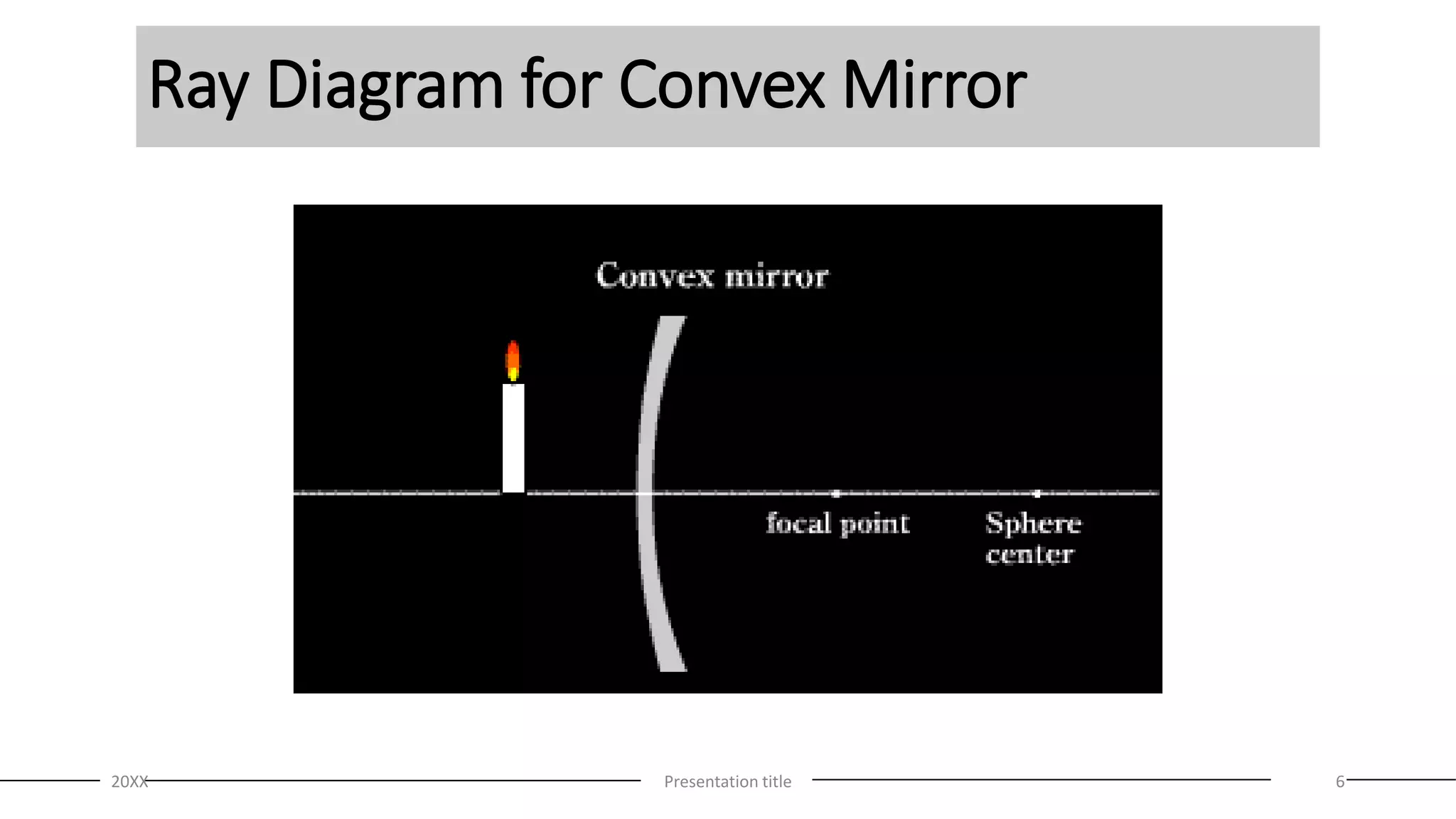
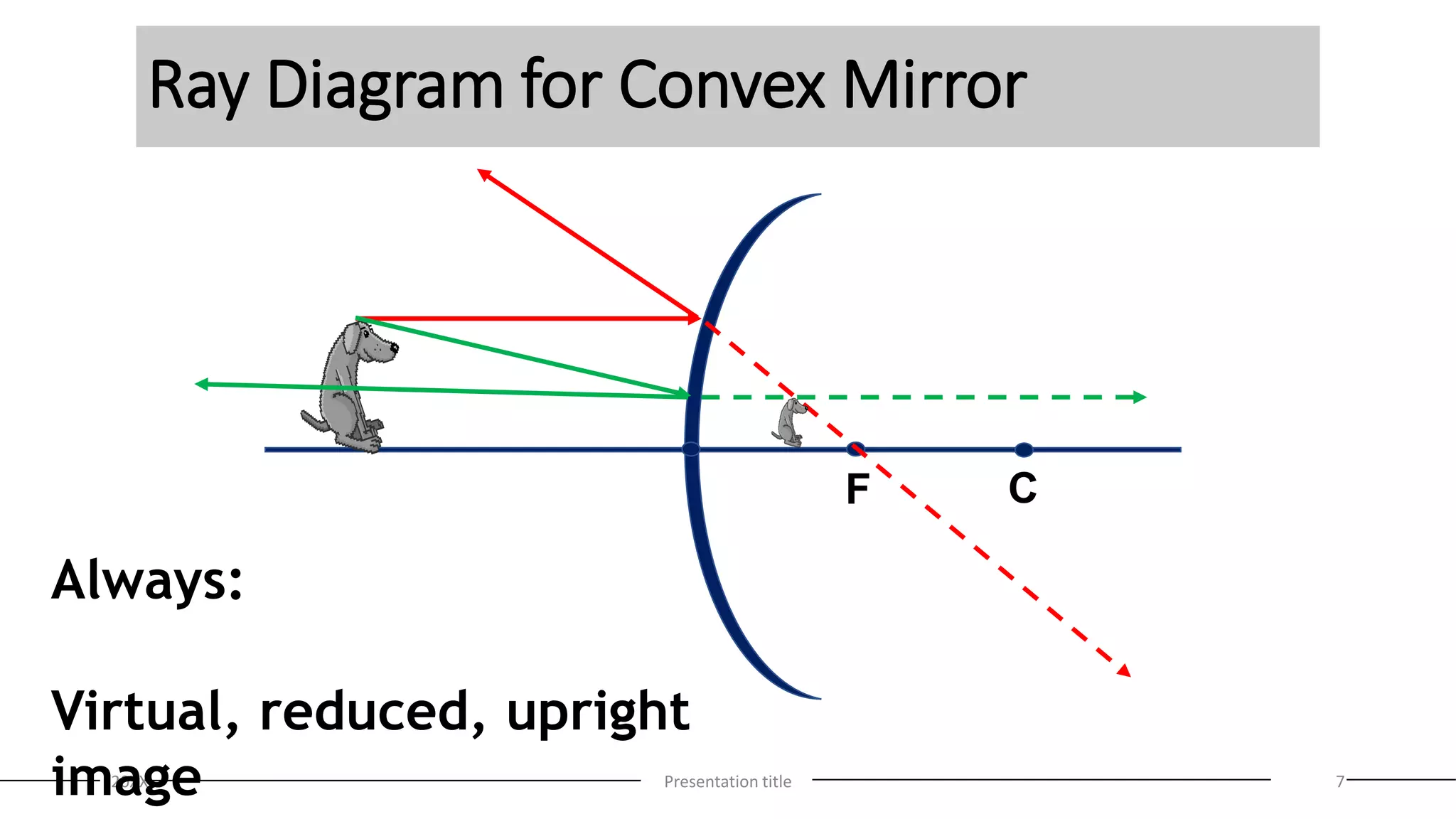
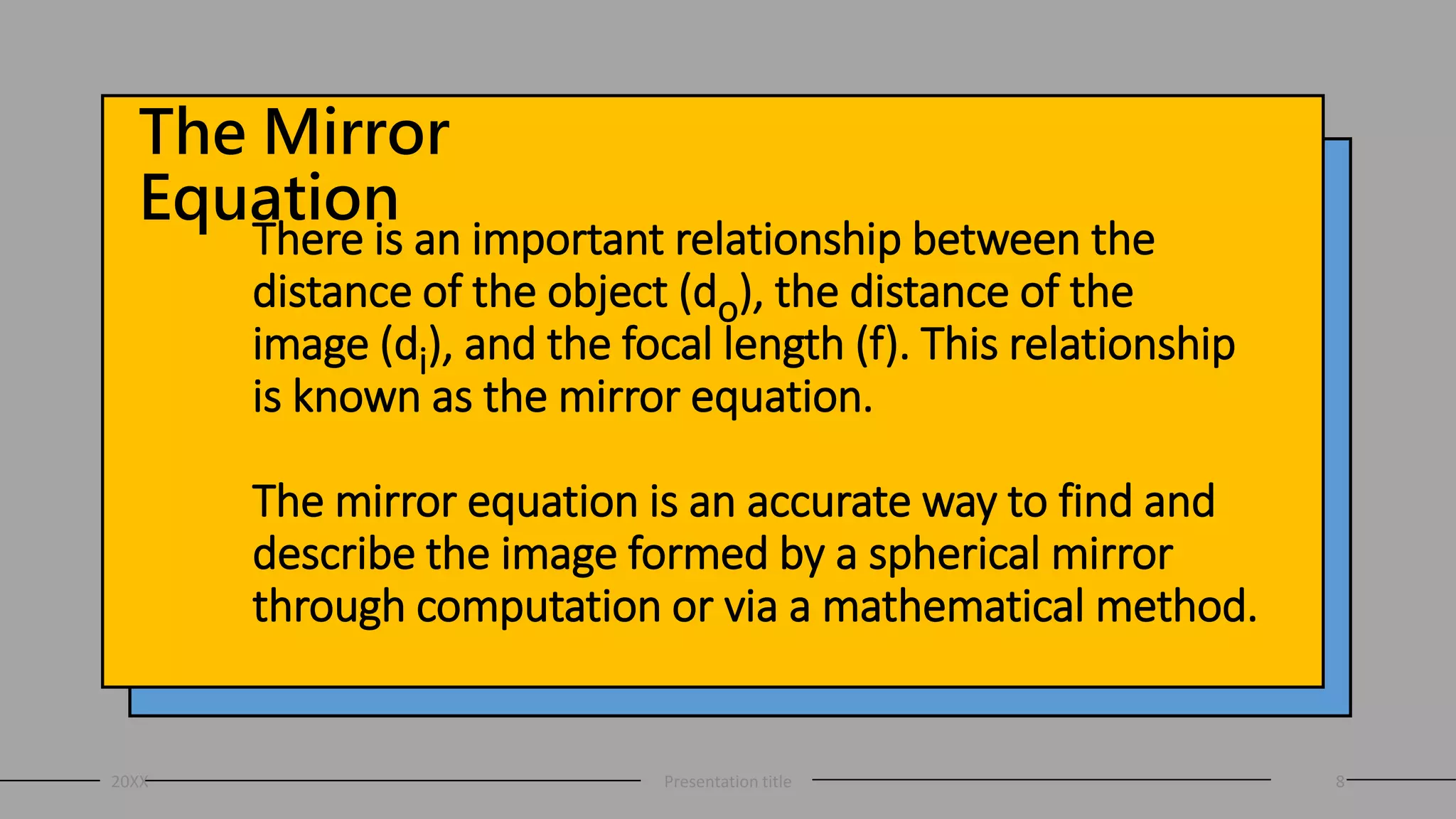
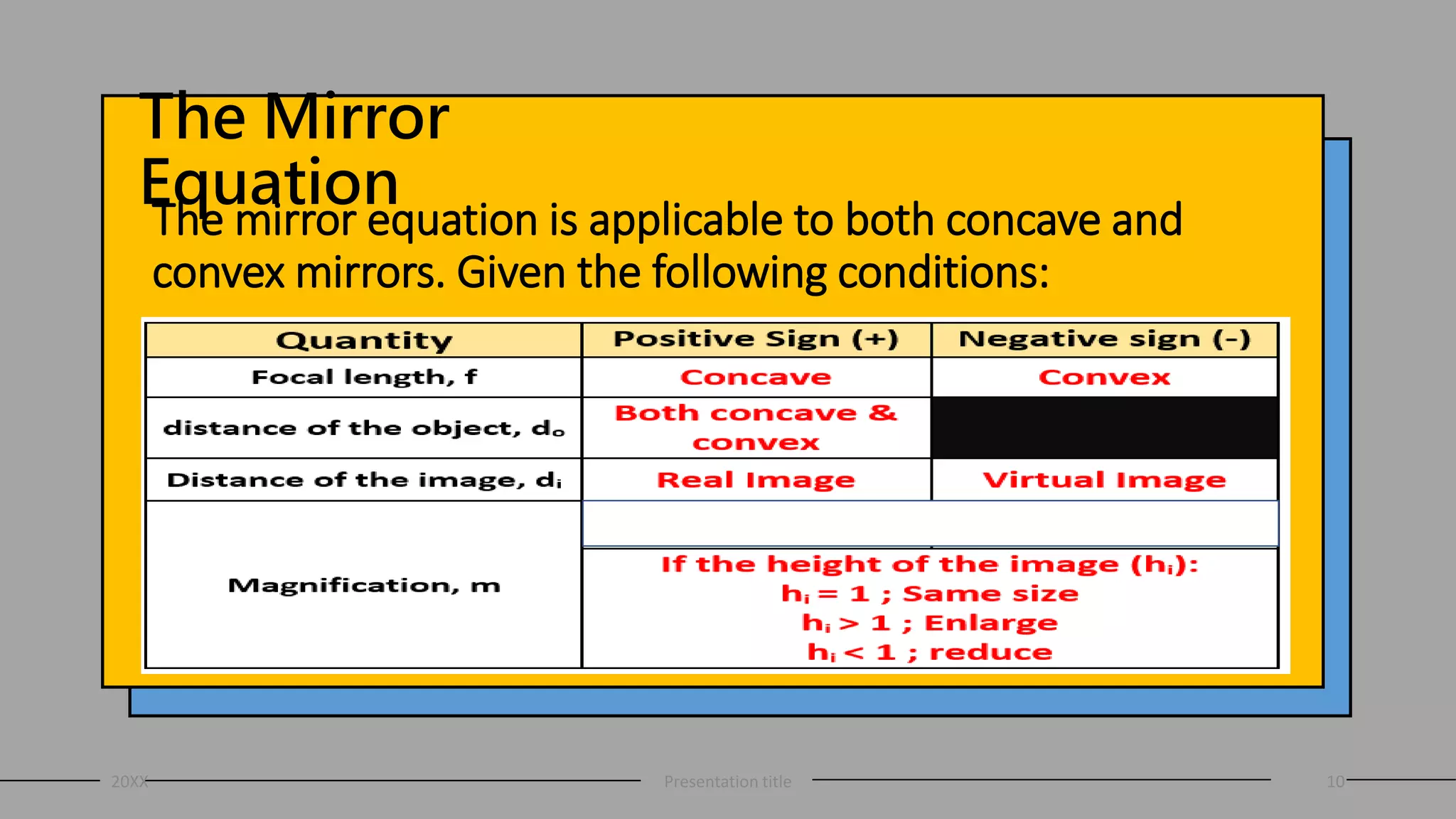
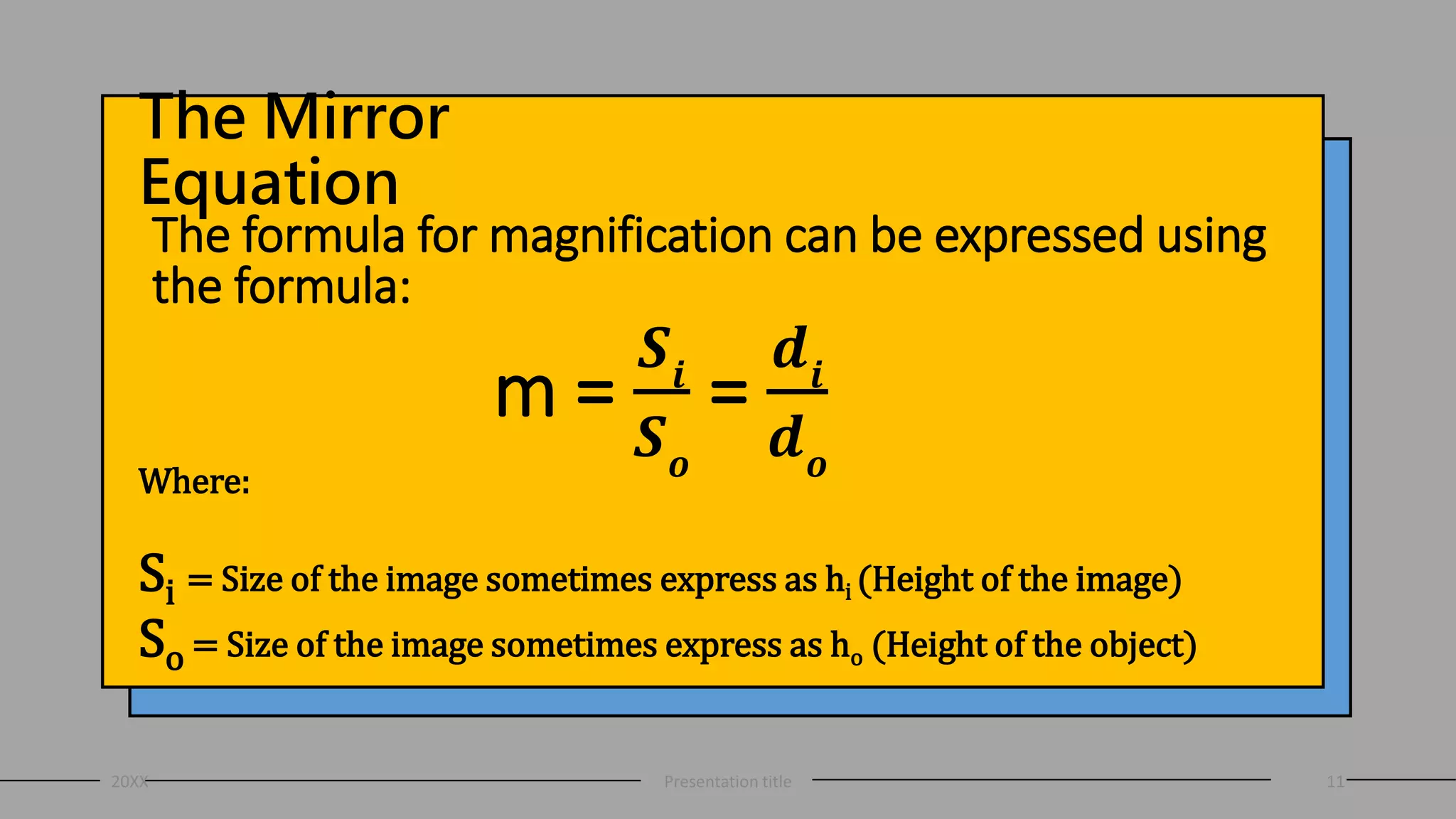
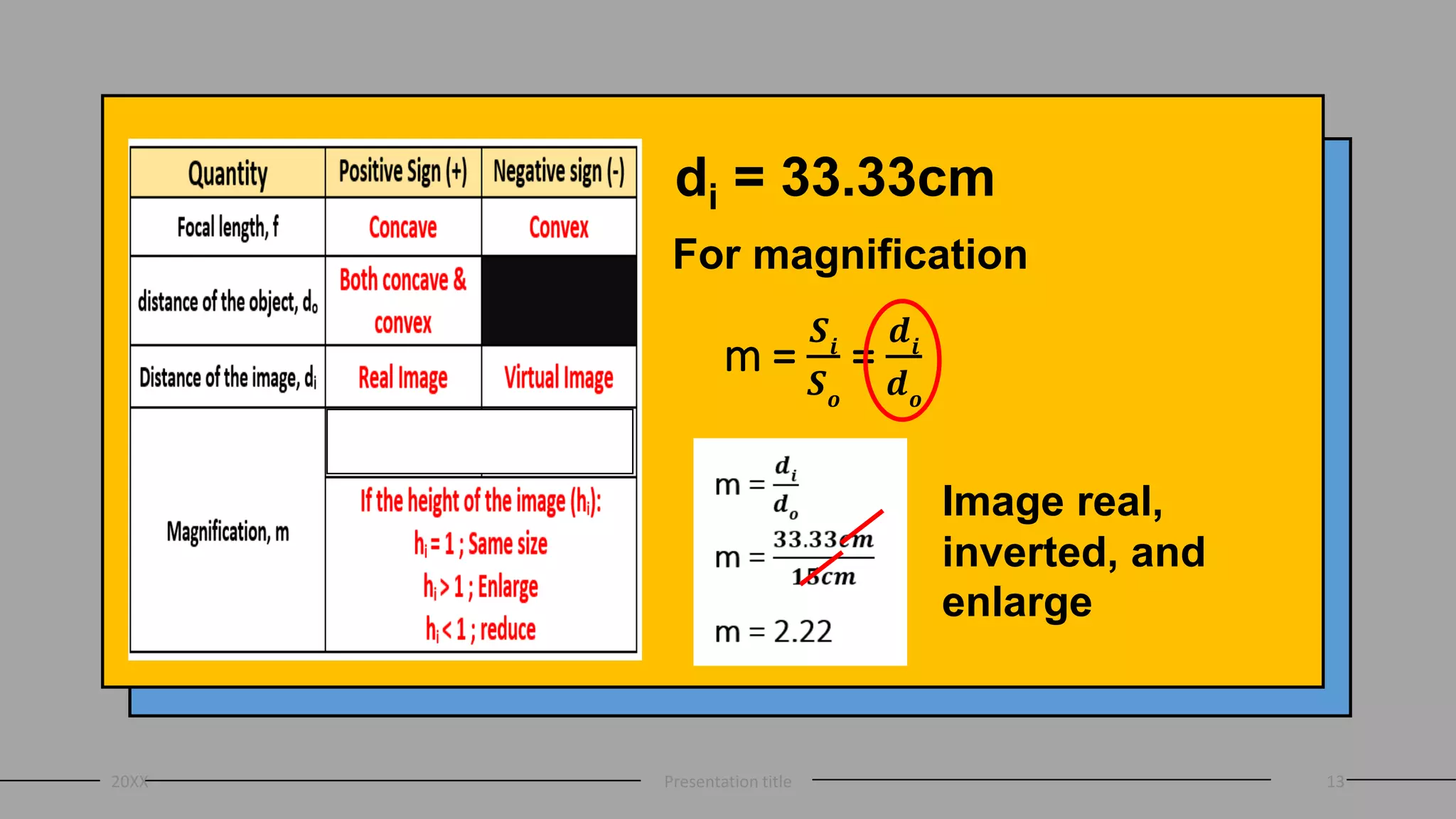
This document discusses curved mirrors and the mirror equation. It defines key terms like focal length, radius of curvature, focal point, vertex, and center of curvature. It explains that the focal length is equal to half the radius of curvature. The location and type of image formed by a concave mirror depends on where the object is placed relative to the center of curvature and focal point. The mirror equation relates the focal length, distance of the object, and distance of the image. Two sample problems demonstrate how to use the mirror equation to calculate the location of an image given information about the focal length and object distance.