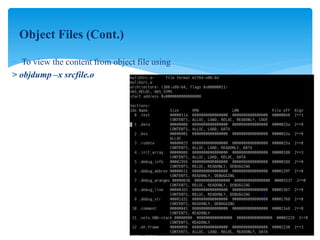
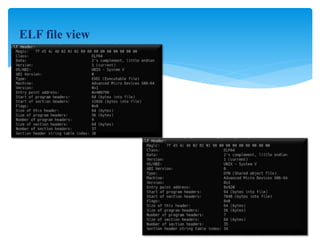
This document discusses shared libraries and dynamic loading in Linux. It begins by explaining how object files are created from source code by compilers and contain machine code, symbols, and other metadata. Libraries are collections of object files that are linked together by linkers. Static libraries copy object code into executables, while shared libraries delay linking until runtime using dynamic linkers. Shared libraries improve modularity and efficiency by loading code only once and sharing it between processes. The document then covers how dynamic linkers load shared libraries at runtime using functions like dlopen(), dlsym(), and dlclose(). It concludes by explaining how to create and link both static libraries and shared libraries in Linux.