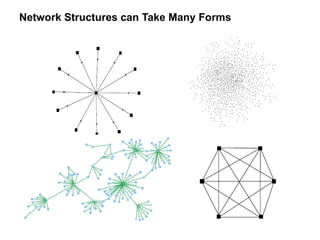
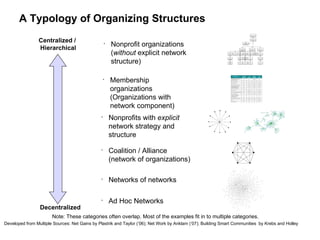
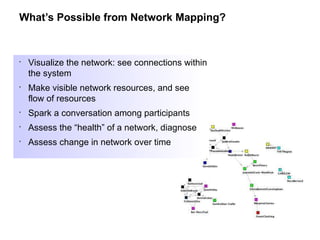
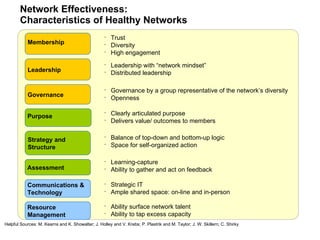
The document discusses a working session for Packard Foundation grantees about network effectiveness. It provides an overview of network structures and characteristics of healthy networks. The session goals are to understand network thinking, map networks, and discuss network effectiveness. Network structures can range from centralized to decentralized. Key characteristics of effective networks include clear purpose, member engagement, leadership, communication, and resource sharing. Challenges in networks include defining boundaries and building trust among participants.