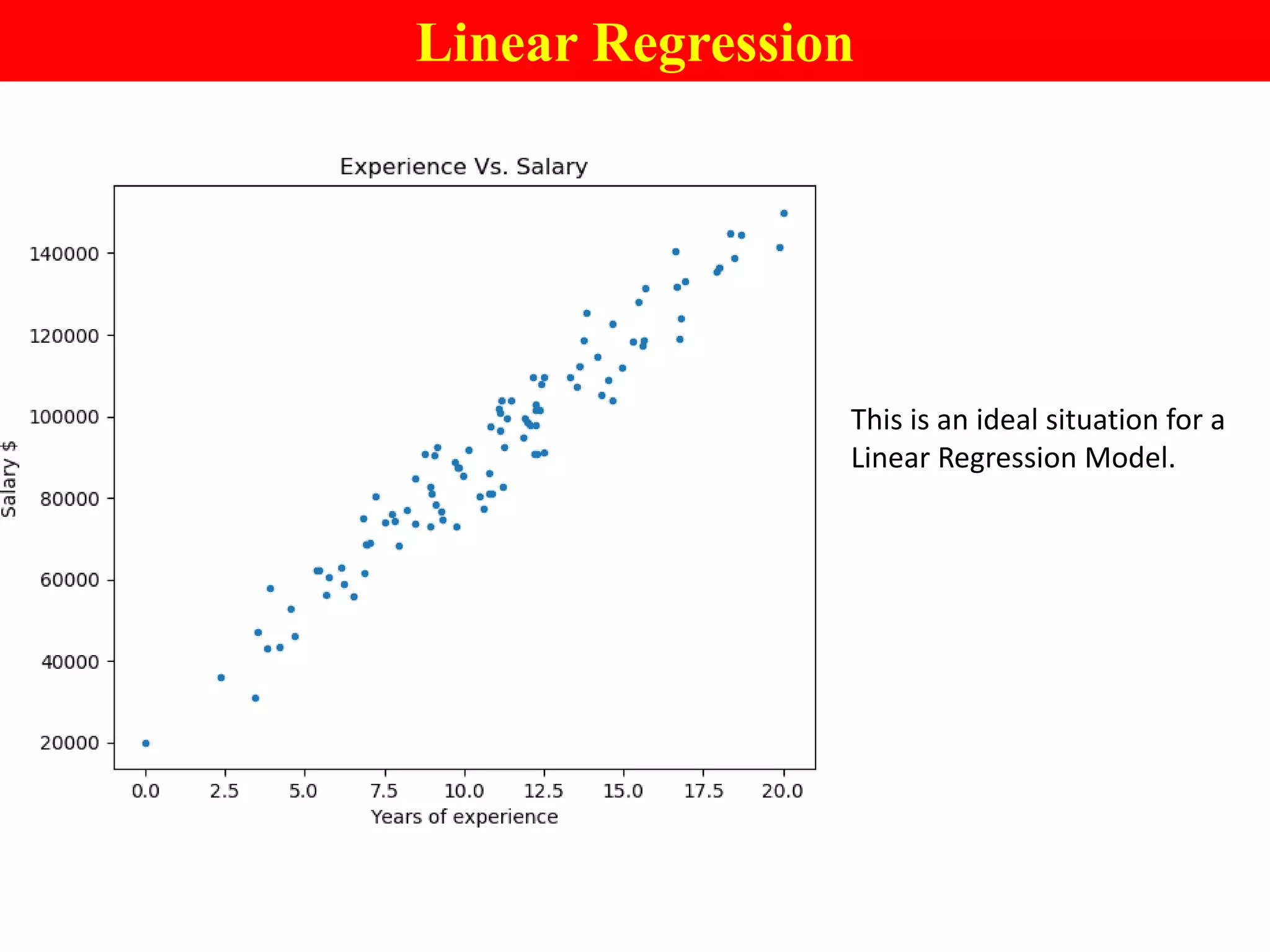
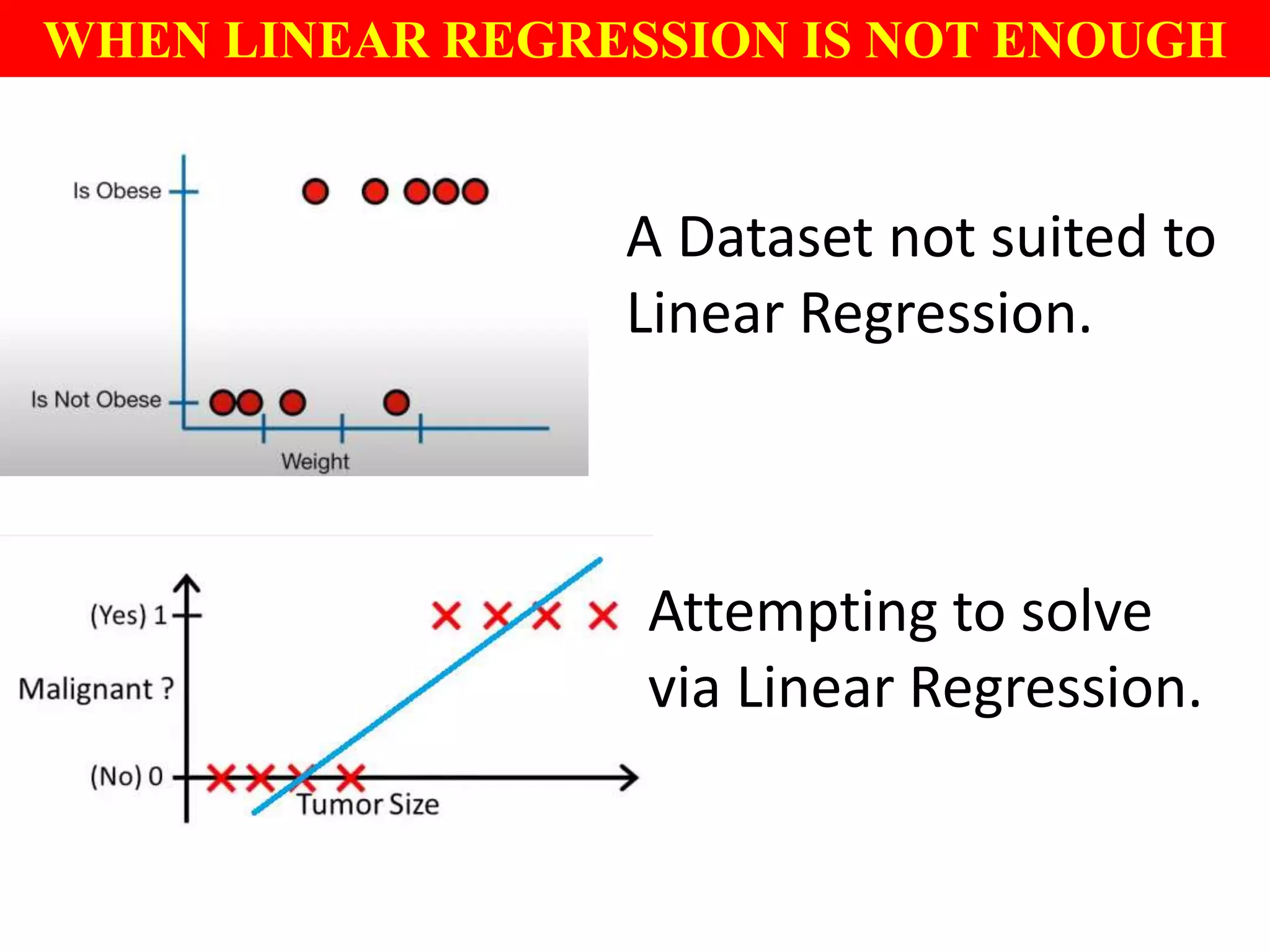
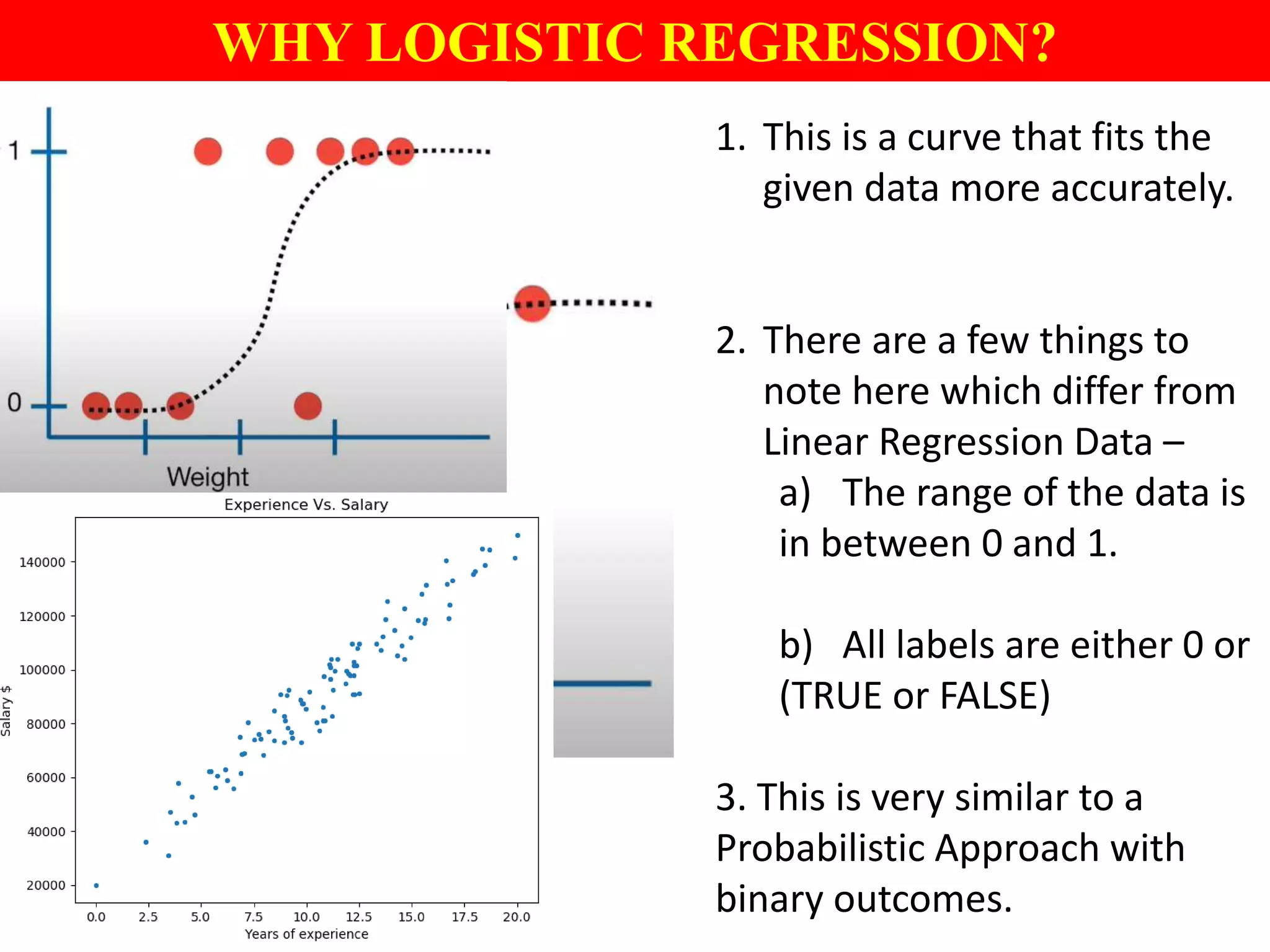
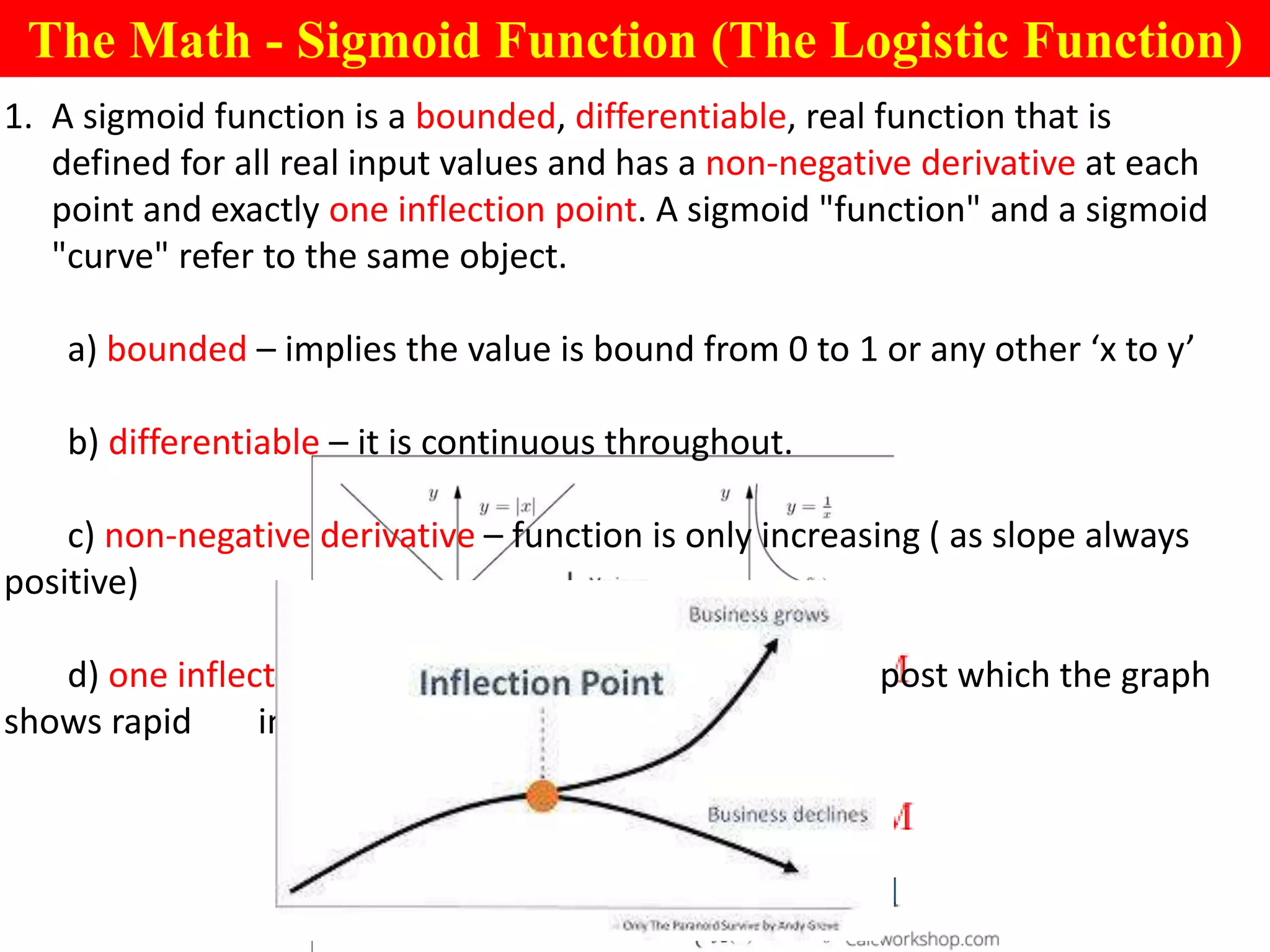
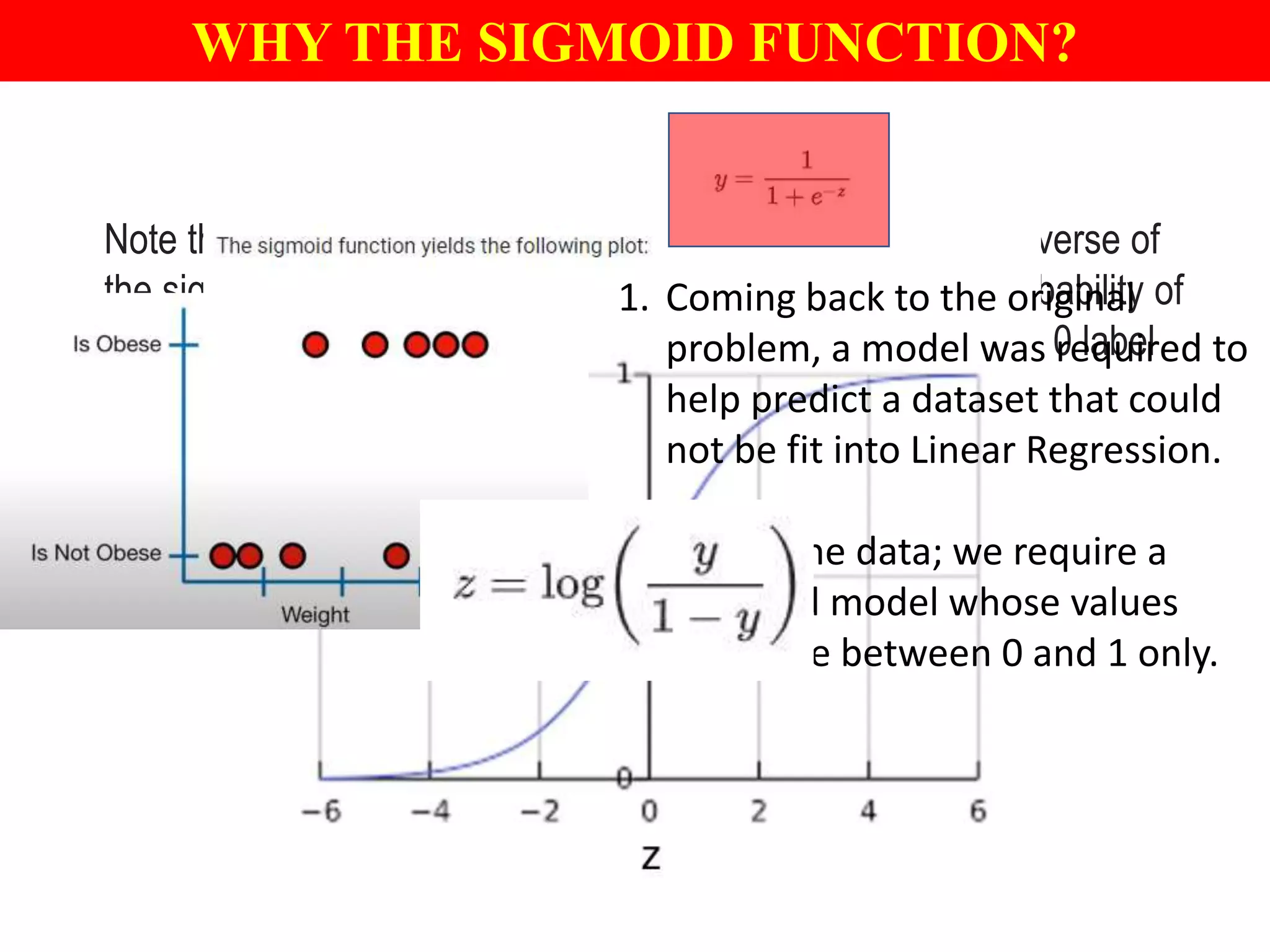
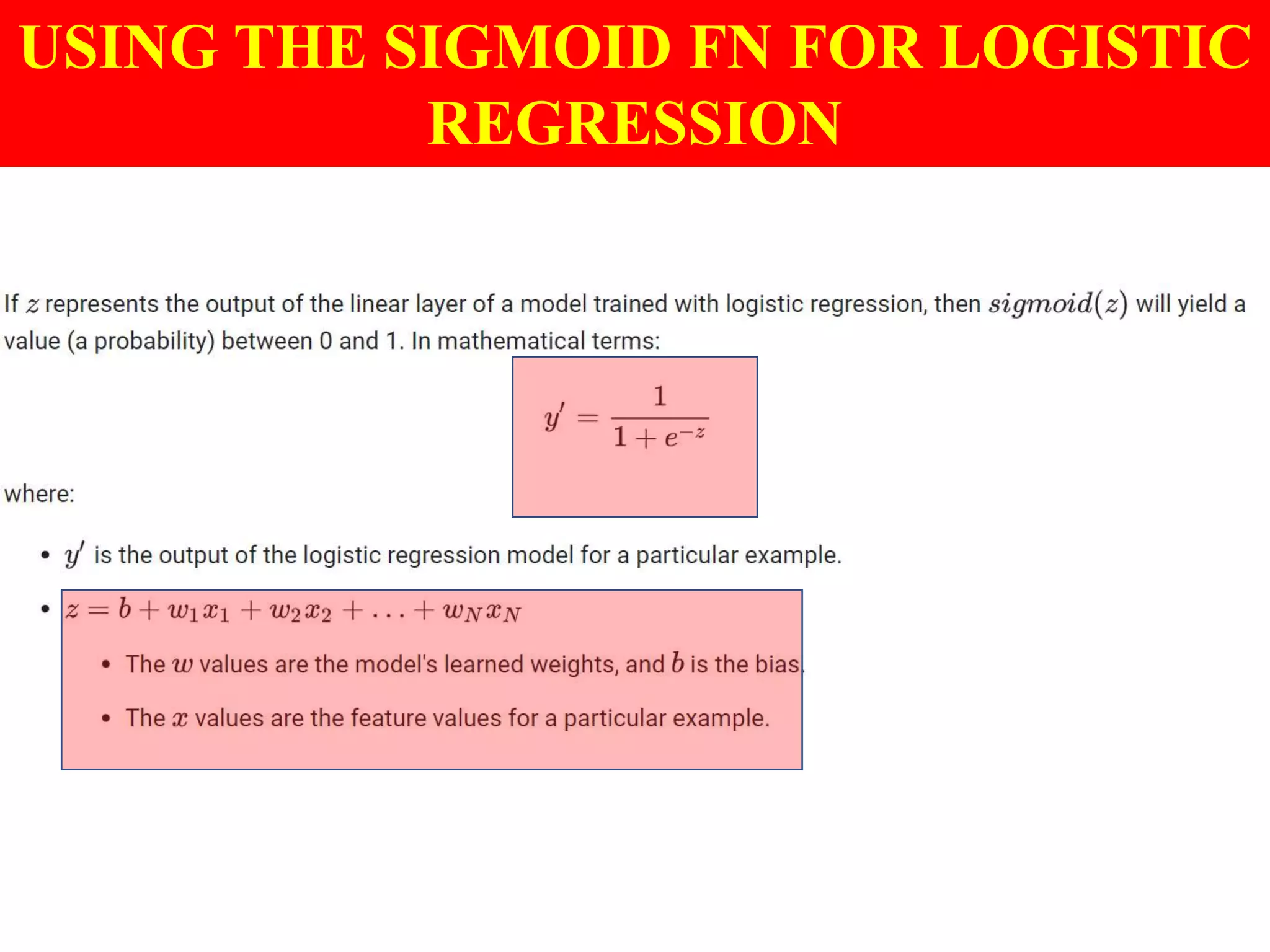
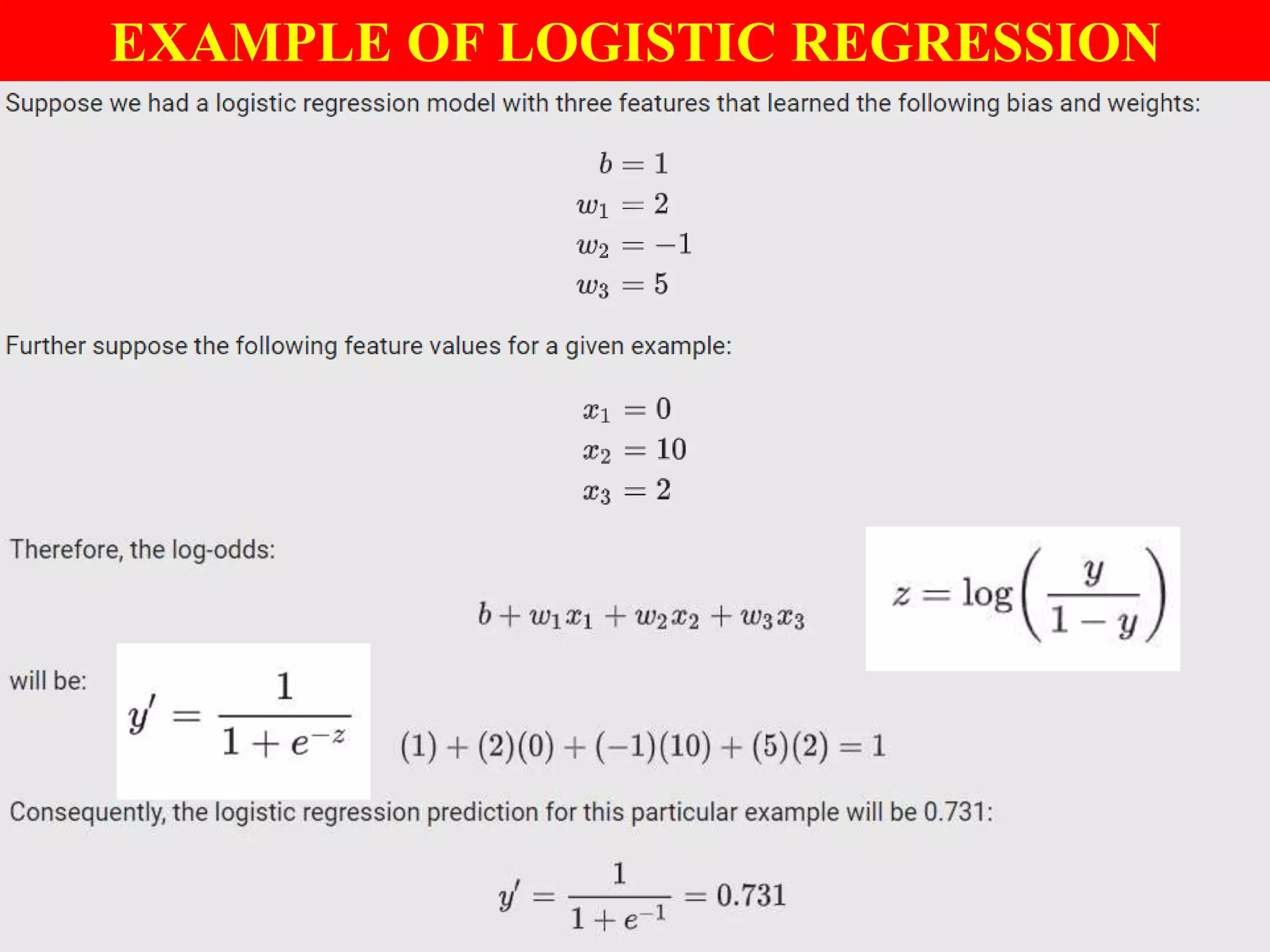
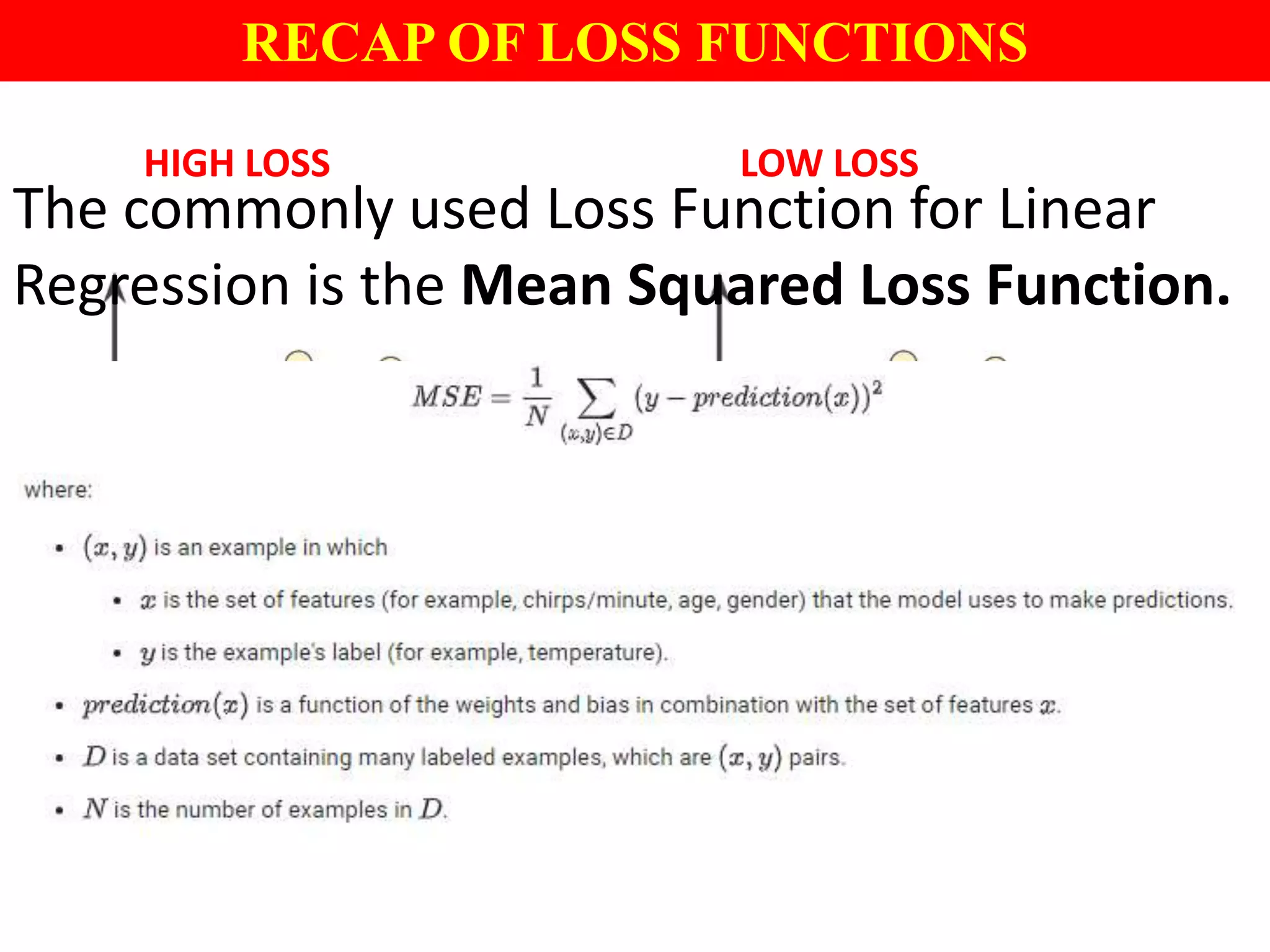
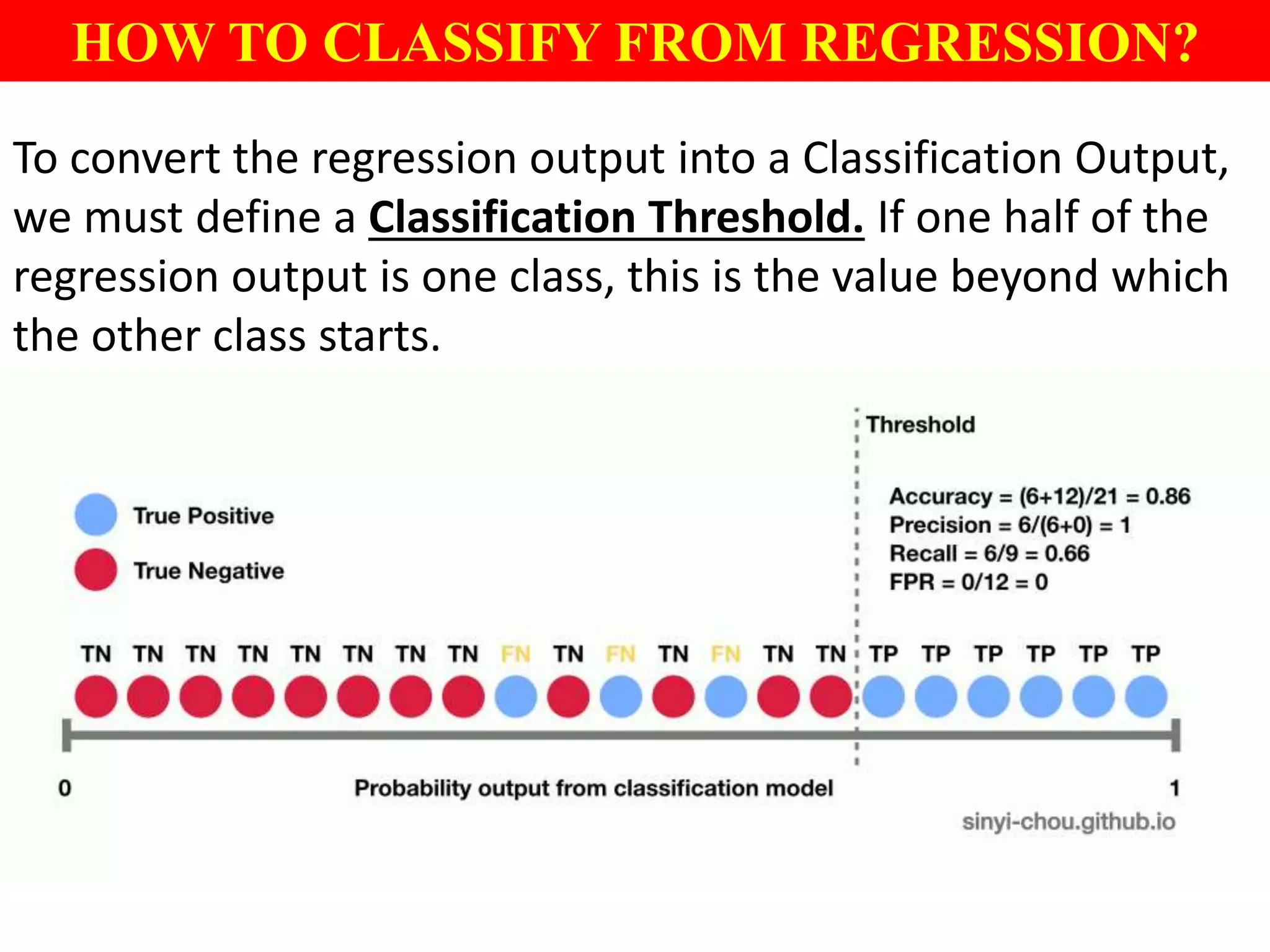
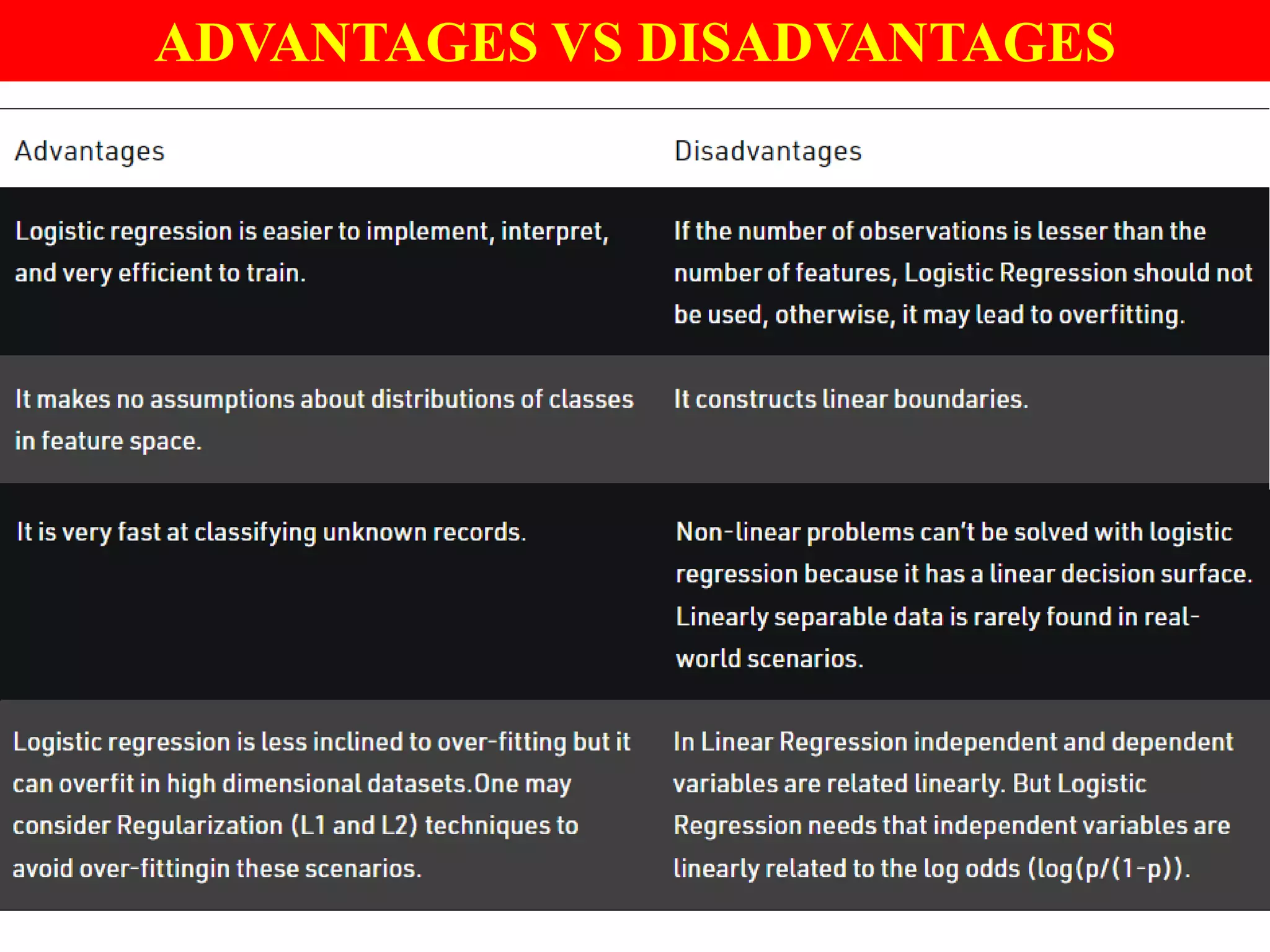
This document provides an introduction to logistic regression, including an overview of its key concepts and applications. Logistic regression can be used for classification problems where the dependent variable is binary. It uses a logistic function to model the probabilities of different outcomes. The loss function for logistic regression is log loss, as it aims to model binary classification probabilities between 0 and 1. Real-world examples of logistic regression include predicting customer purchases, detecting heart disease, and identifying fraudulent activities.