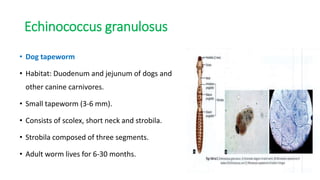
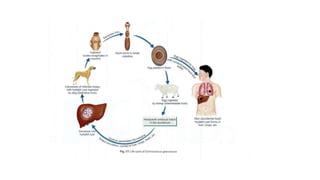
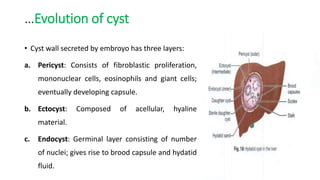
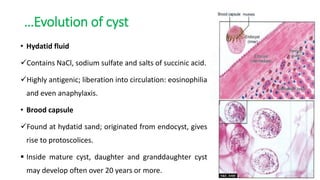
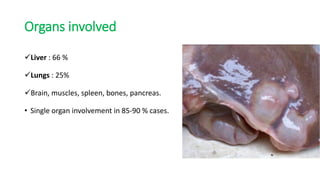
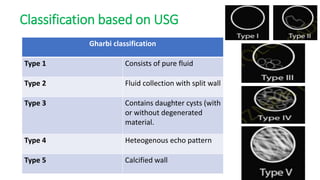
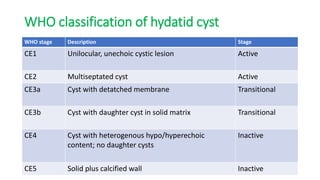
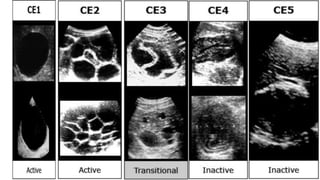
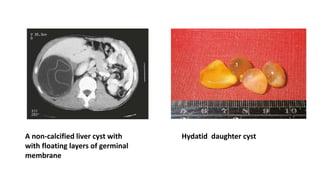
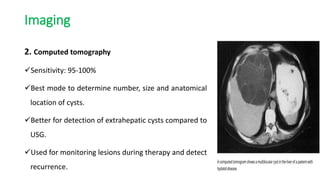
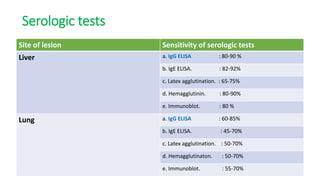
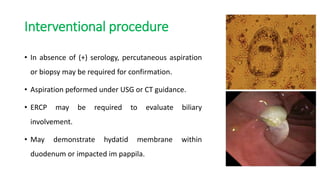
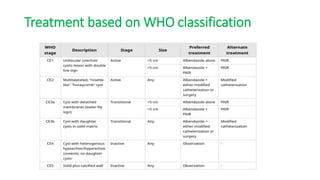
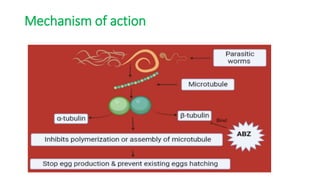
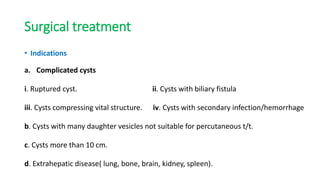
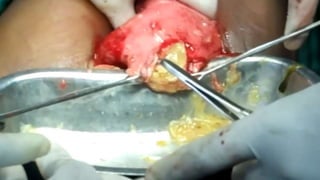
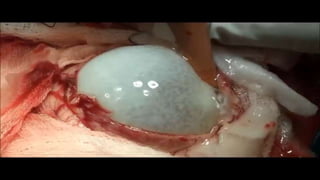
This document summarizes information about hydatid cysts, which are caused by infection with the larval stage of the Echinococcus tapeworm. It describes the lifecycle of E. granulosus and how humans can become infected through contact with dog feces. Hydatid cysts most commonly form in the liver and lungs, and may grow slowly over many years without symptoms. Clinical features depend on the infected organ and size of cysts. Imaging tests and serology can help diagnose cysts, while treatment involves antiparasitic drugs, percutaneous drainage, or surgical removal based on cyst type and location. Close follow up is needed due to risk of recurrence.