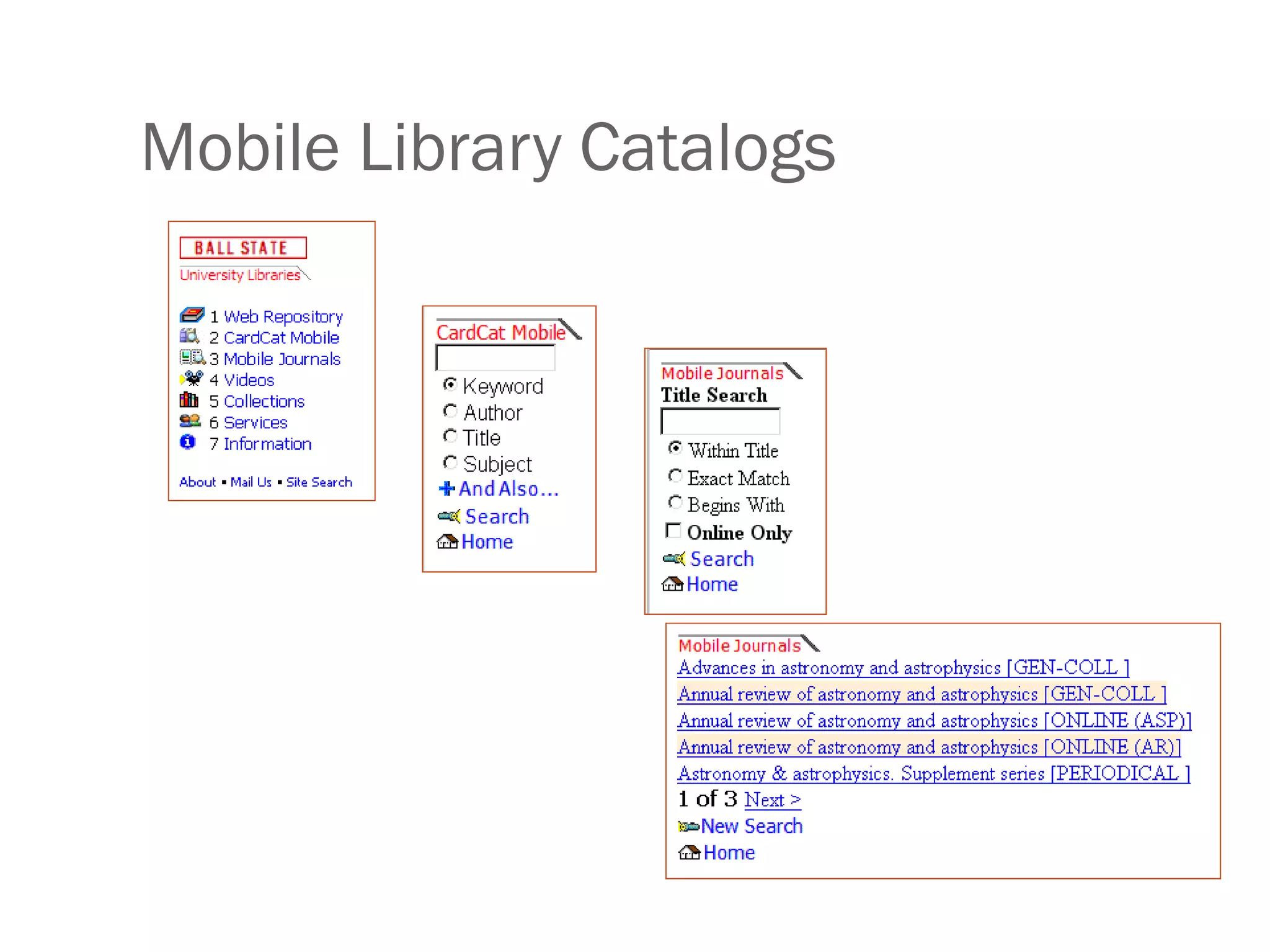
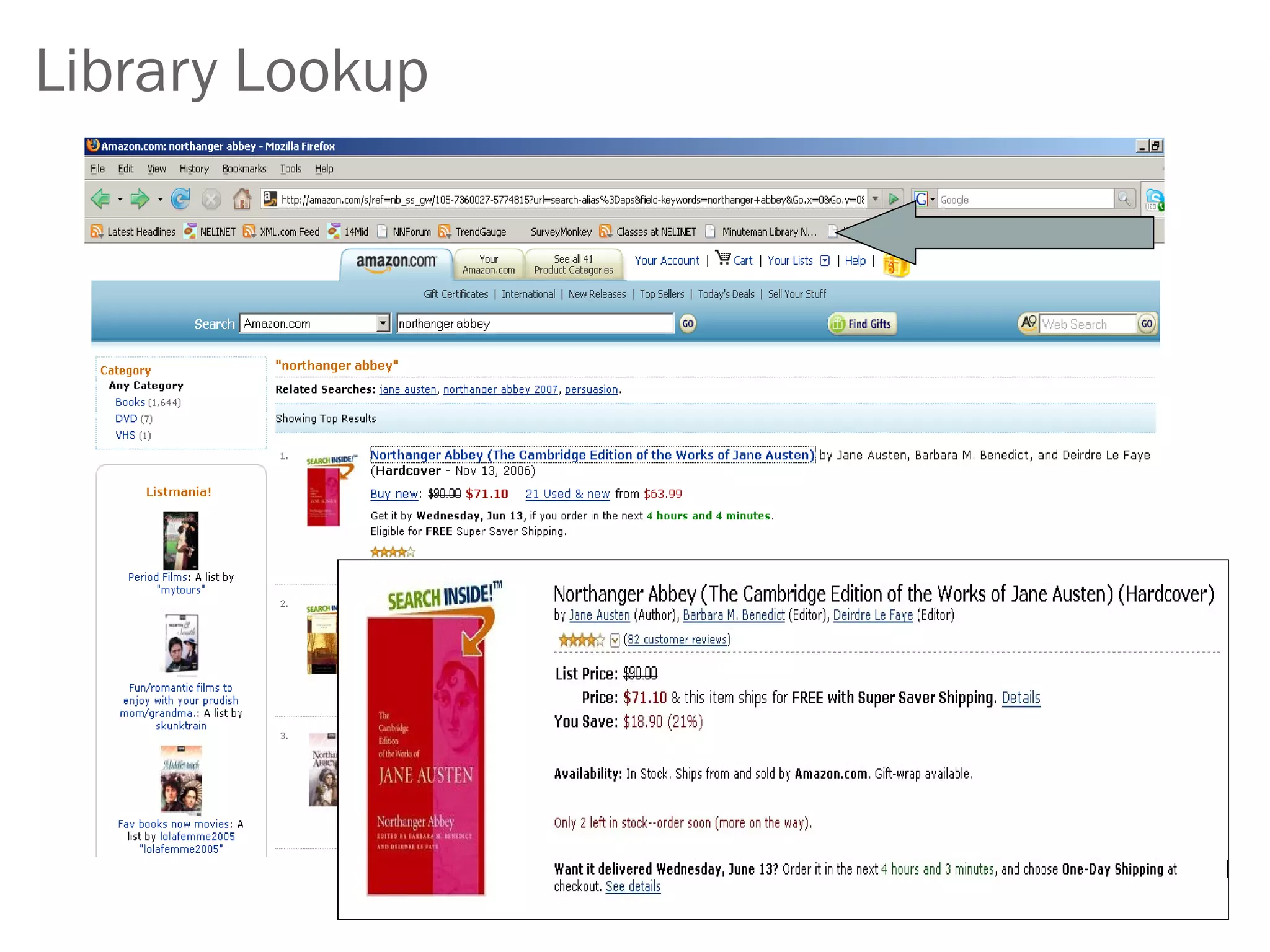
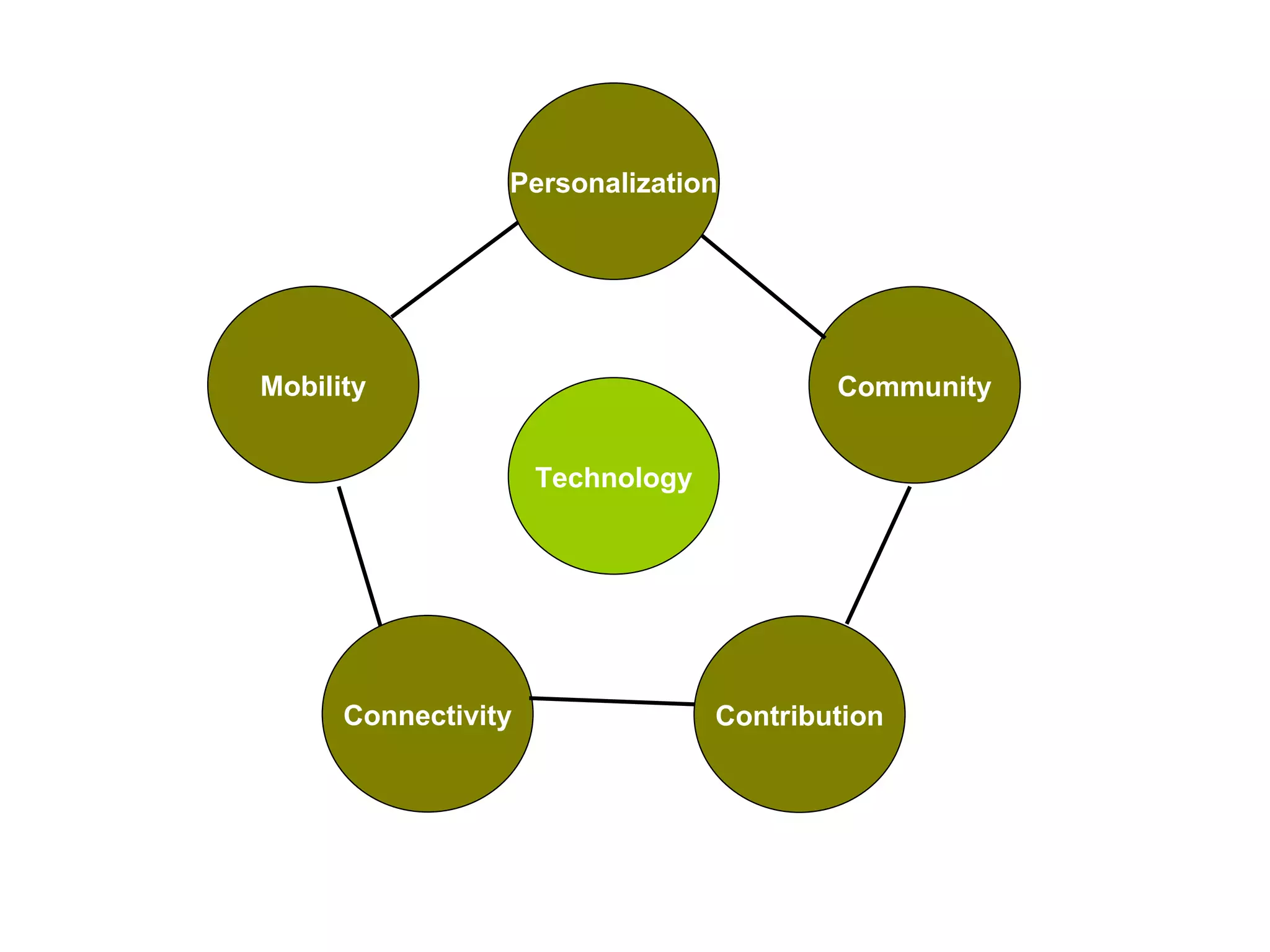
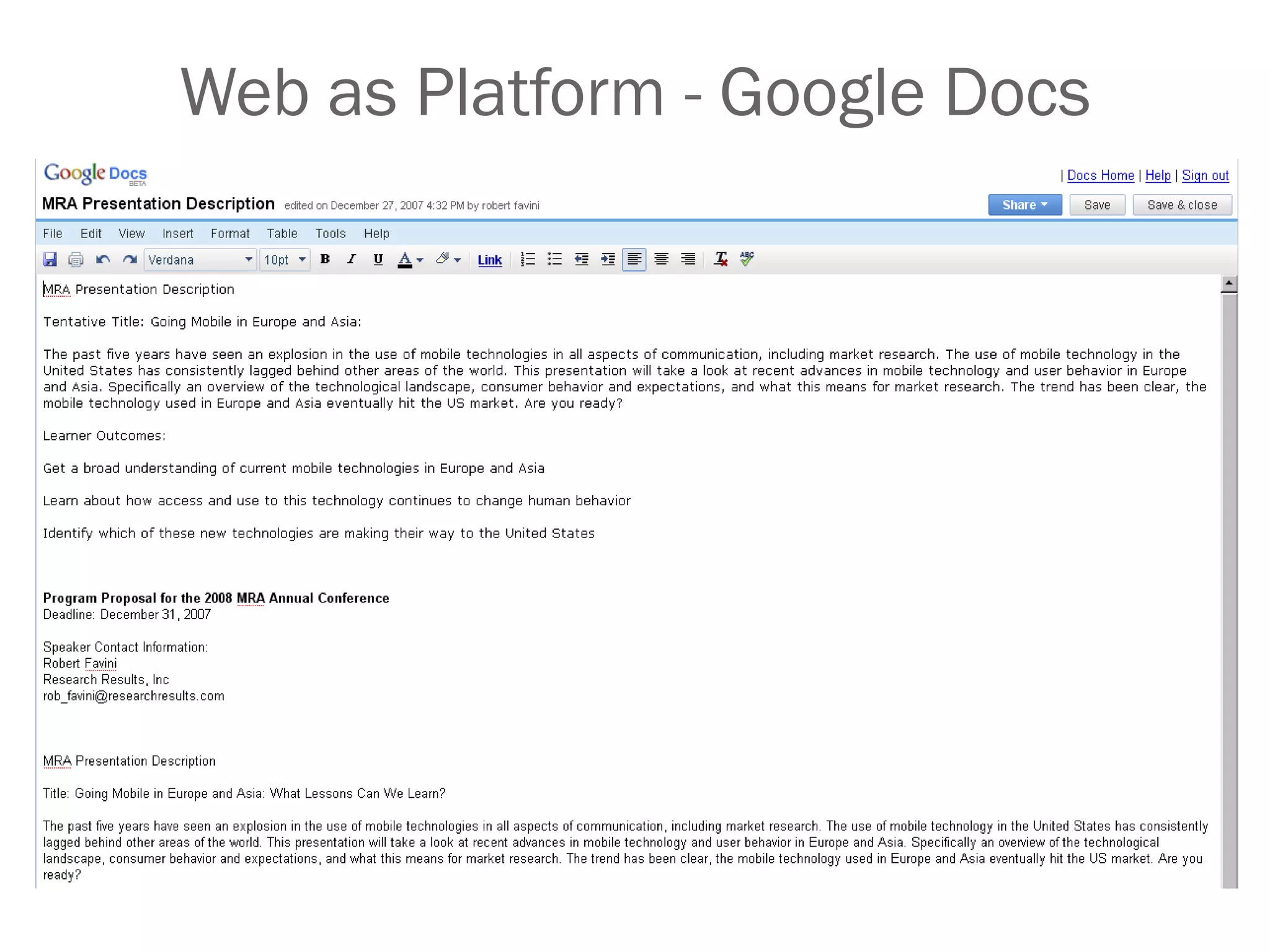
Amy Benson discusses how libraries are evolving to Library 2.0 models to better serve patrons in a Web 2.0 world. Key aspects of this evolution include embracing user participation through user-generated content and social software, providing personalized and mobile services, and integrating library data with external resources through mashups and semantic approaches. Benson urges libraries to explore new technologies, embrace change, and focus on serving patrons through an ethos of collaboration, community, and open information sharing.





















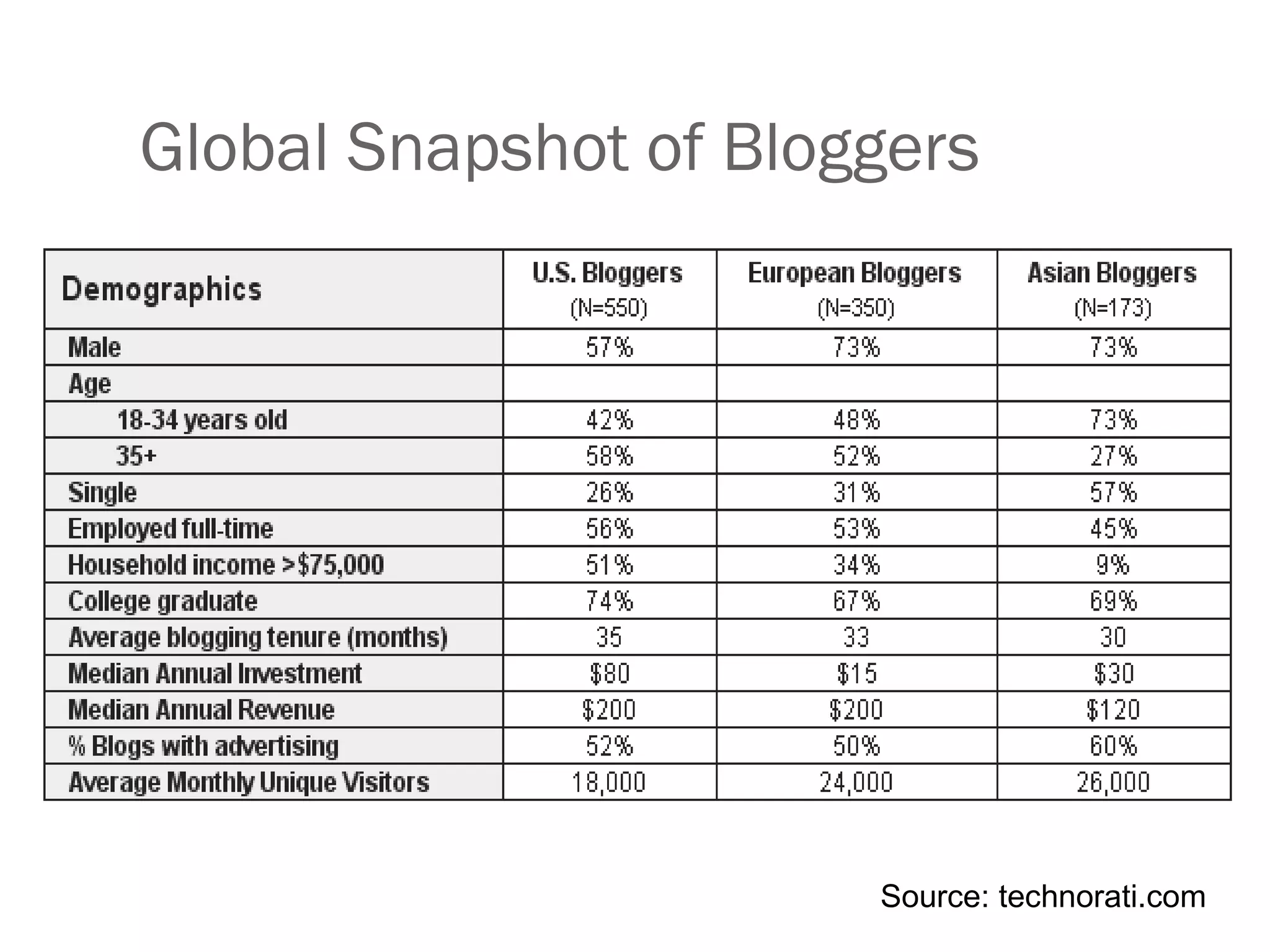




![Has the Blog Craze Peaked? Blogs, to use the words of one 19 year old contact are"so, so yesterday and all my friends are on Facebook" It’s a lot of writing, which can be time-consuming To attract a substantial audience, you have to have something to say on an ongoing basis Researchers for the Oxford English Dictionary claimed in 2007 that "the 15 most frequently used words in the blogosphere" (presumably the Anglo part of the blogosphere) are blogger, blog, stupid, me, myself, my, oh, yeah, ok, post, stuff, lovely, update, nice, [four letter word beginning with s]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web20maastricht20081110-1227319956177709-9/75/Evolving-Web-Evolving-Library-Maastricht-November-10-2008-32-2048.jpg)