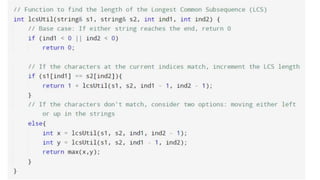
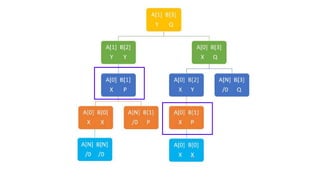
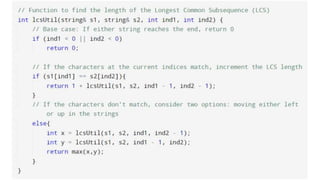
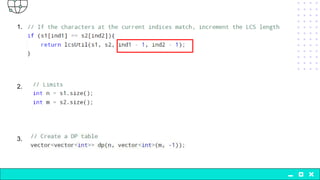
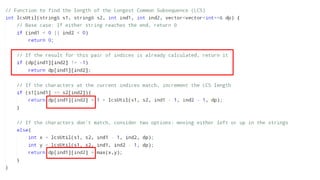
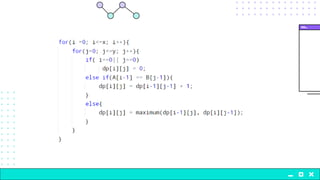
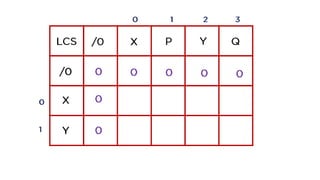
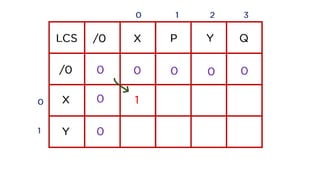
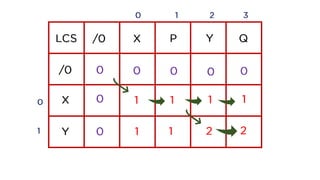
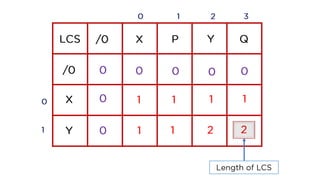
The document discusses the problem of finding the longest common subsequence (LCS) between two strings, explaining definitions and providing examples. It outlines different approaches to solve the problem, including brute force, recursion, memoization, and tabulation, detailing their respective complexities. The document also includes references and credits for resources used in the presentation.