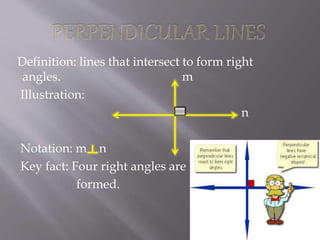
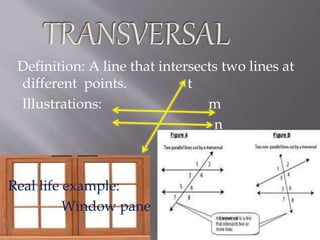
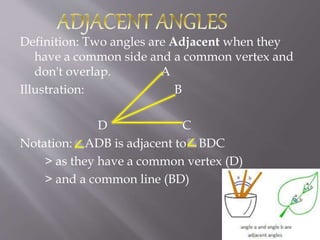
1) The document defines and provides examples of different types of lines and angles. It discusses lines, line segments, rays, intersecting lines, parallel lines, and various angle types such as adjacent angles, vertical angles, corresponding angles, and interior and exterior angles.
2) Illustrations and notations are provided for each term to demonstrate their properties and relationships.
3) Real-life examples are given for some concepts, such as cars parked in a straight line for a line and window panes for line segments.