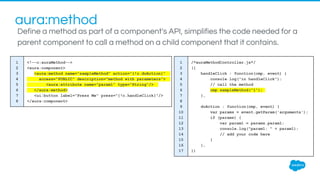
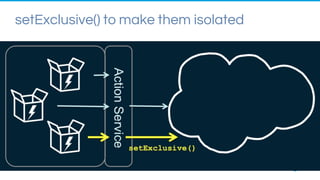
The document discusses Lightning components in Salesforce, detailing their architecture, lifecycle, and advantages of a component-driven approach. It highlights the use of Aura framework, data exchange methods between components, and actions/events for interactions, as well as tools and development practices for building Lightning components. Additionally, it covers the implications of forward-looking statements regarding the risks and uncertainties related to Salesforce's services and operations.









![Attributes that participate in the rendering cycle, of type Aura.Component[]
Facets
Component Definition Component Usage
Output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lightningcomponentseries-episode2-160607175638/85/Lightning-Component-Components-Actions-and-Events-10-320.jpg)