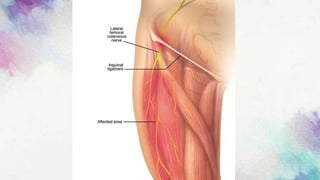
The document covers lumbosacral plexus lesions and diseases, including diabetic neuropathy, lumbosacral plexus syndrome, and lower limb mononeuropathies. It discusses symptoms, causes, classifications, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for various neuropathic conditions affecting the lumbosacral plexus and lower limbs. Diabetic neuropathy is highlighted as a major complication of diabetes, with treatment focusing on improving glycemic control and pain management.