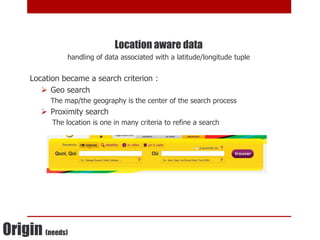
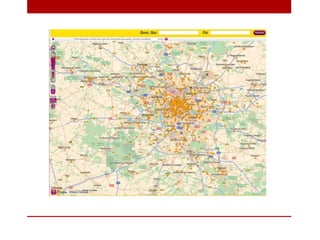
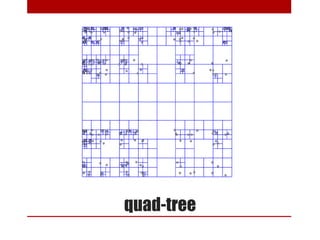
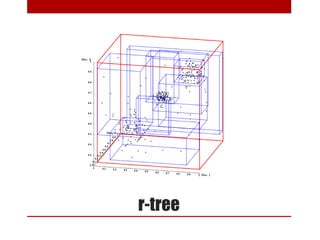
This document discusses using NoSQL databases for geographic search and location-based services. It explains that geographic data is complex to store in SQL databases due to its multiple dimensions and large size. NoSQL databases provide alternatives like quadtrees and R-trees to index and search geographic data more efficiently. The document provides examples of geographic implementations in databases like MongoDB, Lucene, ElasticSearch, and Neo4j. It also gives examples of building point of interest search using technologies like SQL, Lucene, and Hibernate Search.
















![@Indexed
@Spatial
public class Hotel {
@Latitude
Double latitude;
@Longitude
Double longitude;
[...]
Sample indexation code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nogeosqlv3-121003031457-phpapp02/85/No-Geo-SQL-26-320.jpg)


