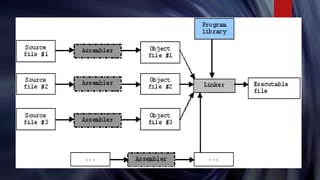
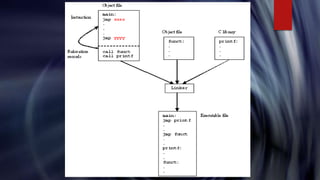
The document discusses the linker, which links object files generated by the assembler into executable files. It defines the linker as a system software that combines object files, resolving references between them. Linkers are needed because large programs are separated into multiple files that must be combined into a single executable. There are two types of linking - static linking embeds library code directly into executables while dynamic linking relies on shared libraries present at runtime. The document provides an overview of the compilation process and role of the linker in linking object files and libraries to produce an executable.