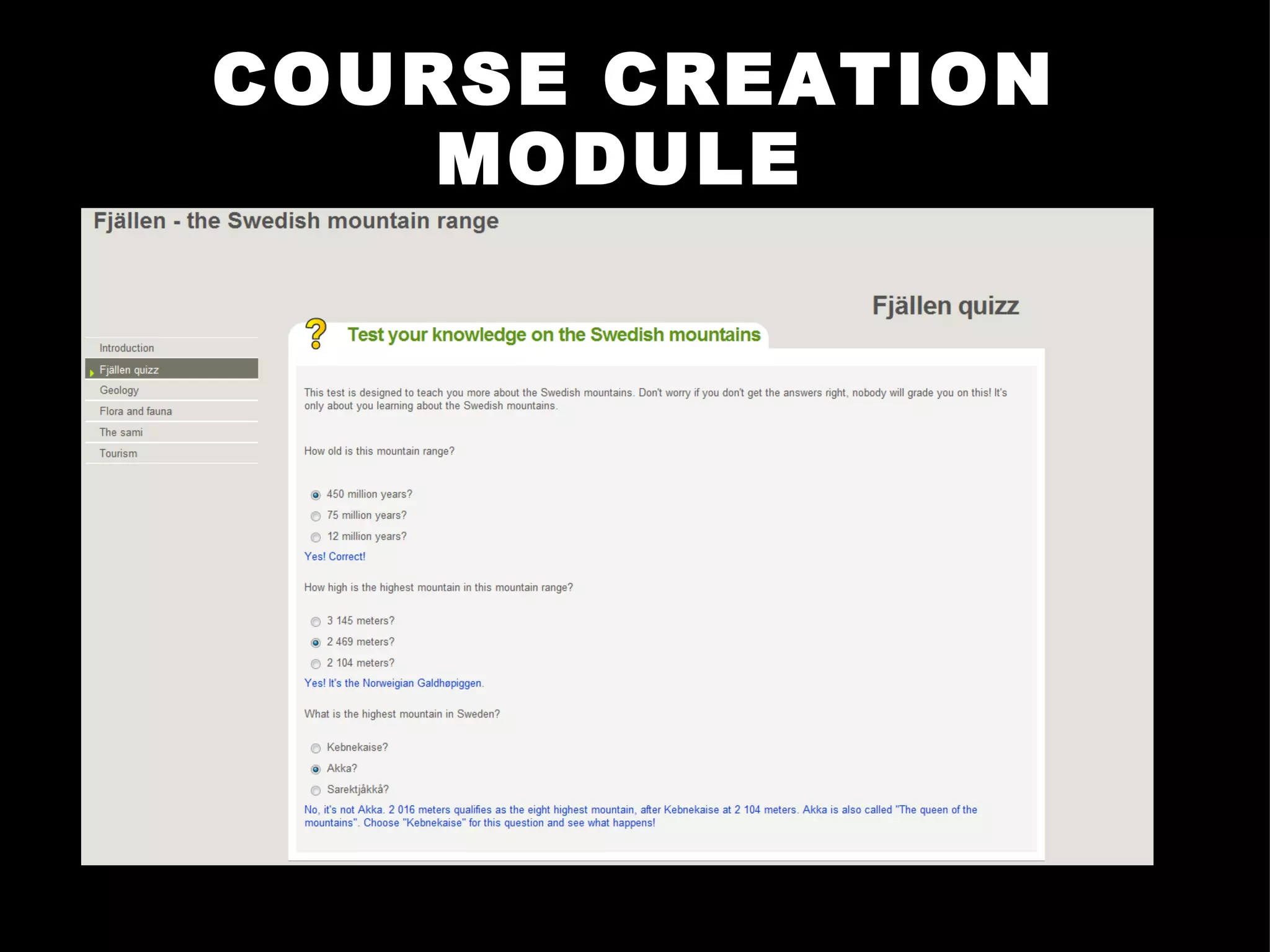
The document discusses introducing computer literacy to a village in Tanzania through an eLearning project. It describes setting up a computer room and training teachers on using an open-source learning management system and course creation software. While teachers benefited from the eLearning initiatives, they required the most support to get started due to low initial computer literacy. The project found that students were more interested in computer classes and spent more time in the computer room than anticipated. Recommendations included simplifying interfaces, considering the oral tradition through Swahili training, and focusing training on more experienced teachers.
![The eLearning paradox or… Ideas to increase the computer literacy in a Tanzanian village Linda Malmqvist [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lindathesispres-100305055222-phpapp01/75/Ideas-on-increasing-the-computer-literacy-in-a-Tanzanian-village-1-2048.jpg)































![QUESTIONS? COMMENTS? Linda Malmqvist [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lindathesispres-100305055222-phpapp01/75/Ideas-on-increasing-the-computer-literacy-in-a-Tanzanian-village-35-2048.jpg)