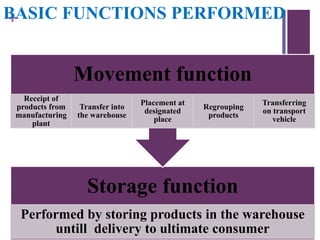
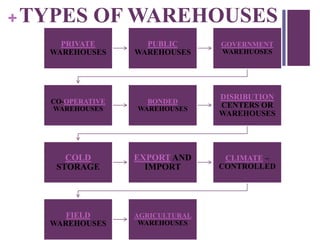
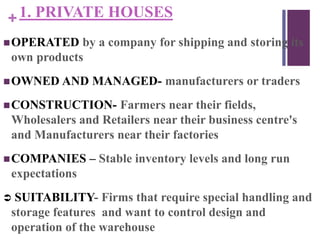
Warehousing involves the large-scale storage of goods in a specified manner. A warehouse is a commercial building used to store goods by various entities until use or delivery. Warehouses perform storage and movement functions. There are different types of warehouses including private, public, government, cooperative, bonded, distribution centers, cold storage, export/import, and field warehouses. Each type has different ownership, management, suitability, and purposes.