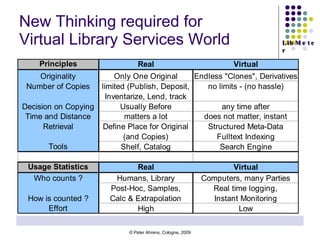
The document discusses the evaluation of electronic library services through usage statistics and performance indicators, focusing on how to interpret these figures for effective library management. It outlines various aspects of usage reporting, including where to find usage data, interpreting trends, and comparing libraries against benchmarks. The presentation includes practical insights, case studies, and theories related to improving library services through data analytics.






![Example for Webometrics: Ranking of World Universities http://www.webometrics.info/top100_continent.asp?cont=europe [2009-04-25]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libmeterseminarv1-0basics-090519152043-phpapp01/85/LibMeter-Seminar-Introduction-Basics-8-320.jpg)
![What „Google Insight“ can tell about German Libraries and Archives ? (I) http://www.google.com/insights/search/# q=Anna%20amalia&cmpt=q [2009-05-18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libmeterseminarv1-0basics-090519152043-phpapp01/85/LibMeter-Seminar-Introduction-Basics-9-320.jpg)
















![Selected Readings to broaden and to deepen your Understanding BIX - Der Bibliotheksindex 2008. B.I.T.online Sonderheft. 2008 Juni ;1-56. Blecic DD, Fiscella JB, Wiberley Jr SE . Measurement of Use of Electronic Resources: Advances in Use Statistics and Innovations in Resource Functionality. College and Research Libraries. 2007 ;68(1):26-44. Ceynowa VK, Coners A . Balanced Scorecard für wissensch. Bibliotheken. Vittorio Klostermann; 2002. Gallagher J, Bauer K, Dollar DM . Evidence-based librarianship: Utilizing data from all available sources to make judicious print cancellation decisions. Lib. Collections, Acq. & Tech. Serv.. 2005 ;29(2):169-179. George Boston, Whang M . E-Resources Usage Data: Apples to Oranges and Fixing Holes [Internet]. Atlanta: 2008. [zitiert 2009 Apr 22] Available_from:http://209.85.129.132/search?q=cache:mj5wfYDT2BoJ:https://smartech.gatech.edu/bitstream/1853/20874/13/Boston_Whang_ERL_final.ppt+scholarly-stats+sfx&cd=4&hl=de&ct=clnk&gl=de&client=firefox-a Hutzler E . Bibliotheken gestalten Zukunft : Kooperative Wege zur digitalen Bibliothek. Dr. Friedrich Geißelmann zum 65. Geburtstag. Universitätsverlag Göttingen; 2008. Kreische J . Die Messung von Vernetzung. Nutzungsstatistiken mit SFX [Internet]. Münster: 2006. Available from: http://docserv.uni-duesseldorf.de/servlets/DocumentServlet?id=9728 7. Kreische J . Zwischen Ranking und Qualitätsmanagement: BIX WB [Internet]. Mannheim: 2008. Available from: http://www.opus-bayern.de/bib-info/volltexte/2008/583/pdf/BIX%20Mannheim%20(Word%202003).pdf Poll R, te Boekhorst P , Measuring quality, Saur, München, 2007. Lossau N . digital services in academic libraries. In: Digital Convergence - Libraries of the Future: Libraries of the Future. Springer; 2008. Shepherd P . The feasibility of developing and implementing journal usage factors: a research project sponsored by UKSG. Serials. 2007;20(2):117-123.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libmeterseminarv1-0basics-090519152043-phpapp01/85/LibMeter-Seminar-Introduction-Basics-28-320.jpg)




