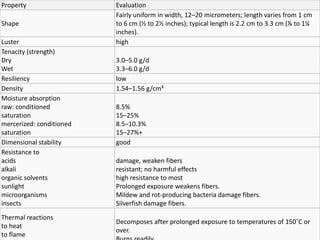
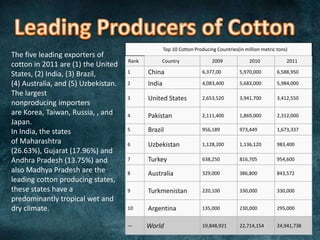
Cotton is a soft staple fiber that grows in seed pods called bolls. It has been cultivated for at least 7,000 years and was independently domesticated in both the Old and New Worlds. The largest diversity of cotton species exists in Mexico. Successful cotton cultivation requires long frost-free periods with moderate rainfall or irrigation. The United States, India, and Brazil are three of the top cotton producers. Cotton fibers are processed through ginning, spinning, weaving, and finishing to make fabrics. The fibers provide strength but also absorbency. Major cotton textile industries exist in India, China, the US, and other countries. Common cotton products include t-shirts, jeans, towels, and bedsheets.