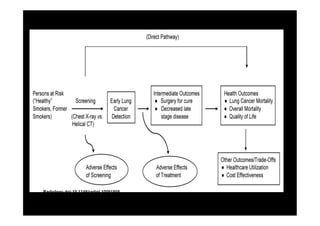
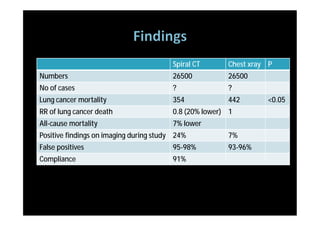
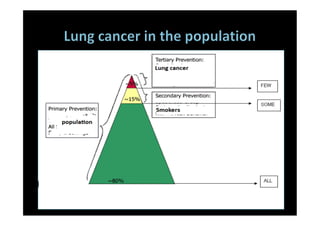
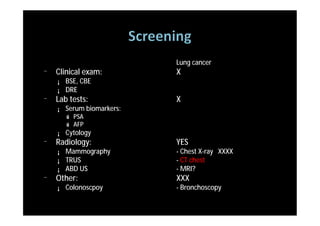
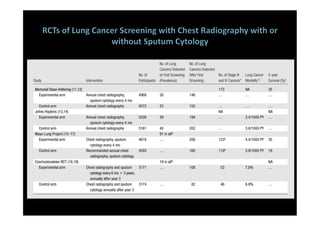
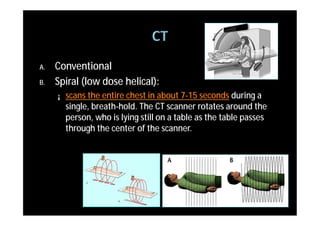
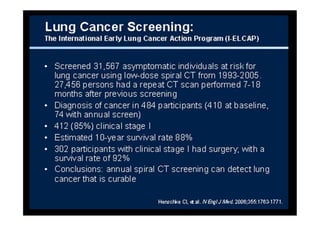
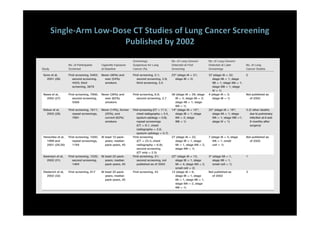
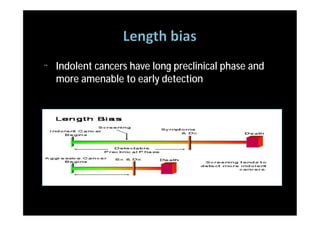
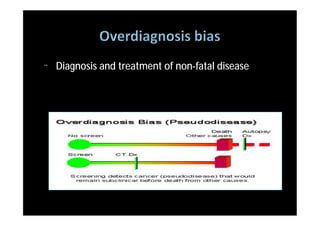
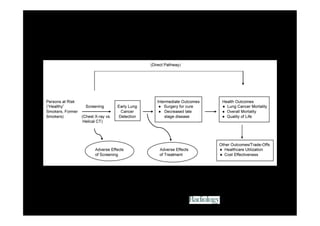
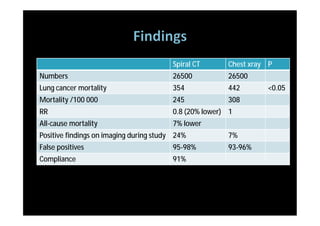
The study evaluated annual low-dose helical CT screening versus standard chest x-ray for lung cancer screening in high-risk individuals aged 55-74 years who were heavy smokers. Over 53,000 participants were randomized across 33 sites in the U.S. The trial was stopped early based on a recommendation when interim results found a 20% reduction in lung cancer mortality with CT screening. CT screening found more positive cases but also had higher false positive rates compared to chest x-ray.