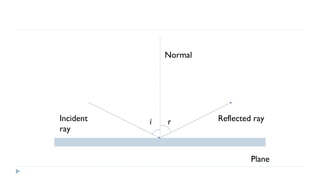
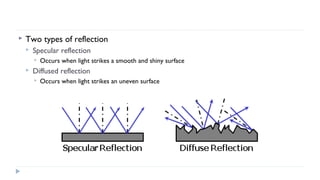
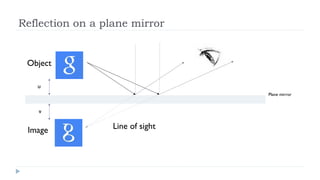
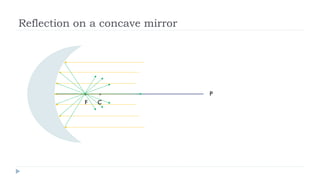
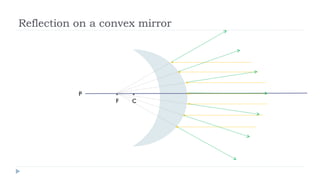
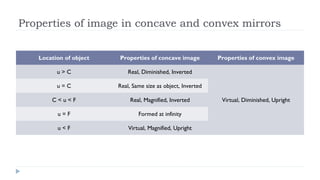
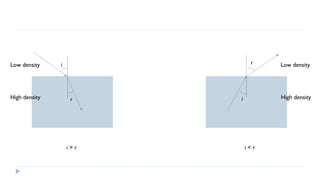
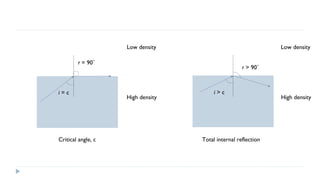
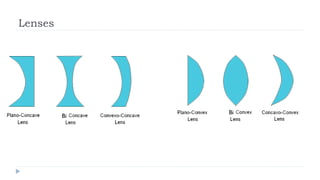
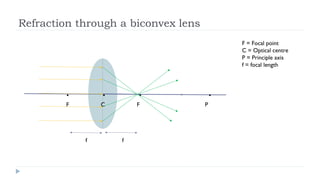
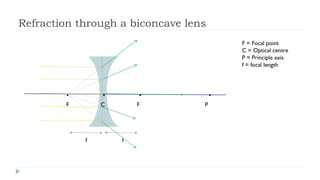
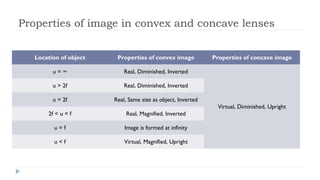
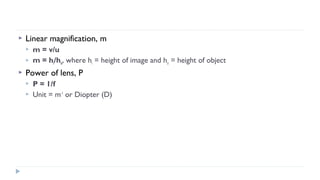
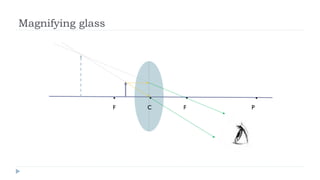
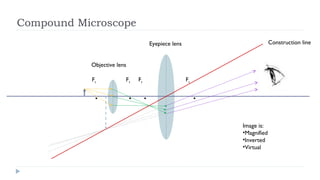
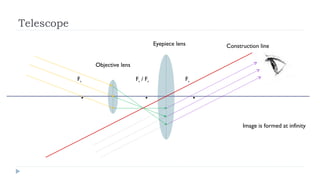
This document provides an overview of light and optics. It discusses that light has wave and particle properties and travels in straight lines. It also describes the wave properties of light including reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference. Optics is defined as the study of light interacting with objects. Key concepts such as the ray model of light, reflection and refraction on different surfaces, the use of lenses, and applications of optical phenomena are explained. Diagrams illustrate these optical principles and definitions of important terms are provided.