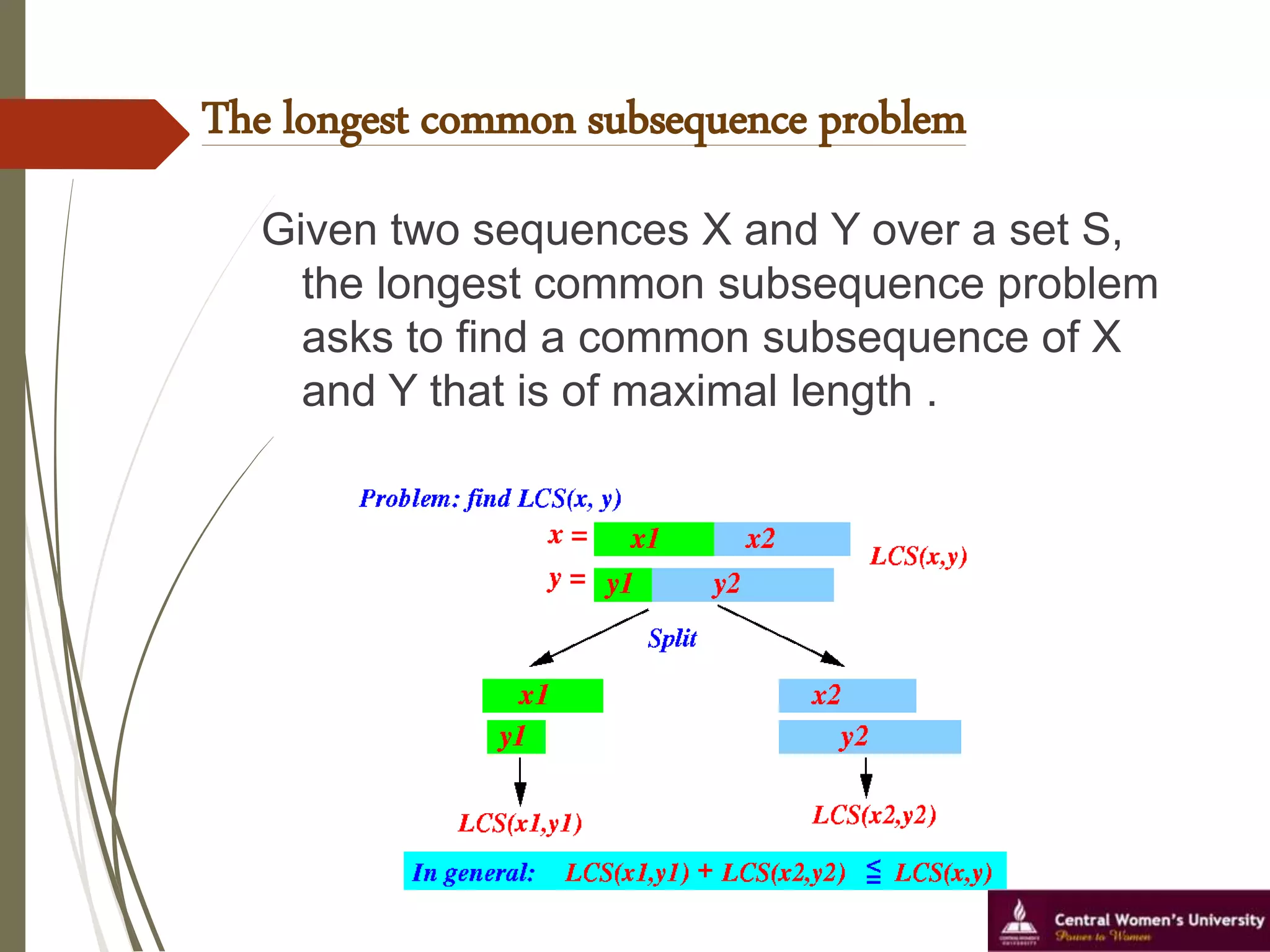
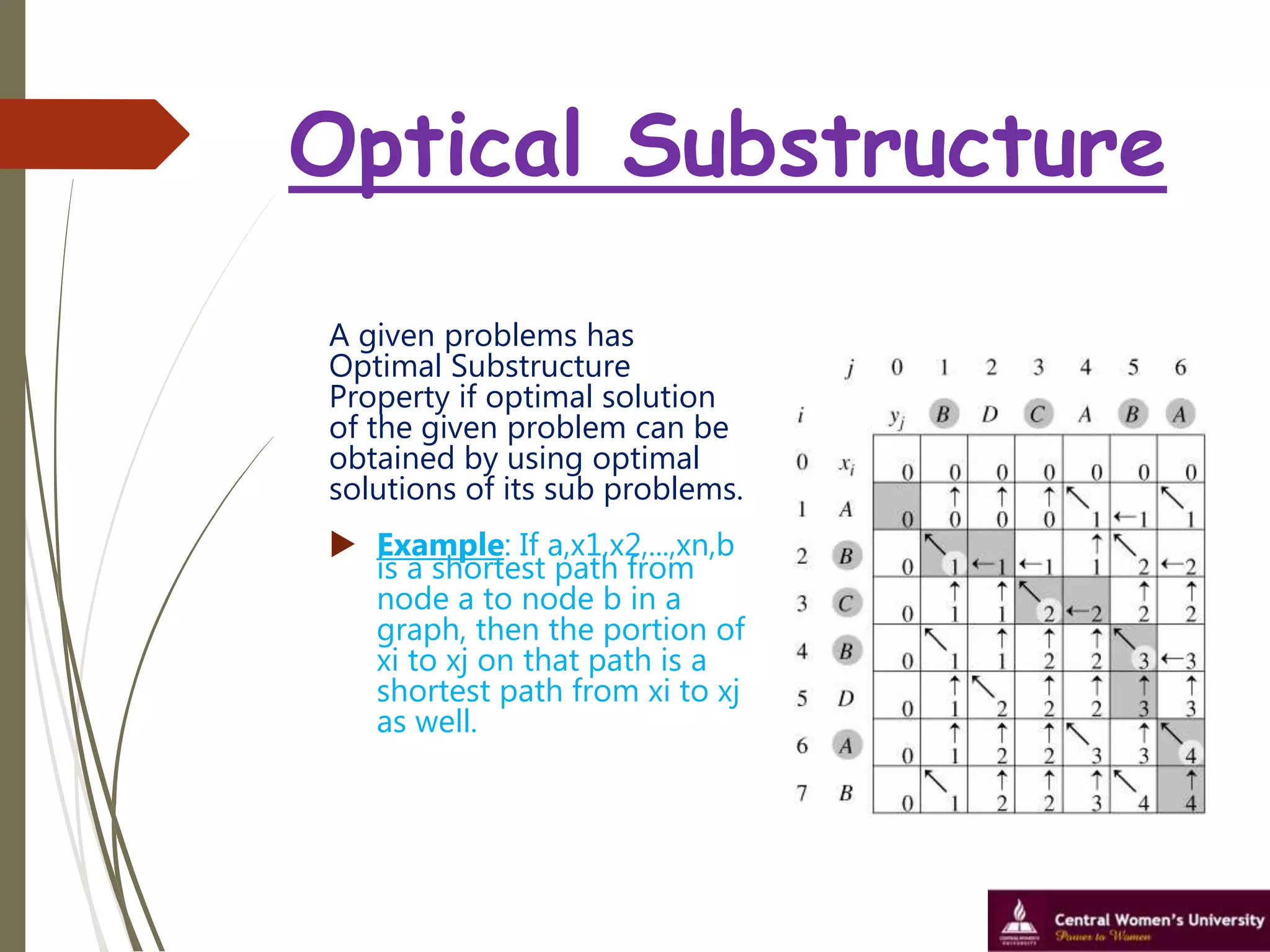
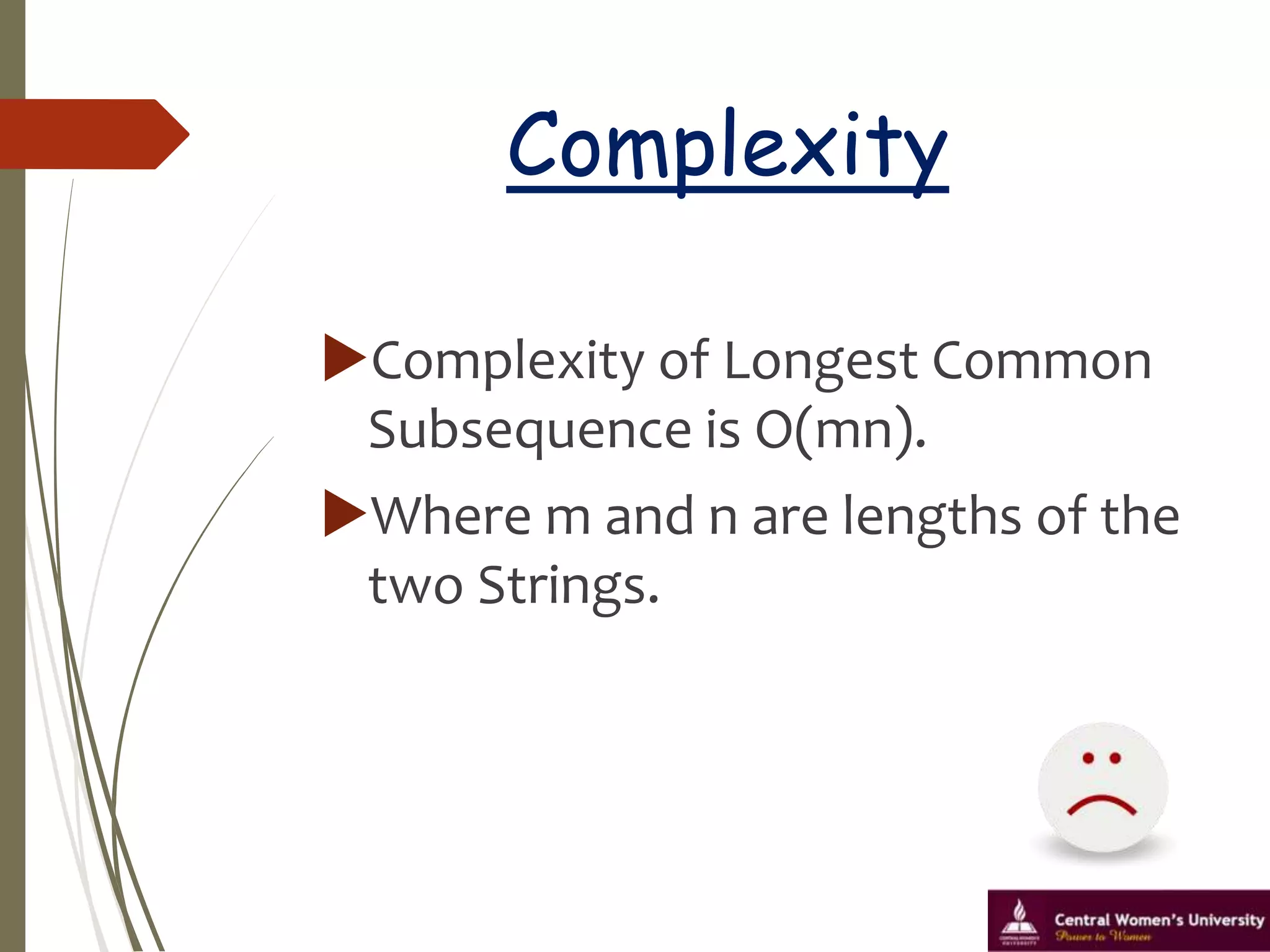
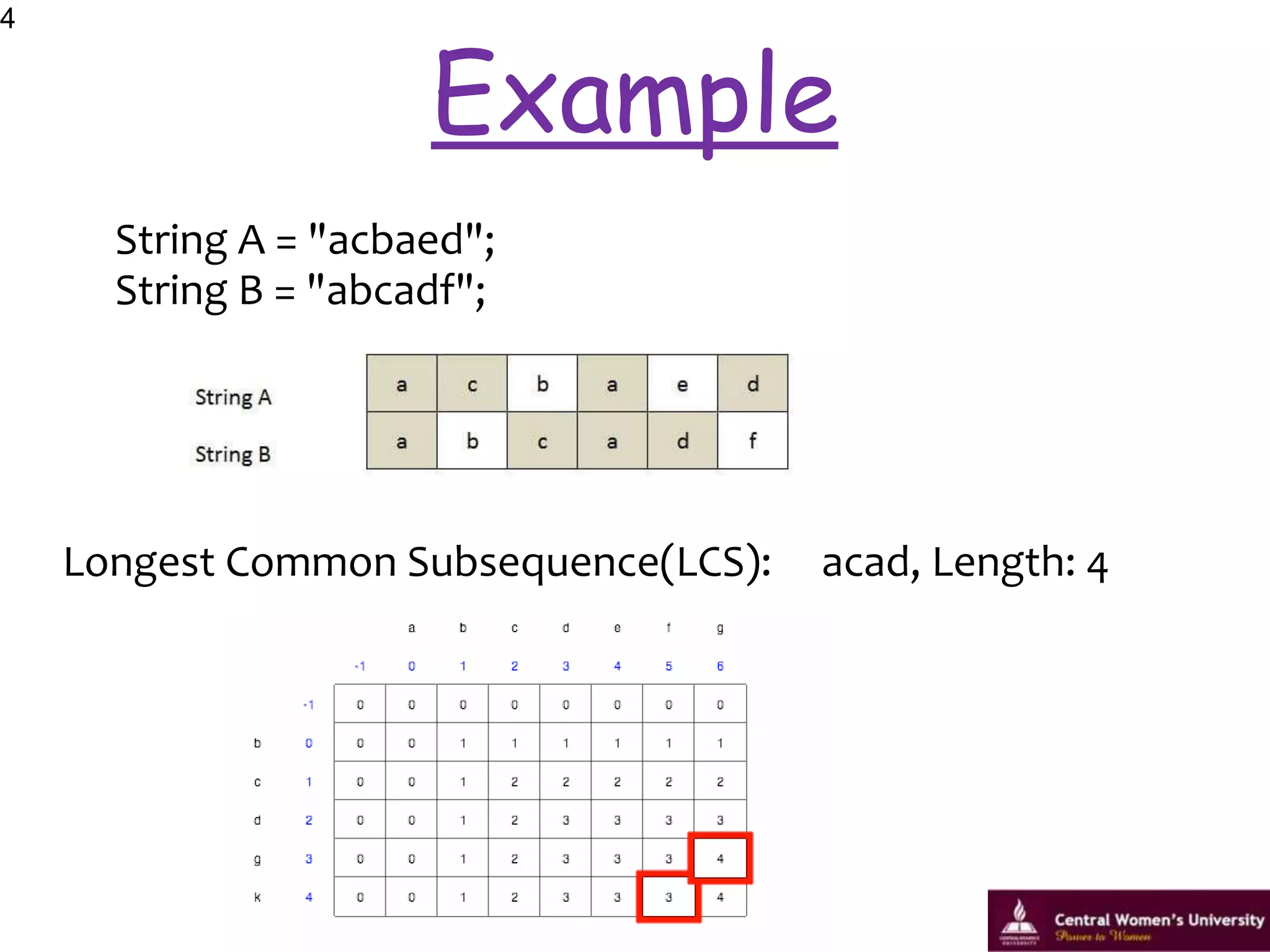
This document discusses the longest common subsequence problem. It defines a longest common subsequence as a sequence that appears in the same relative order in two strings, but not necessarily contiguously. It presents an example longest common subsequence of length 4 between two strings of lengths 6 and 7. It describes a dynamic programming algorithm that runs in O(mn) time, where m and n are the lengths of the input strings, to find the longest common subsequence.




![Algorithm
Algorithm LCS(X,Y ):
Input: Strings X and Y with m and n elements, respectively
Output: For i = 0,...,m; j = 0,...,n, the length C[i, j] of a longest string that is a
subsequence of both the strings.
for i =0 to m
c[i,0] = 0
for j =0 to n
c[0,j] = 0
for i =0 to m
for j =0 to n do
if x i = y j then
c[i, j] = c[i-1, j-1] + 1
else
L[i, j] = max { c[i-1, j] , c[i, j-1]}
return c
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lcsrepaired203-191121203531/75/Longest-Common-Subsequence-6-2048.jpg)