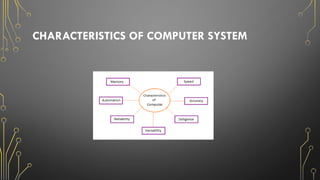
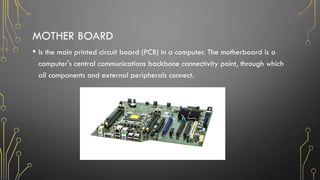
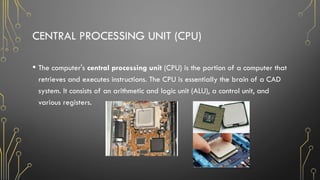
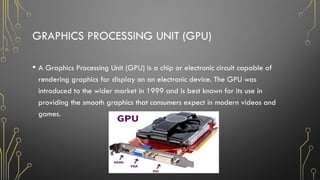
The document outlines the fundamentals of computers, including their definition, types, characteristics, and uses across various sectors such as education, healthcare, and business. It describes components of computer systems like the CPU, memory, and input/output devices, as well as the distinction between hardware and software. Additionally, it discusses safety procedures and care for computer systems to ensure proper functioning.