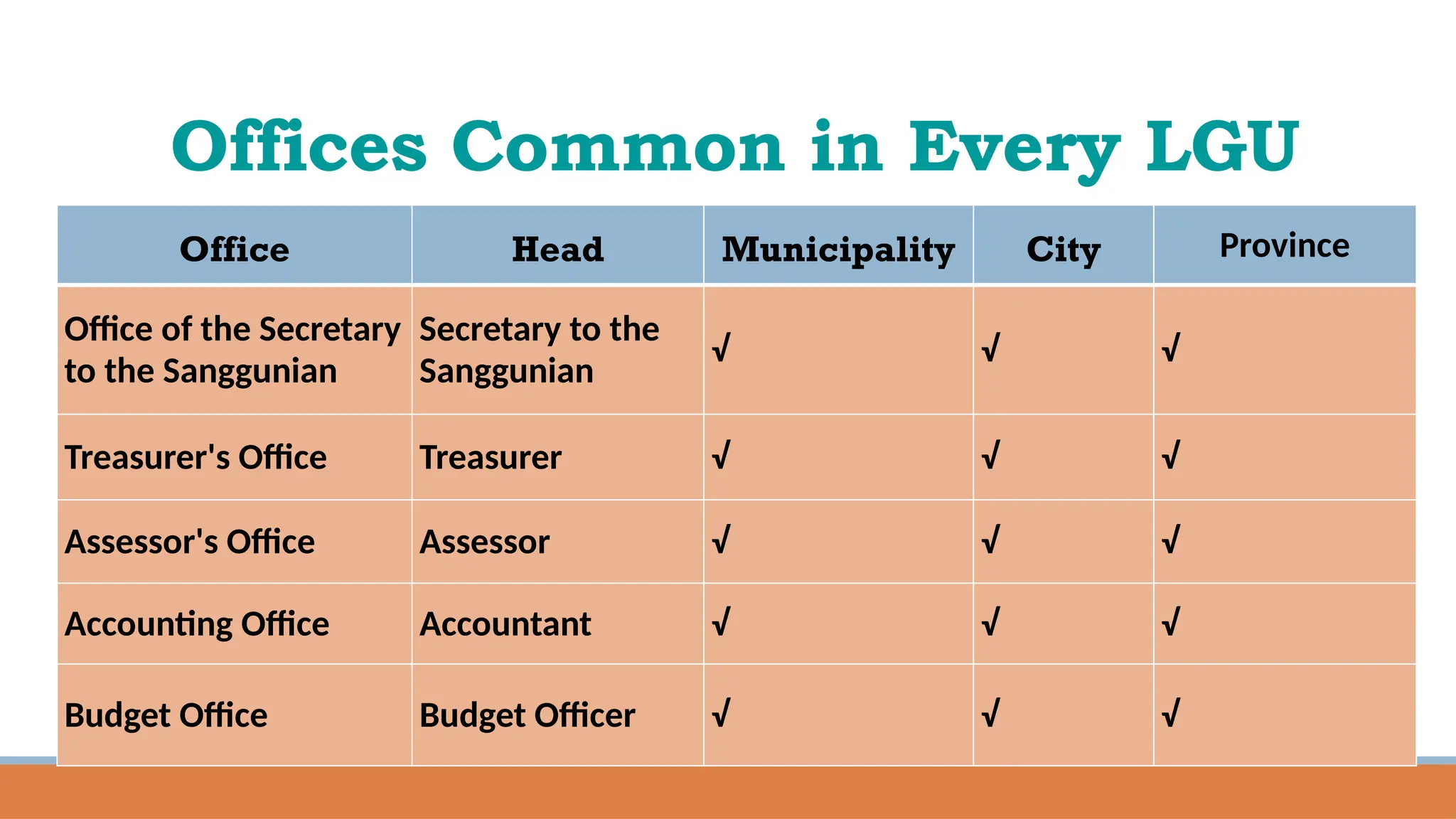
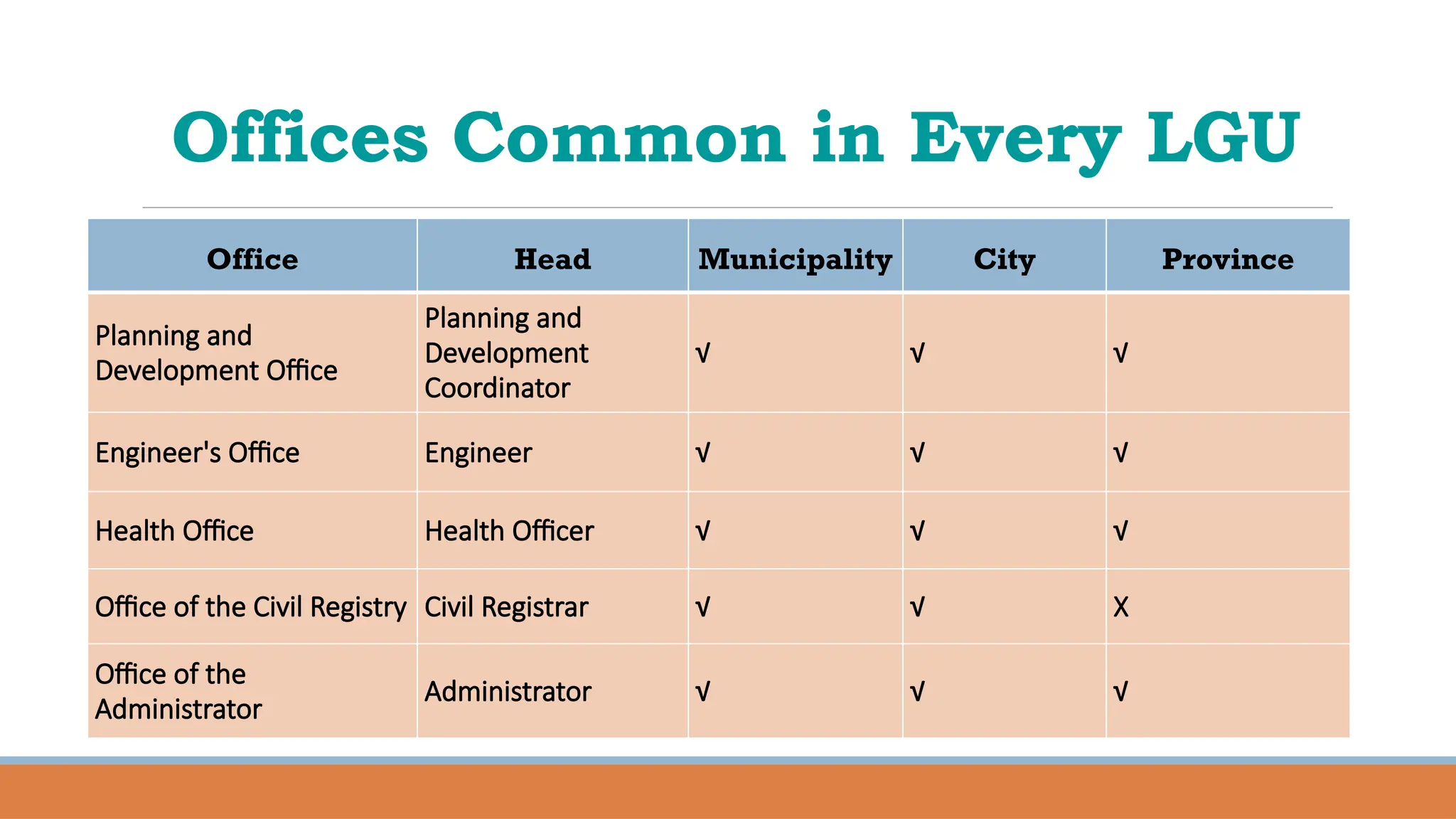
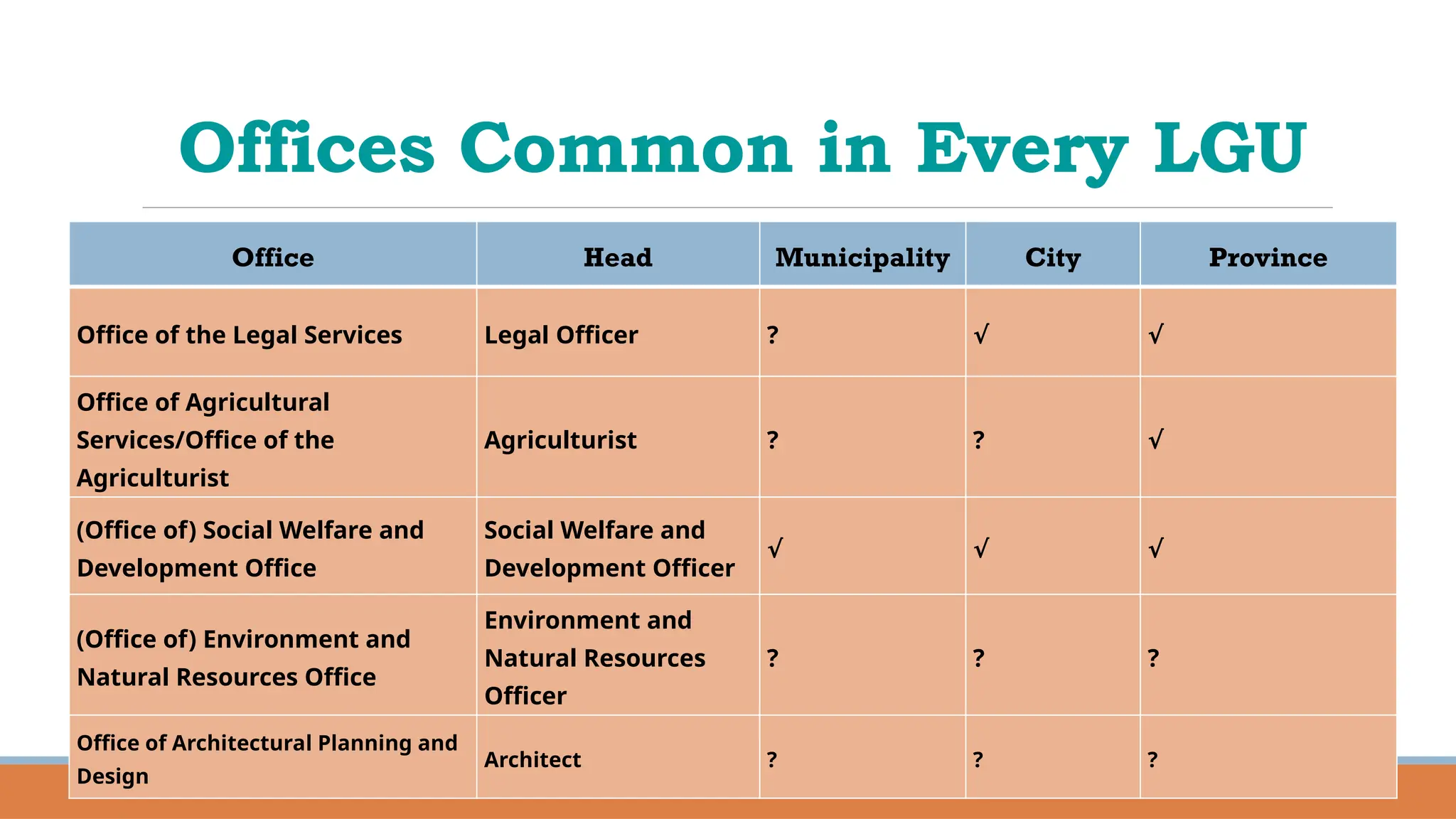
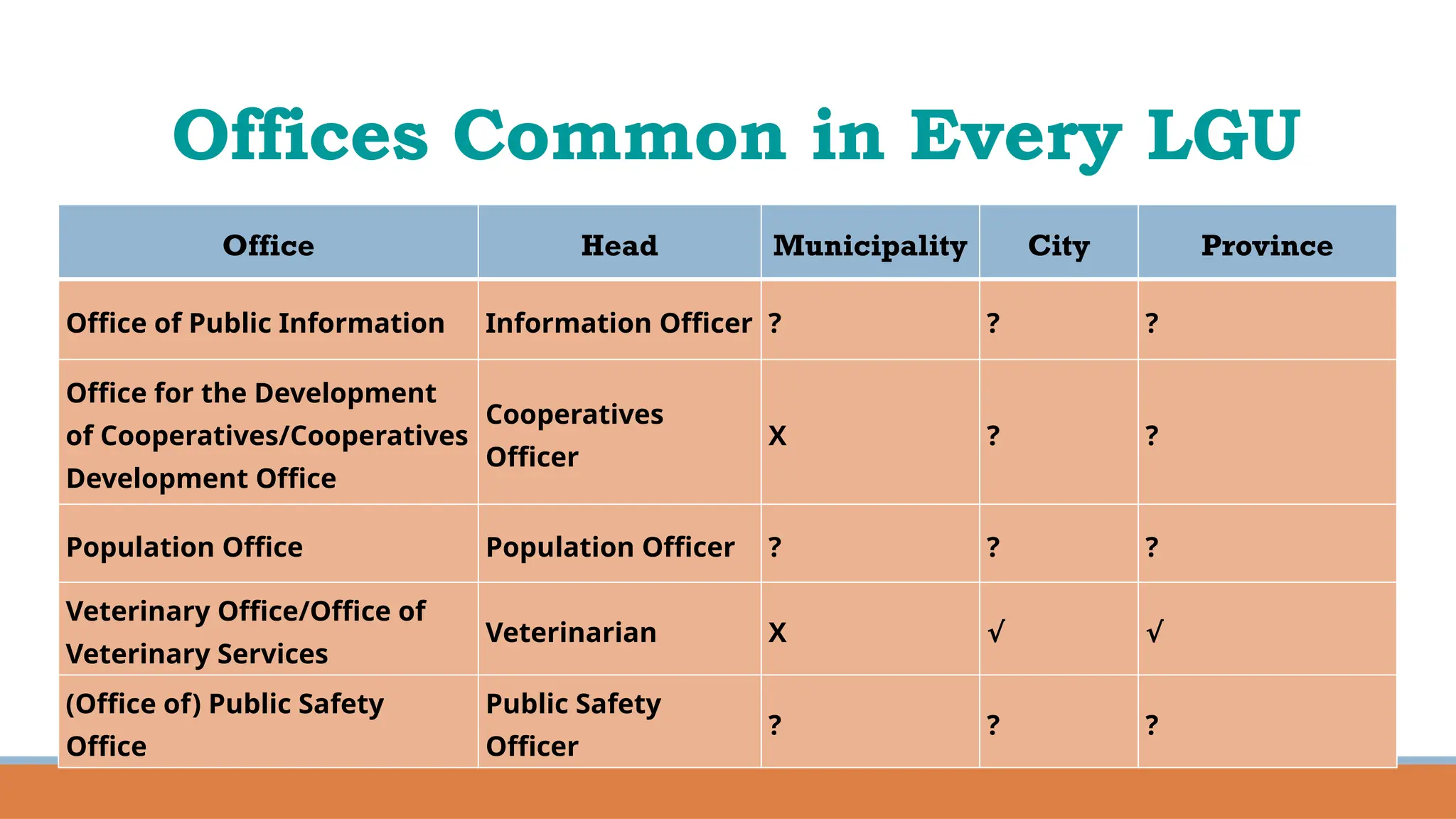
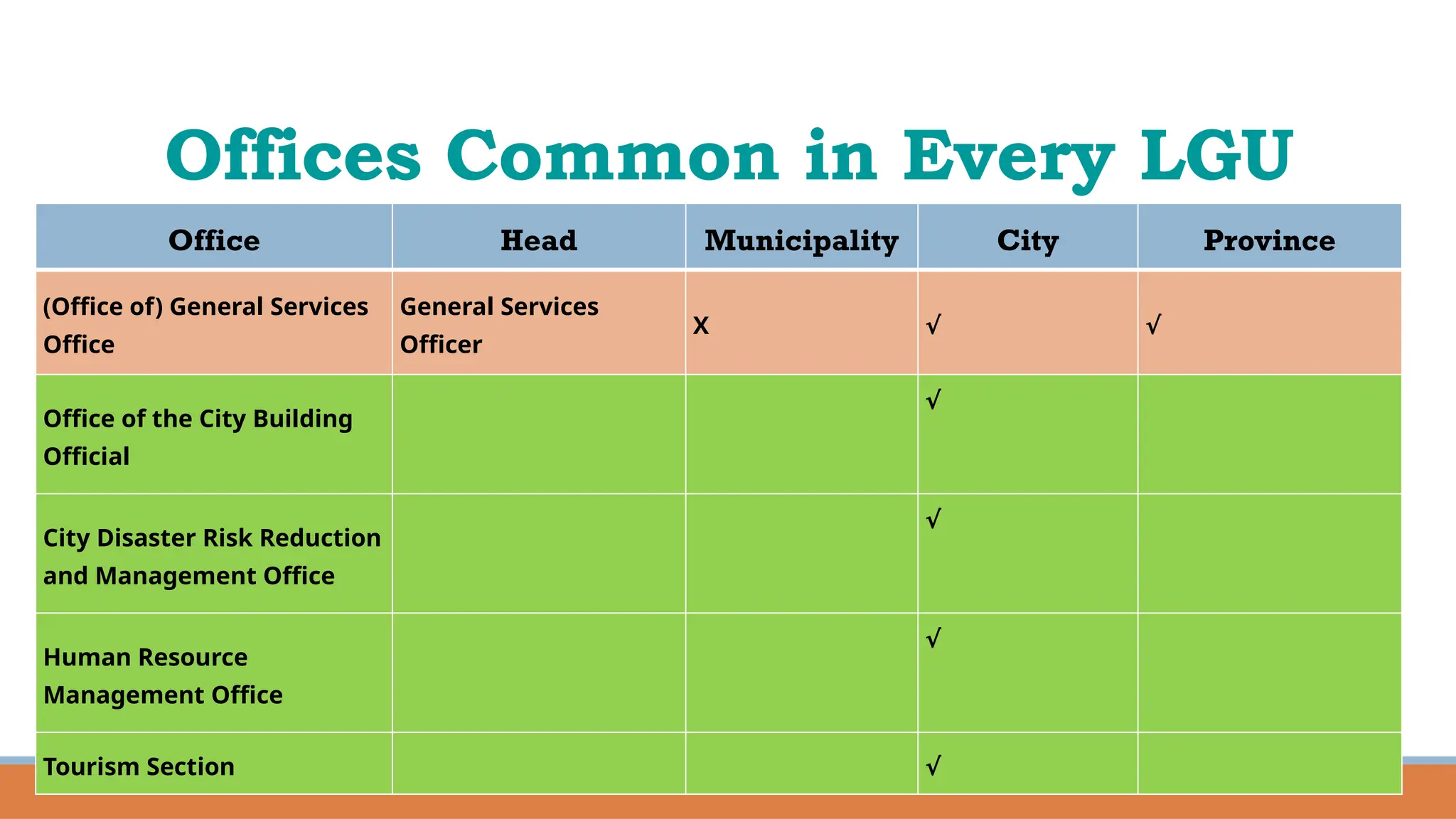
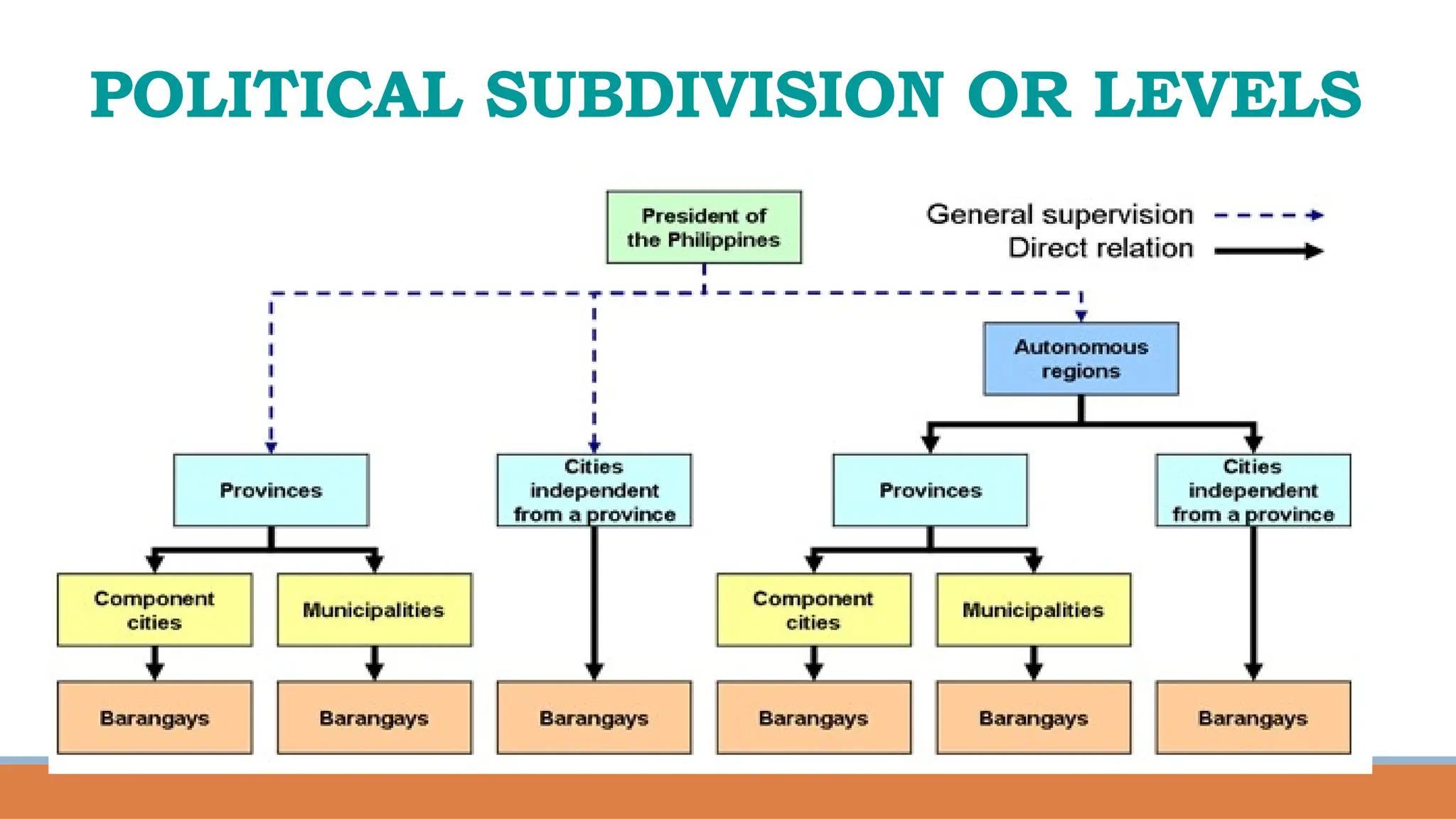
The document provides a comprehensive overview of local governance in the Philippines, defining local governance and local government, and detailing the different levels of local government units (LGUs), including autonomous regions, provinces, cities, municipalities, and barangays. It outlines the roles, responsibilities, and powers of each level of LGU, along with the officials and their minimum age requirements for election. Furthermore, it discusses the Seal of Good Local Governance, its objectives, and El Salvador City as an example of a successful LGU that received this seal.

































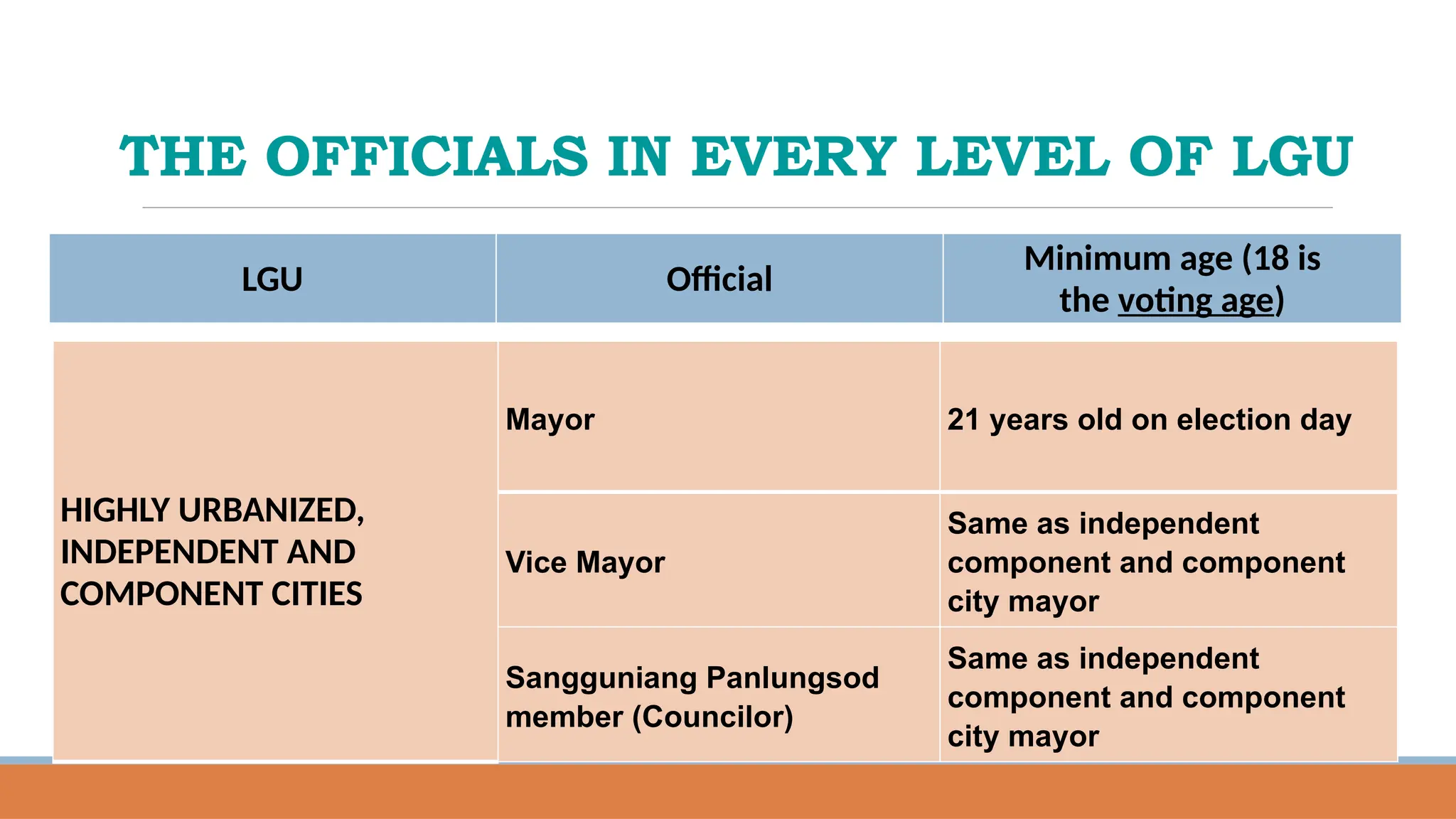
![THE OFFICIALS IN EVERY LEVEL OF LGU
LGU Official
Minimum age (18 is the voting
age)
AUTONOMOUS REGION
Regional Governor 35 years old on election day[7]
Regional Vice Governor Same as regional governor
Regional Legislative
Assembly Member
21 years old on election day[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewonlocalgovernance-250208083028-5a30637a/75/OVERVIEW-ON-LOCAL-GOVERNANCE-IN-THE-PHILIPPINES-35-2048.jpg)
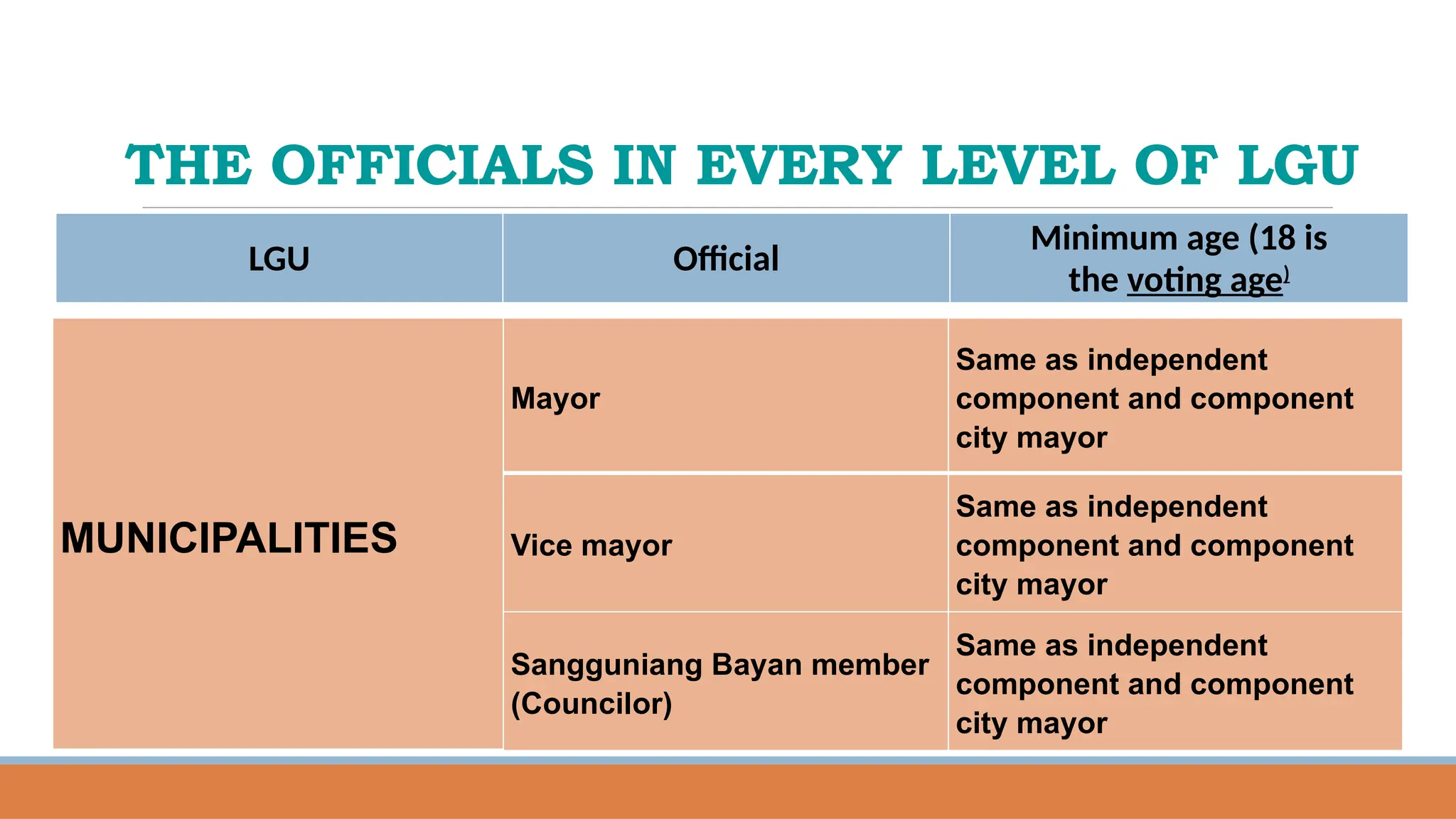
![THE OFFICIALS IN EVERY LEVEL OF LGU
LGU Official
Minimum age (18 is
the voting age)
PROVINCES
Governor 23 years old on election day[5]
Vice Governor Same as governor
Sangguniang
Panlalawigan Member
Same as governor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewonlocalgovernance-250208083028-5a30637a/75/OVERVIEW-ON-LOCAL-GOVERNANCE-IN-THE-PHILIPPINES-36-2048.jpg)