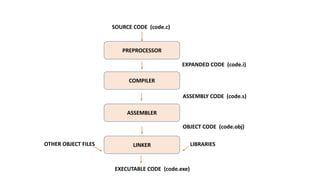
The compilation process in C consists of four steps: preprocessing, compiling, assembling, and linking. During preprocessing, the source code is checked for errors and macros and includes are expanded. The compiler then converts the preprocessed code into assembly code. In the assembling step, assembly code is converted into object code. Finally, the linker combines the object code with code from library files to generate the executable file.