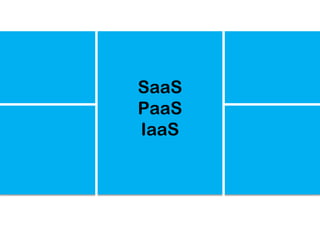
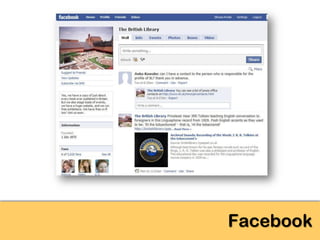
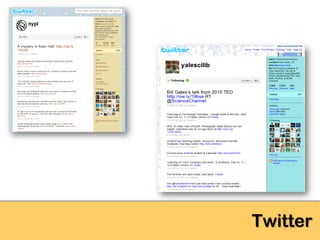
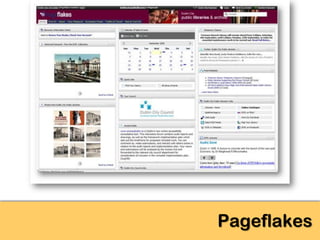
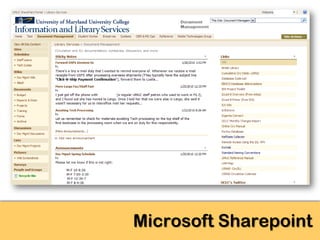
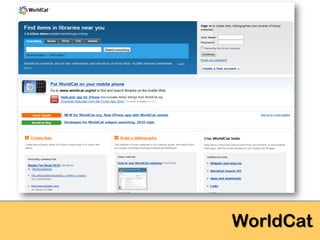
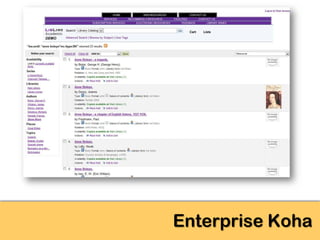
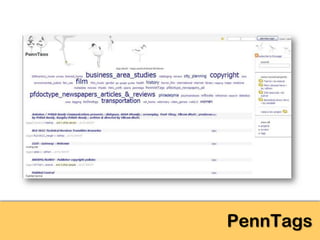
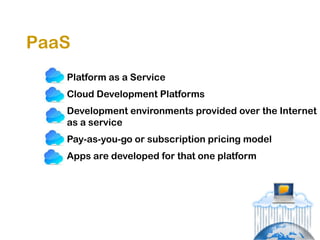
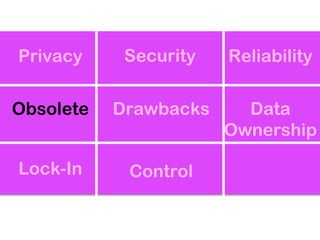
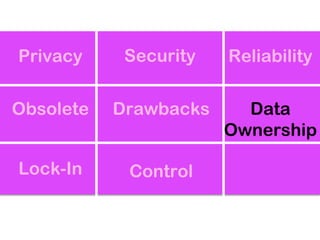
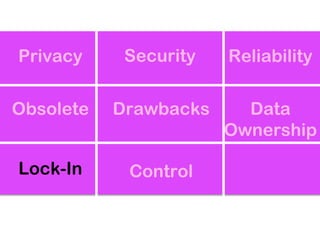
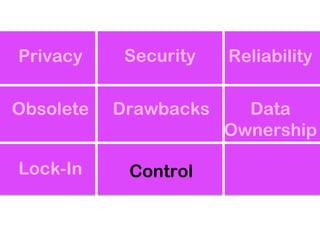
The document explores the significance of cloud computing for libraries, discussing its various types, benefits, and drawbacks. It highlights how libraries can leverage Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of transitioning to cloud services for improved scalability and collaboration, while also noting concerns around privacy and data ownership.


































![Resources
Carr, Nicholas G. The Big Switch: Rewiring the
World, from Edison to Google. New York: W. W.
Norton & Co, 2008.
Kroski, Ellyssa. "Library Cloud Atlas: A Guide to
Cloud Computing and Storage", Library Journal
9/10/2009. http://tinyurl.com/yc479ko
Katz, Richard N. The Tower and the Cloud: Higher
Education in the Age of Cloud Computing.
[Boulder, CO]: EDUCAUSE, 2008.
Buck, Stephanie. "Libraries in the Cloud: Making a
Case for Google and Amazon." Computers in
Libraries 9/2009.
Arnold, Erik. "Leveraging Clouds to Make You More
Efficient: How SaaS-Y Are You? " Online. 32. 3
6/2008.
ReadWrite Cloud:
http://www.readwriteweb.com/cloud](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputinginlibraries3-100305140634-phpapp02/85/Libraries-and-the-Cloud-91-320.jpg)
