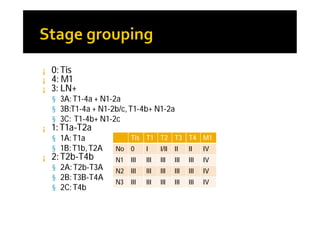
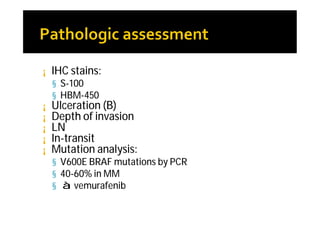
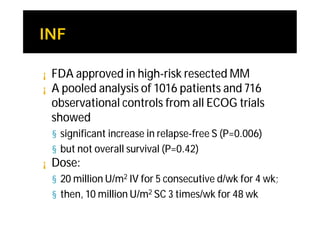
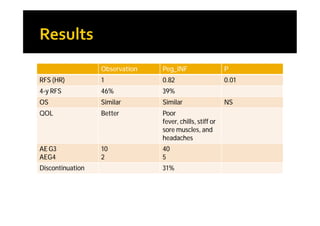
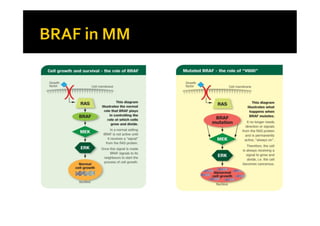
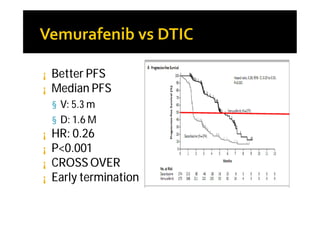
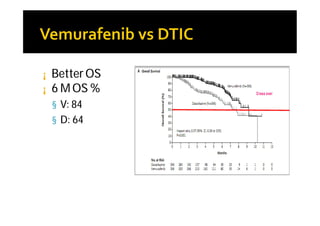
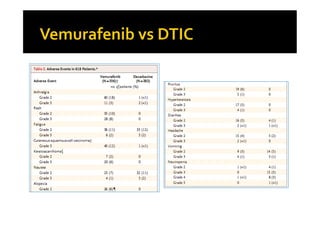
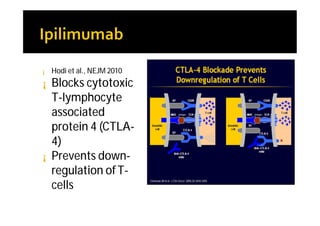
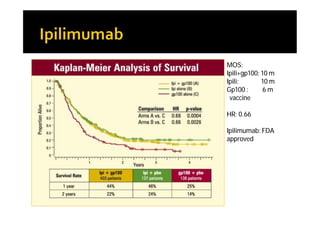
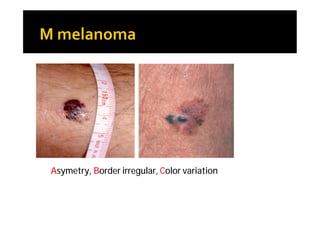
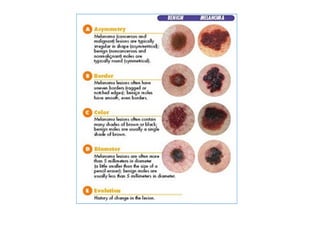
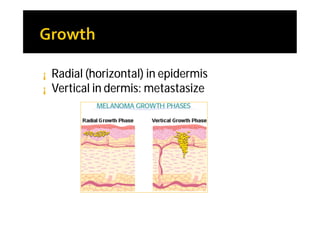
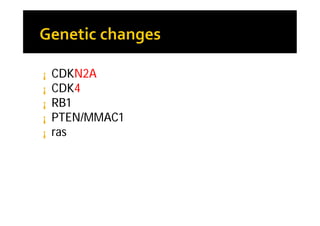
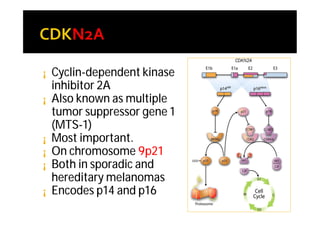
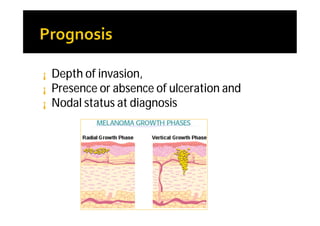
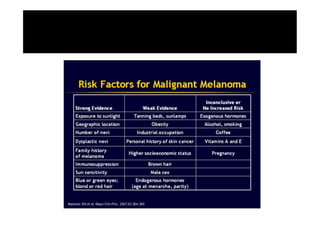
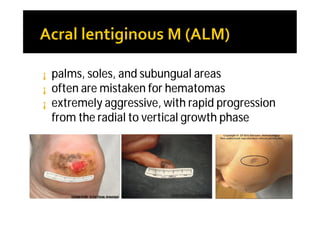
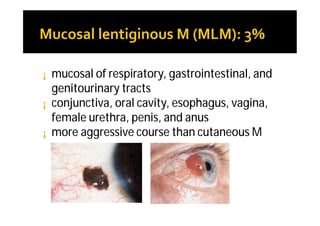
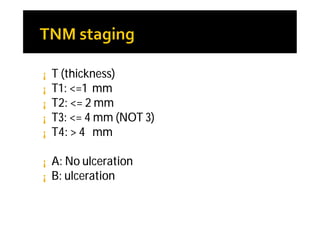
Melanoma arises from neural crest cells that migrate and produce the pigment melanin. It can present in skin or mucosal surfaces and commonly spreads from radial to vertical growth phases as it invades deeper tissues. Treatment depends on tumor stage and characteristics as well as mutation status, and may involve surgery, radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.





![¡ N
¡ N1: 1 LN+ [a: micrometastasis (clinically occult), b: macrometastasis (clinically apparent)]
¡ N2: 2-3 LN+ [a: micrometastasis b: macrometastasis , c: intransit without LN]
¡ N3: >3 (=>4) LN+ or matted LN or intransit+LN
¡ M
¡ M1a: distant skin, SC, LN with normal LDH
¡ M1b: lung mets with normal LDH
¡ M1c: other sites or elevated LDH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/melanoma102011-130324145447-phpapp02/85/Malignant-Melanoma-10-2011-21-320.jpg)