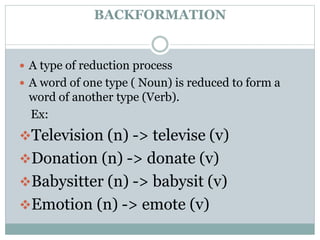
This document discusses various processes of word formation, including etymology, coinage, borrowing, compounding, blending, clipping, backformation, conversion, acronyms, derivation, and multiple processes. It provides definitions and examples for each type of word formation. Coinage refers to inventing new terms, borrowing means taking words from other languages, and compounding is joining two words to form one. Clipping, backformation, and conversion involve changing parts of speech or shortening words. Acronyms form words from initial letters and derivation uses prefixes, suffixes, and infixes.