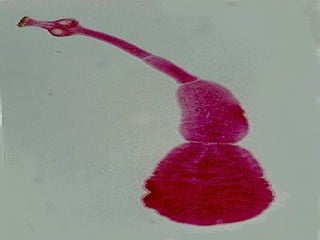
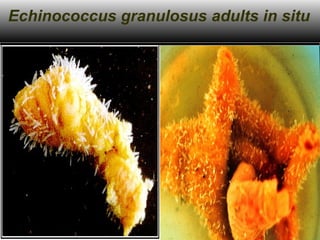
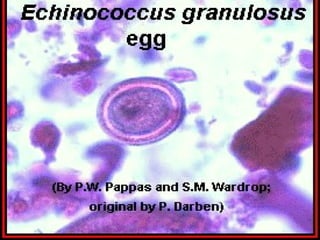
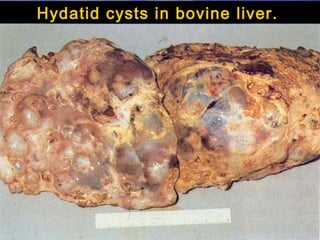
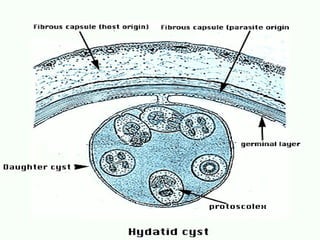
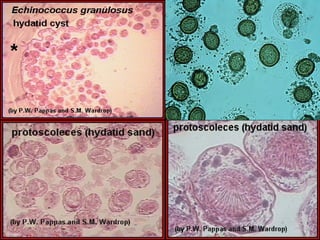
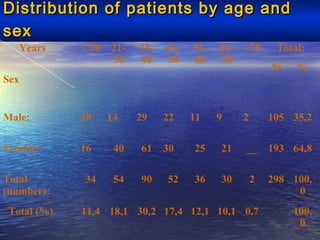
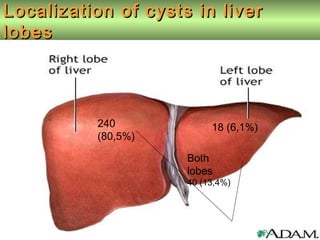
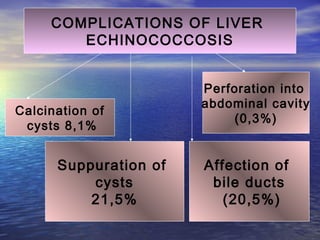
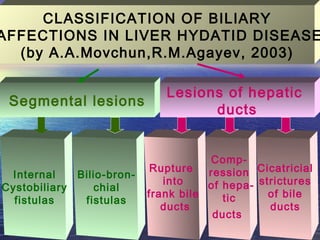
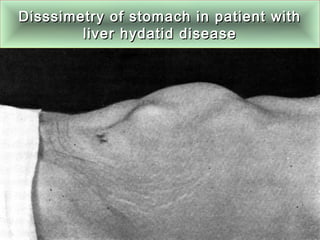
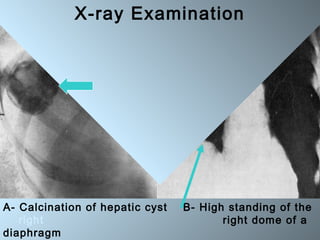
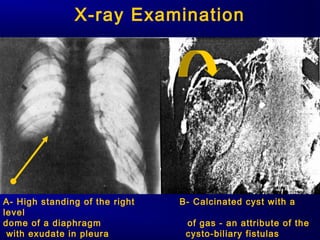
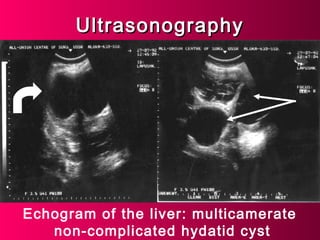
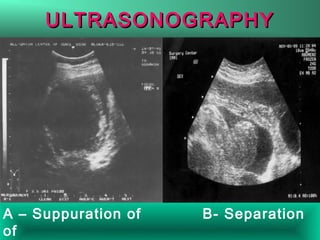
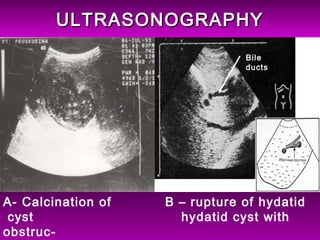
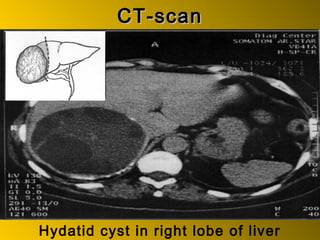
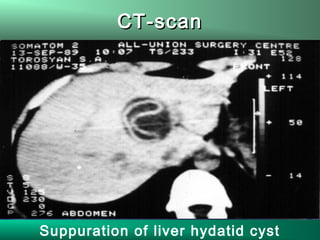
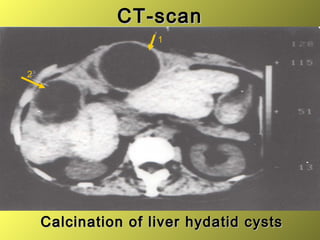
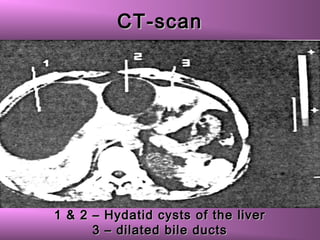
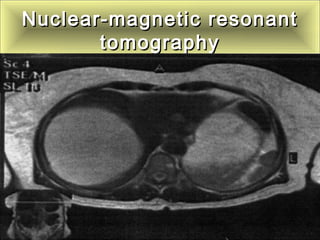
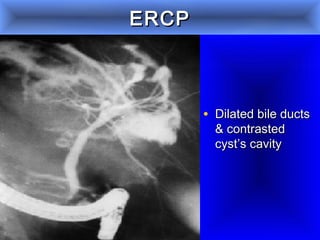
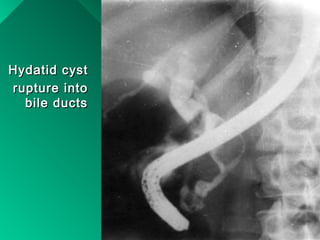
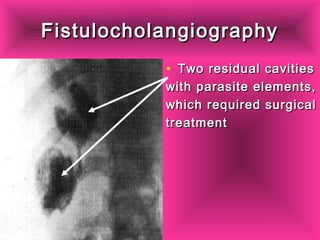
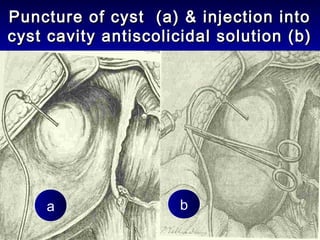
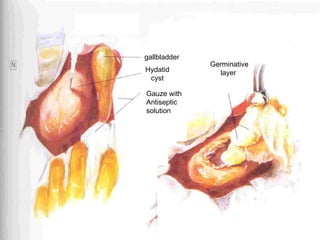
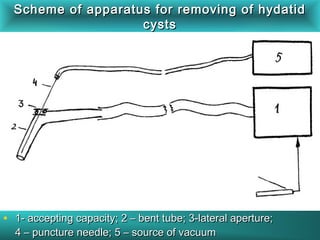
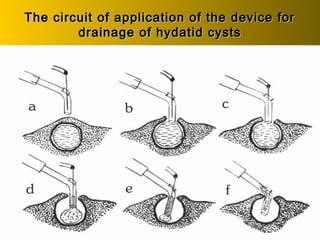
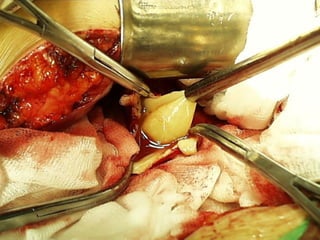
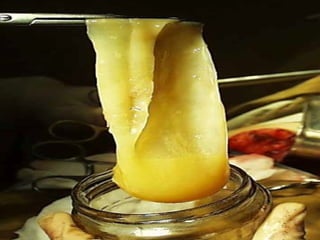
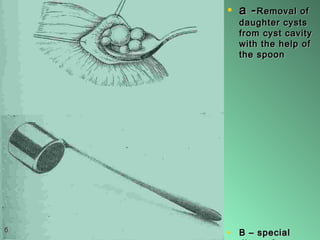
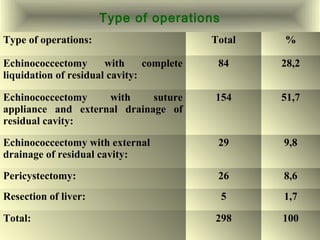
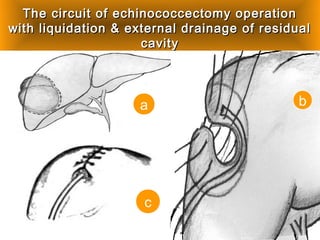
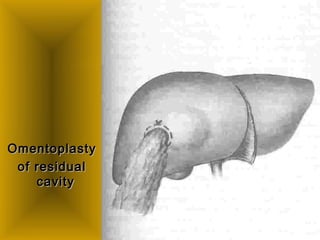
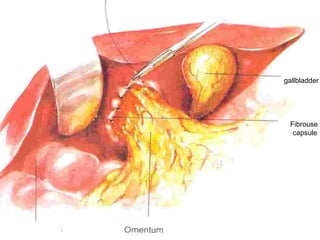
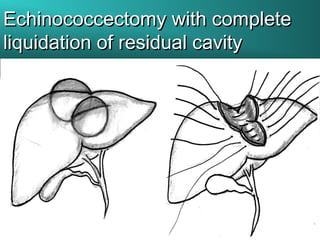
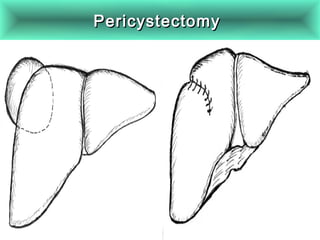
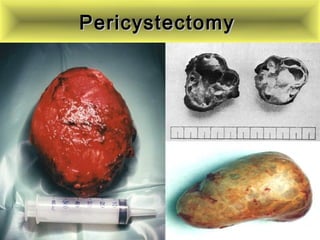
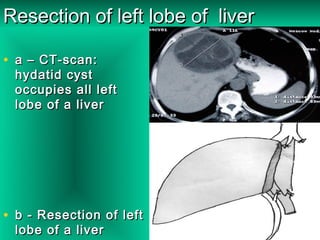
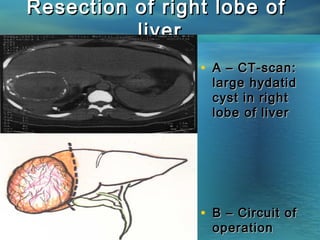
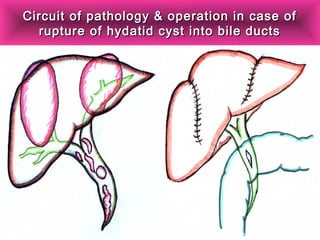
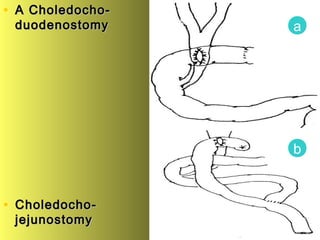
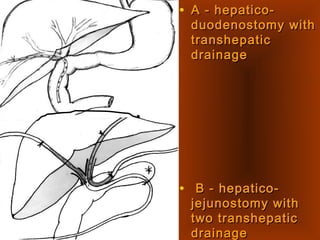
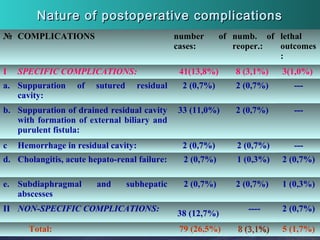
This document discusses liver hydatid disease, including its etiology, diagnosis, and surgical treatment. It causes by the parasite Echinococcus granulosus entering the body through the gastrointestinal or respiratory tracts. Symptoms can include pain, weight feeling in the liver, and jaundice. Diagnosis involves ultrasound, CT scans, and other imaging to detect cysts in the liver. Surgical treatment options are discussed, including complete cyst removal with cavity liquidation or drainage. Postoperative complications are reported in about 26.5% of cases, with specific issues being suppuration or hemorrhage in the residual cavity. Risk factors for worse outcomes include older patient age, longer disease duration, and cyst complications like suppuration.