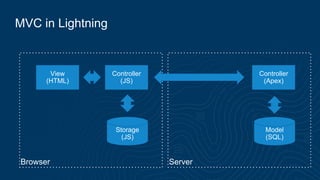
The document provides an in-depth overview of the Lightning Framework, focusing on its programmatic aspects, including XML component definitions, styling, and the roles of JavaScript and Apex controllers. It covers the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, discussing the functions of controllers, events, and helpers within the framework. Additionally, it details the Apex controller's structure and the Lightning Action Service, emphasizing performance, security, and action states.