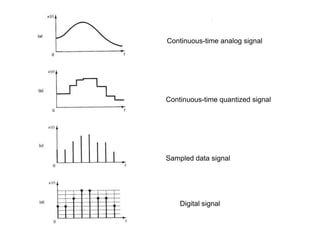
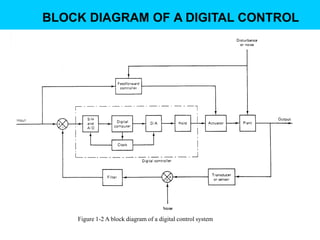
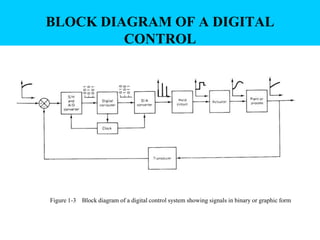
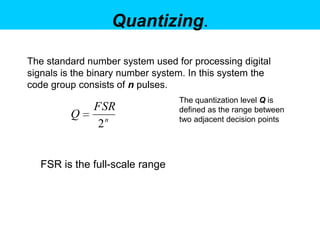
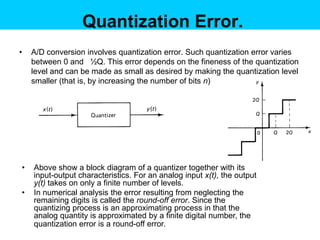
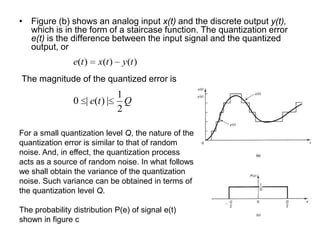
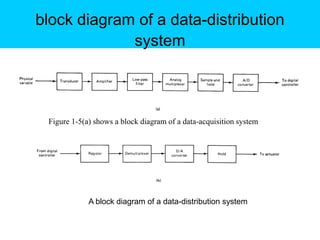
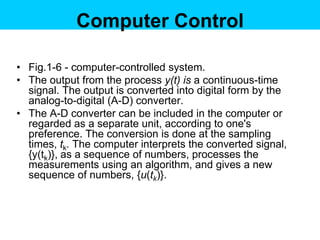
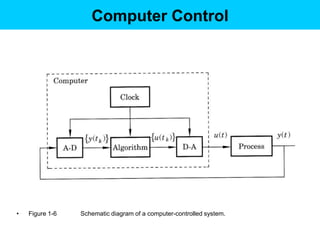
Digital control systems have several advantages over analog systems like flexibility, decision-making capability, and high performance for cost. Digital signals are discrete-time signals with quantized amplitude that can be represented by sequences of numbers. A digital control system involves sampling a continuous signal, converting it to digital with analog-to-digital conversion, processing the digital signal with a computer, converting it back to analog with digital-to-analog conversion, and using the analog output to control a plant. Quantization error is introduced during analog-to-digital conversion and depends on the quantization level, which can be reduced by increasing the number of bits used.