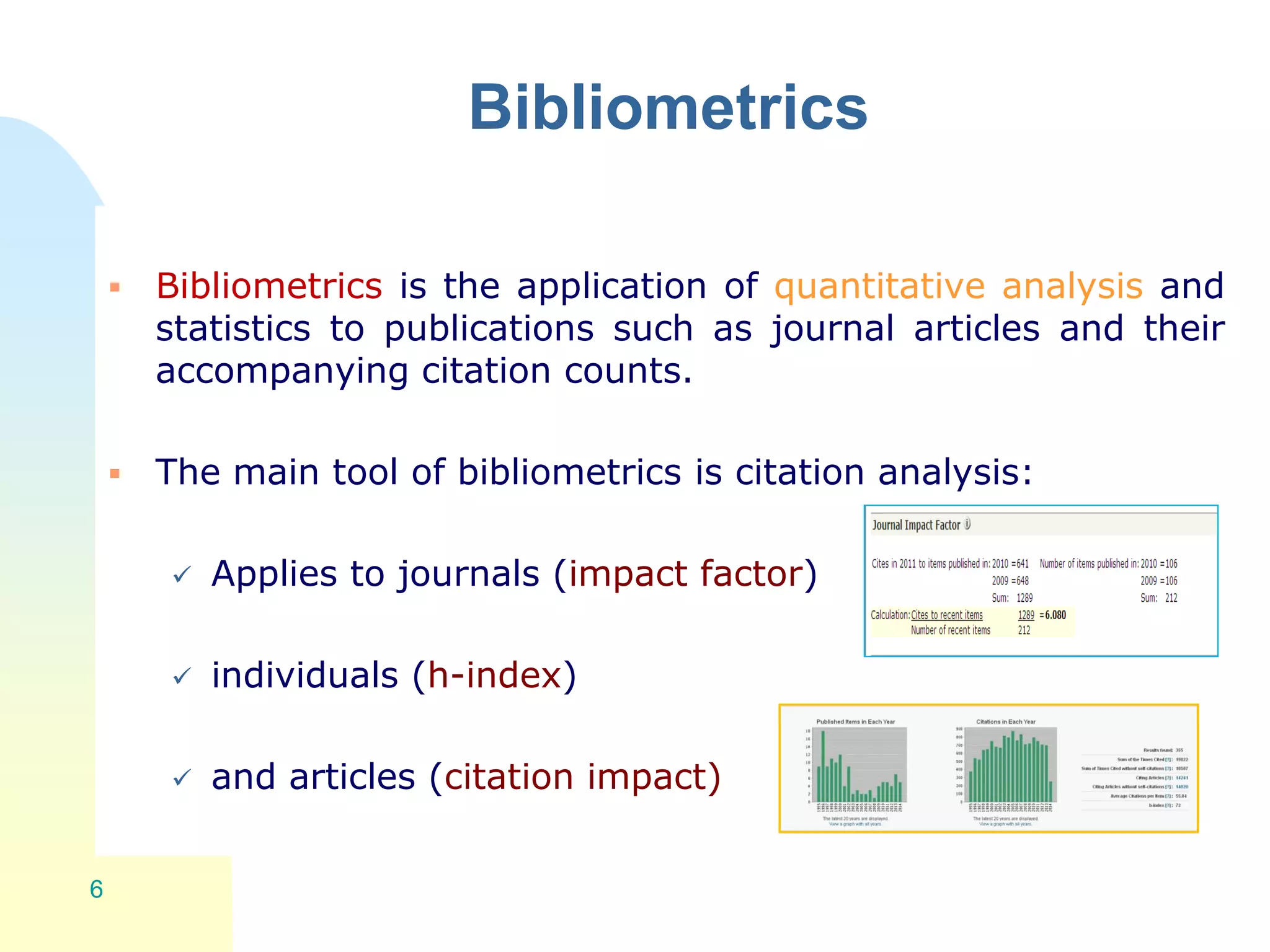
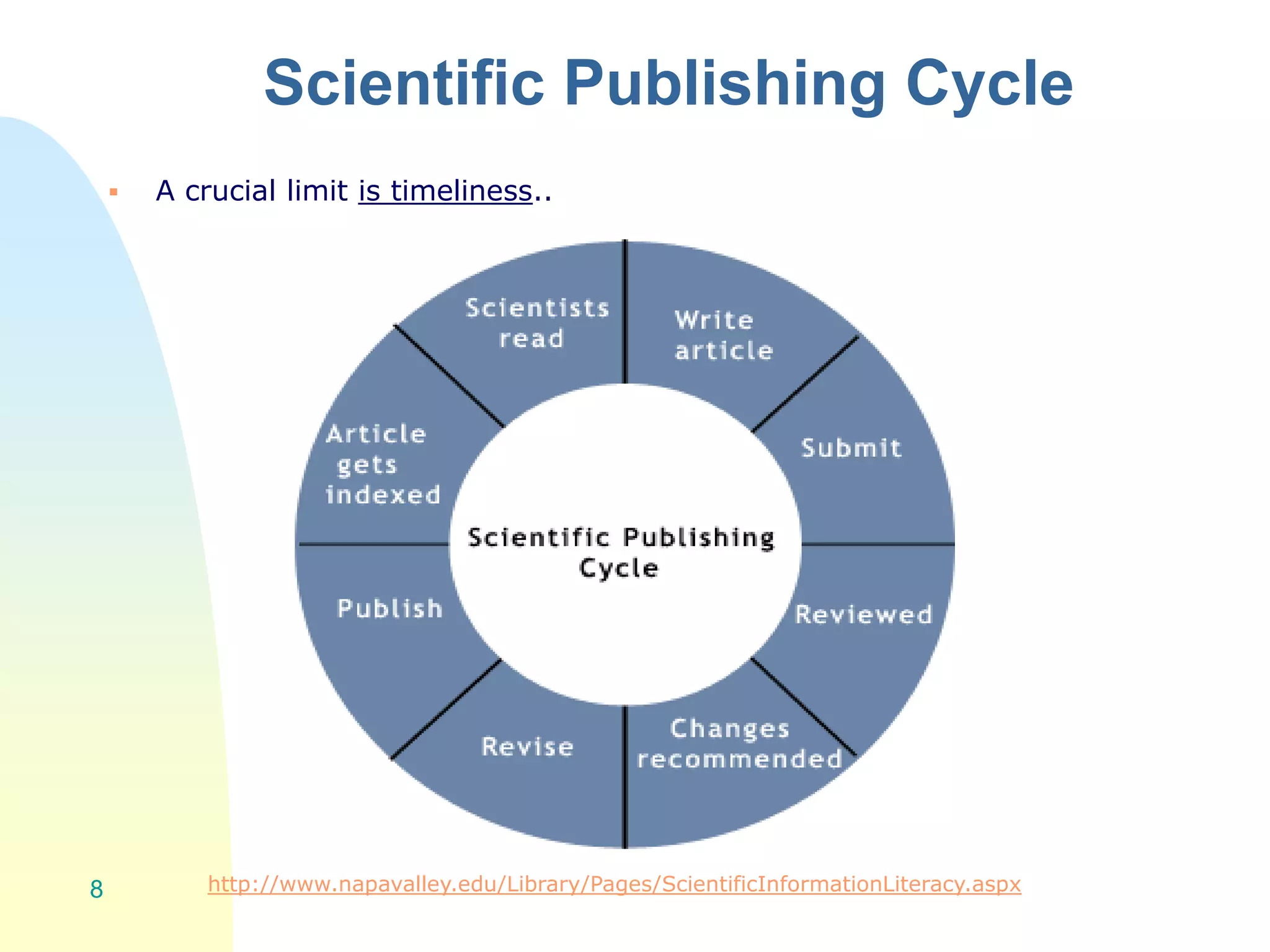
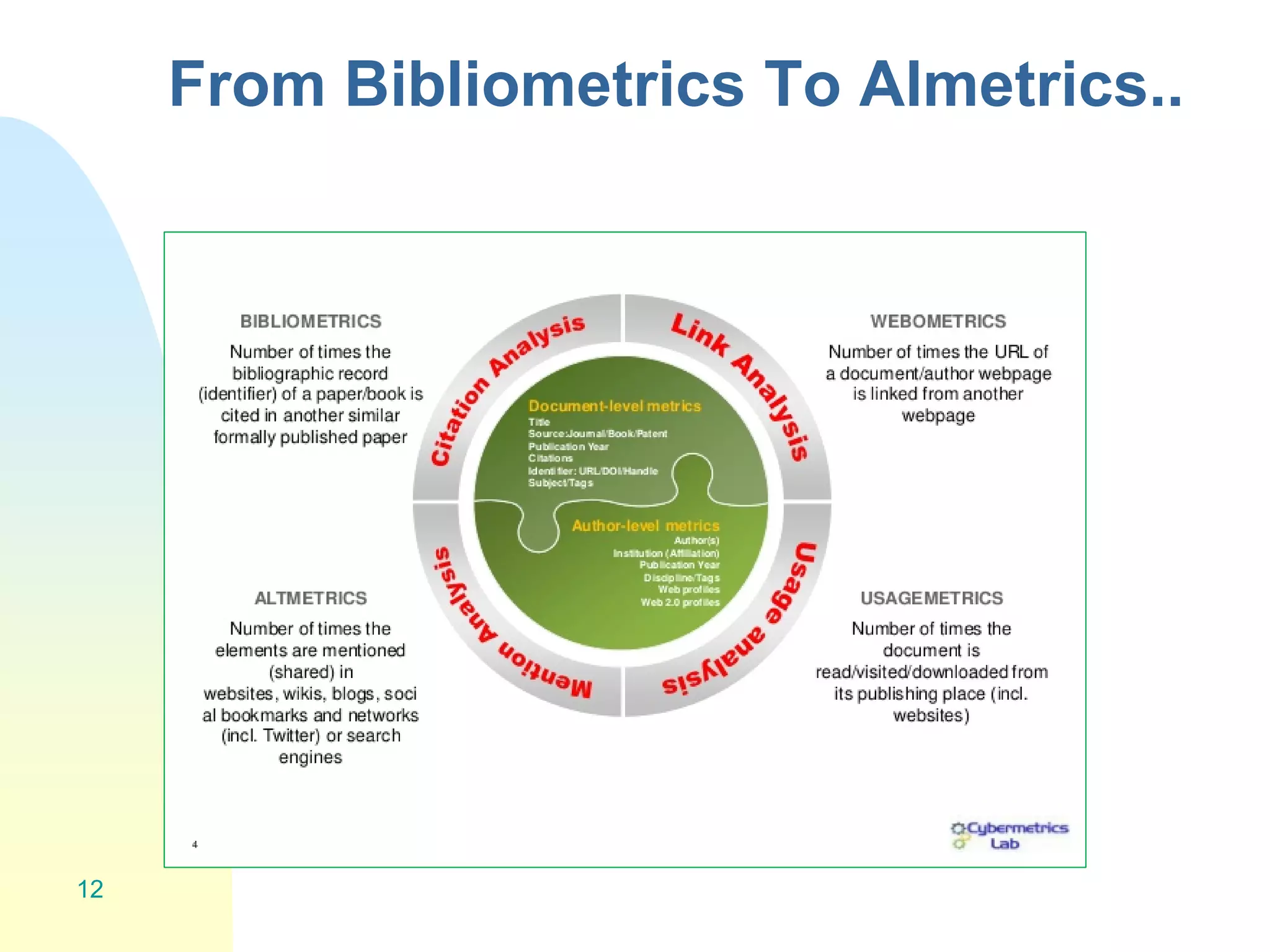
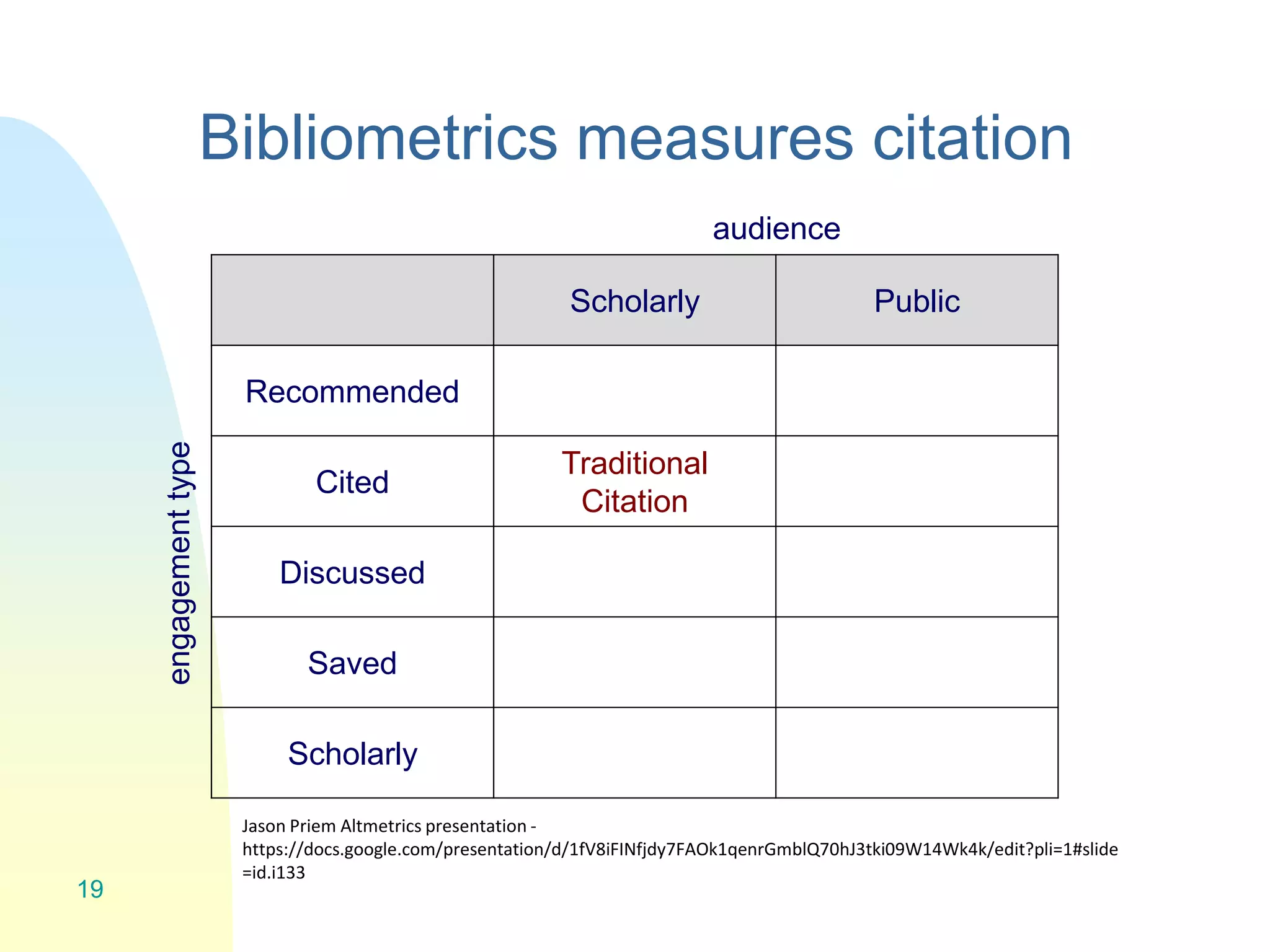
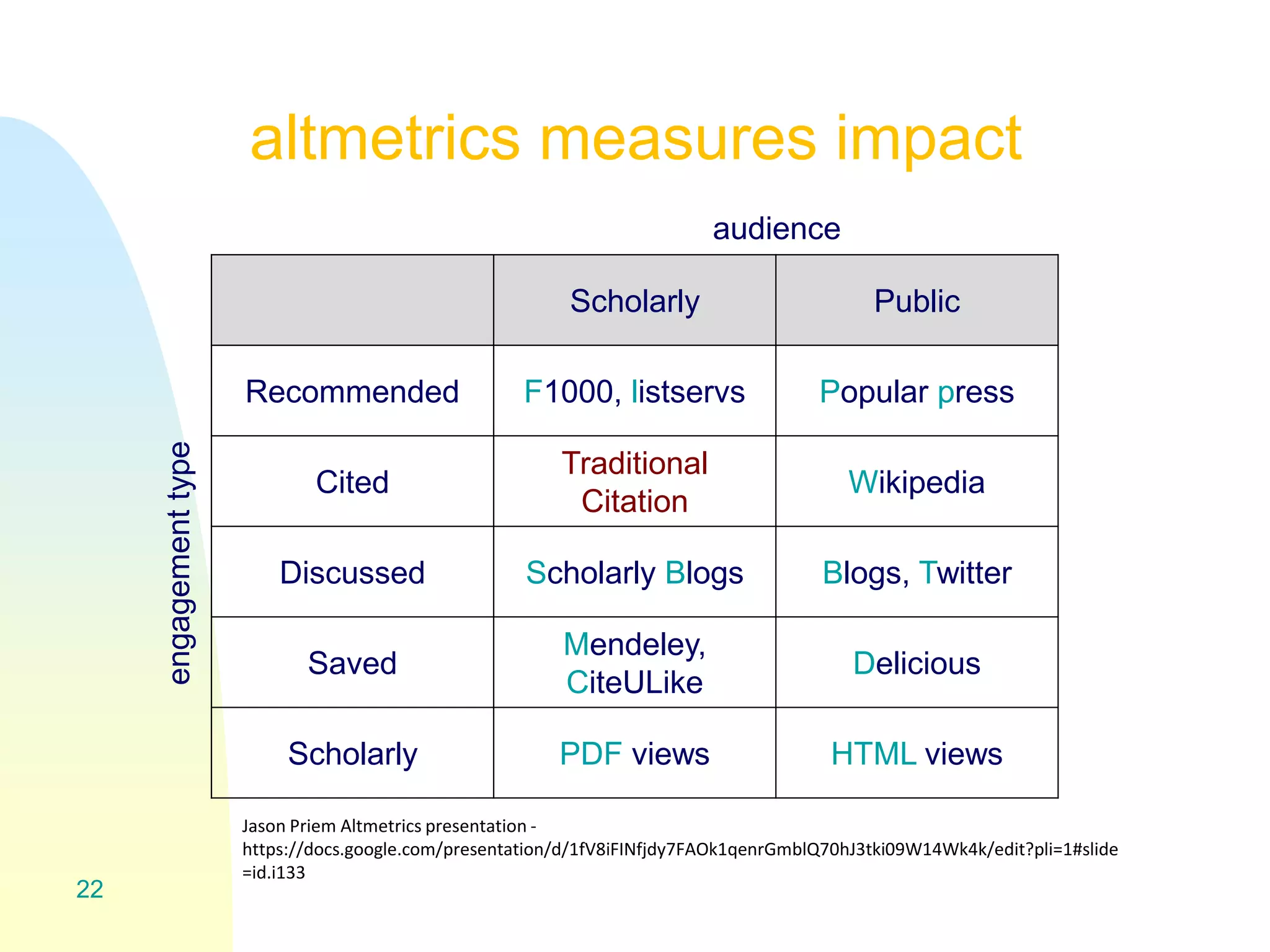
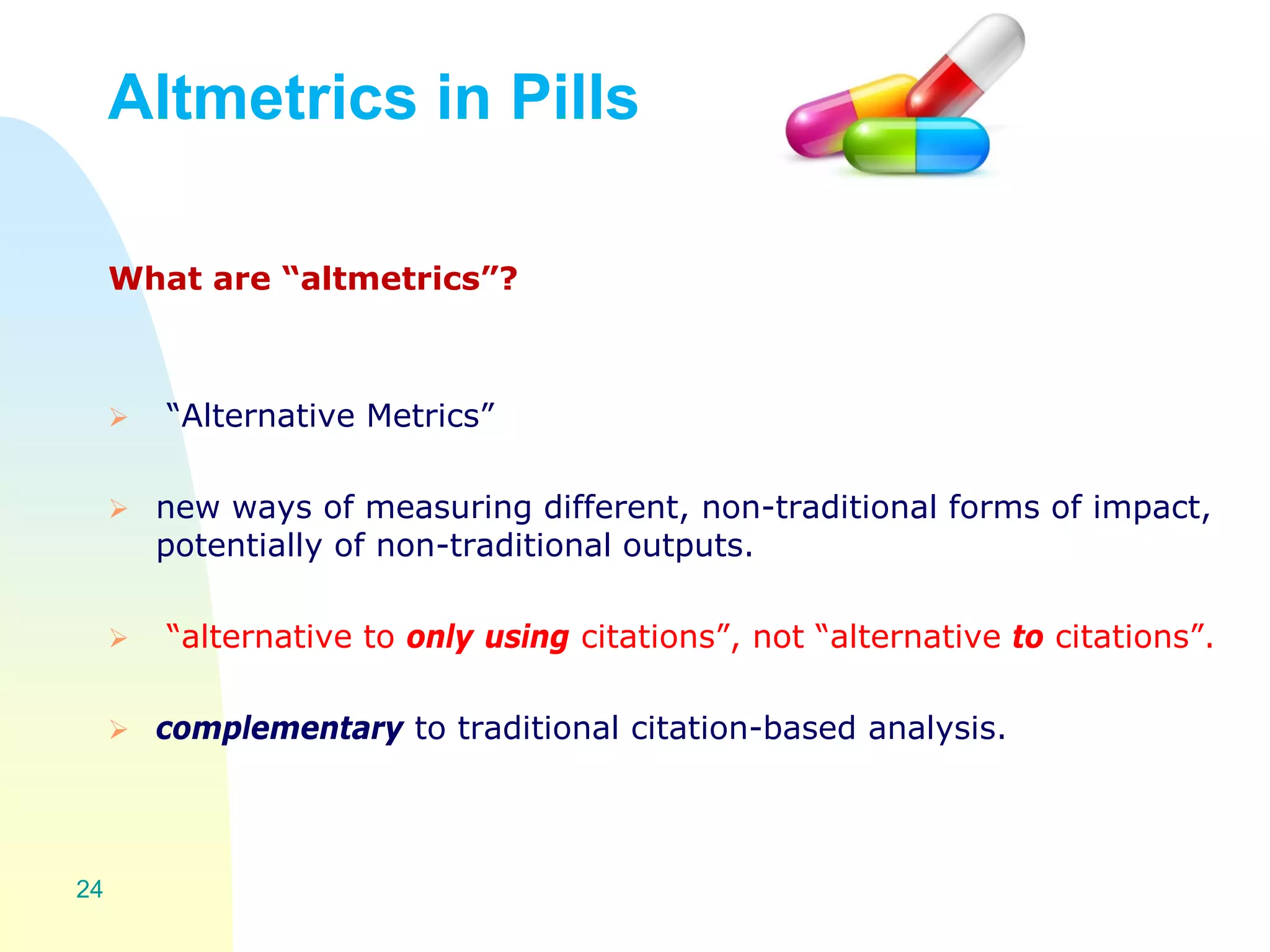
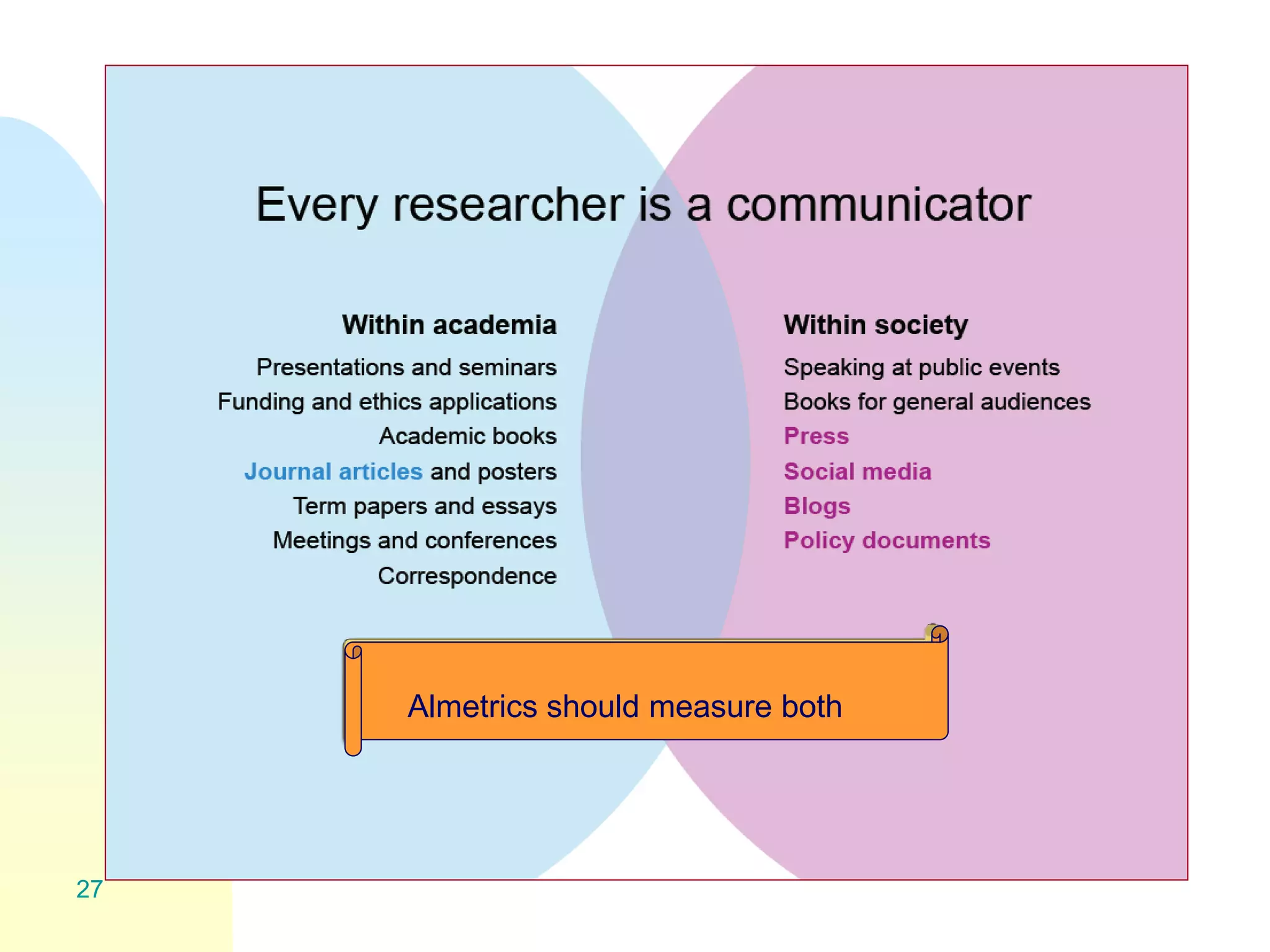
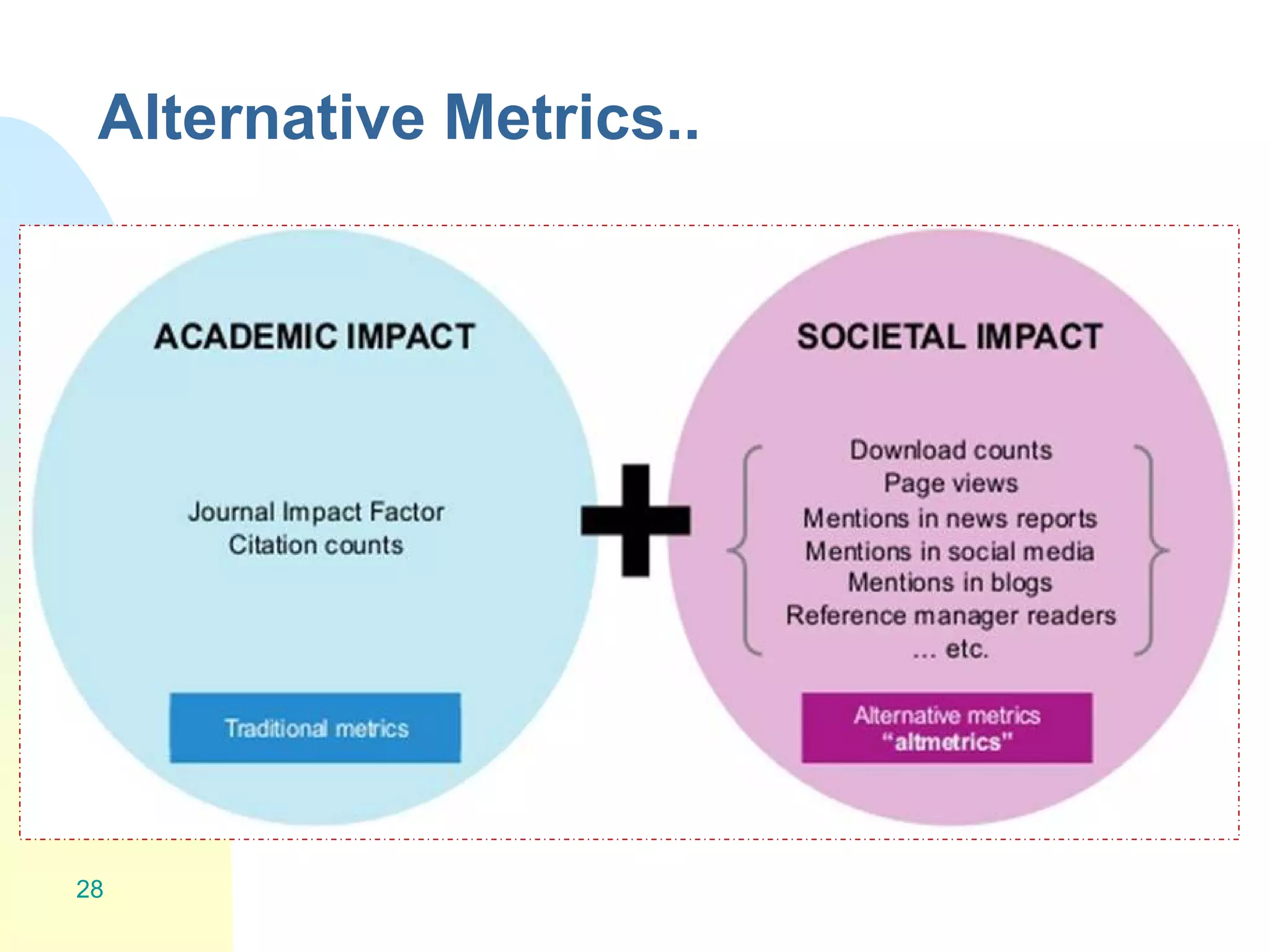
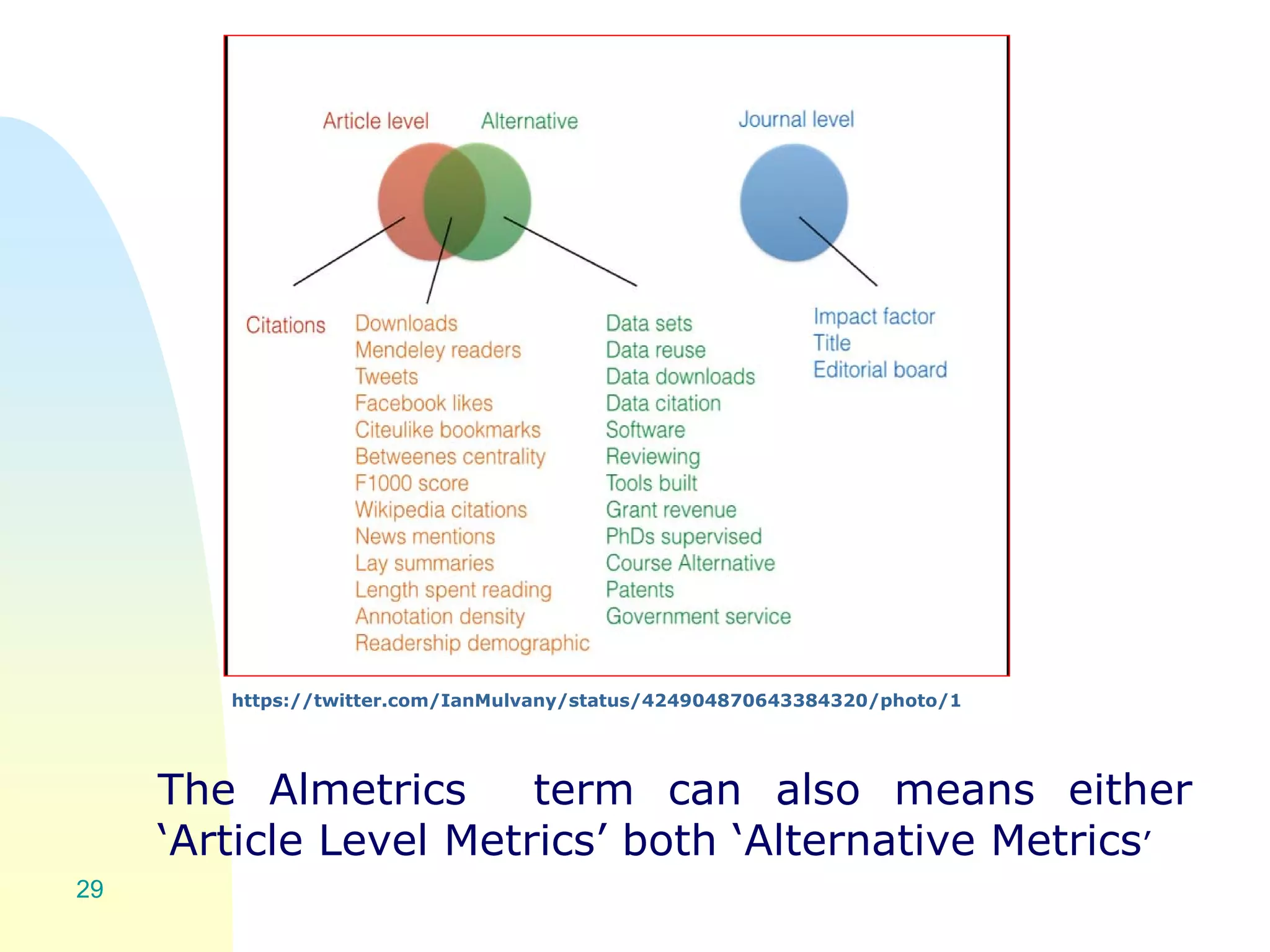
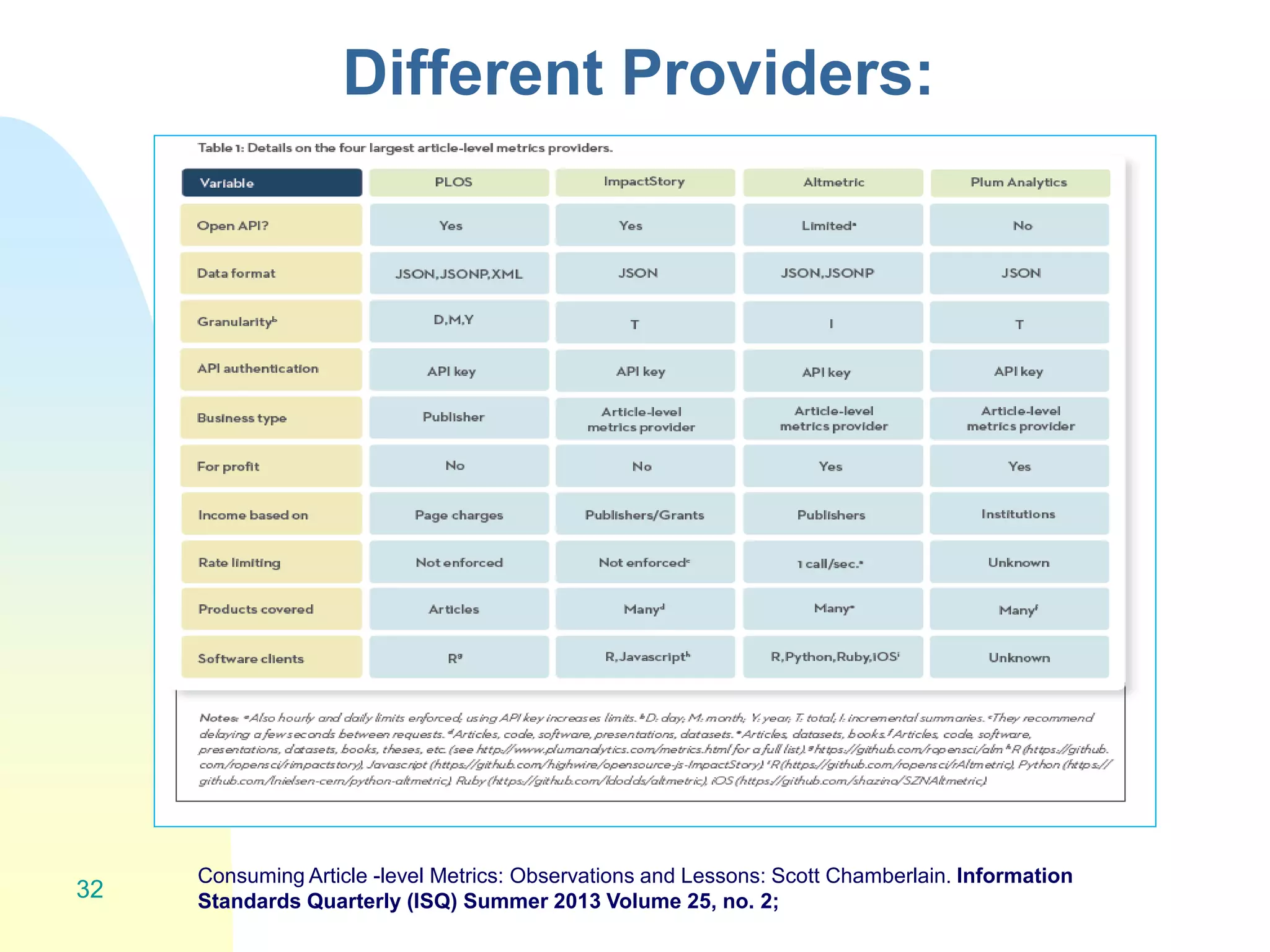
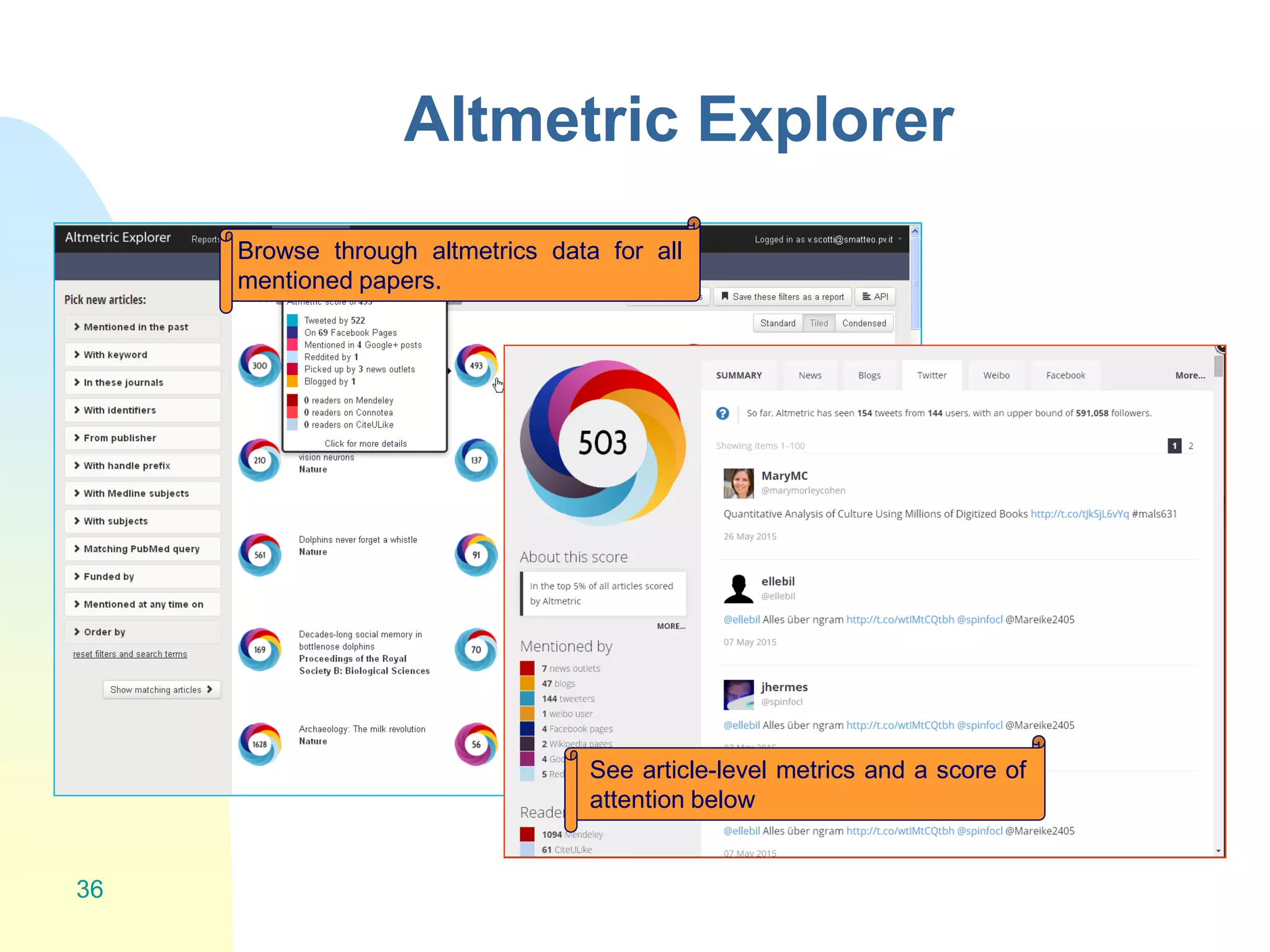
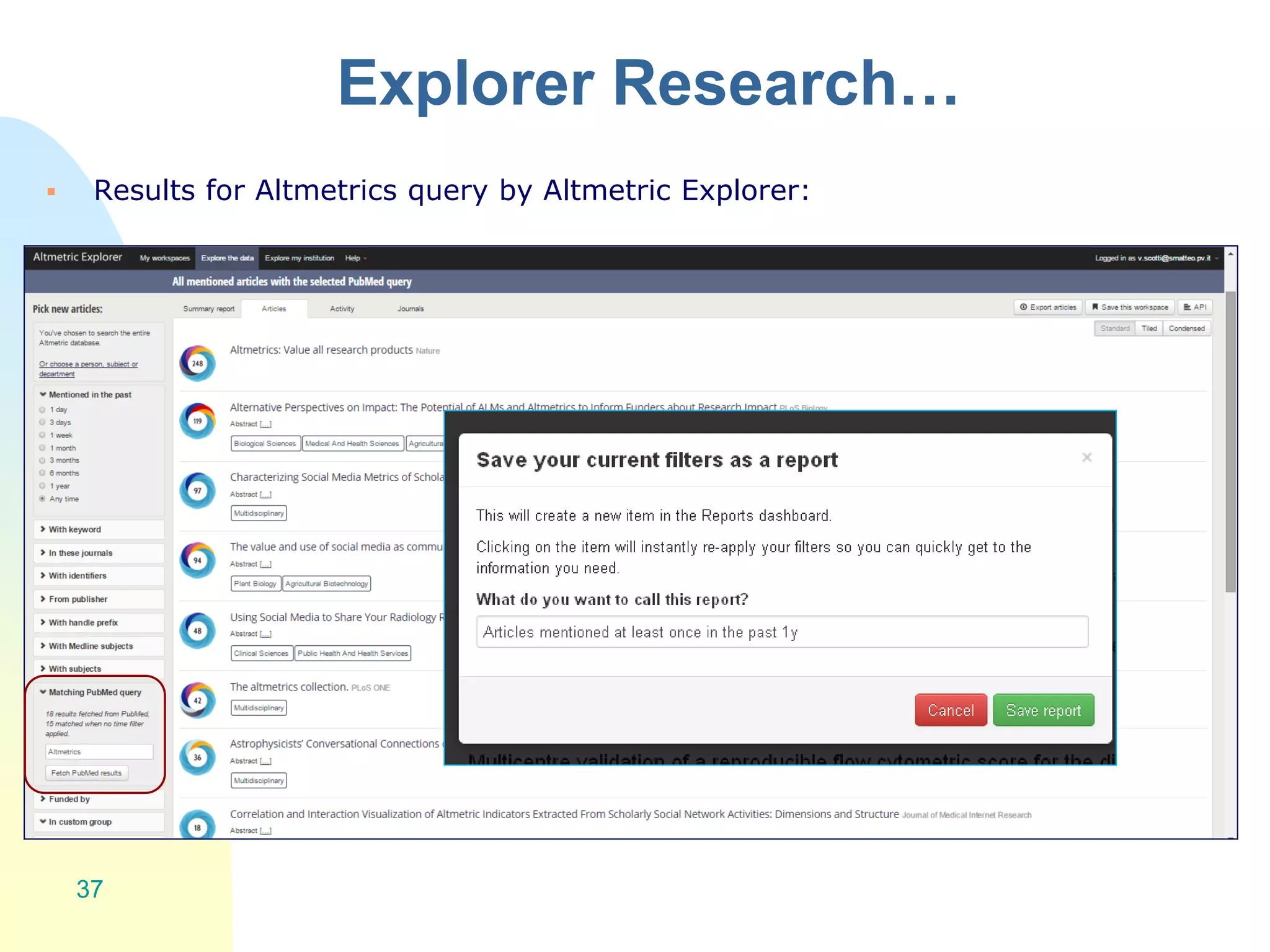
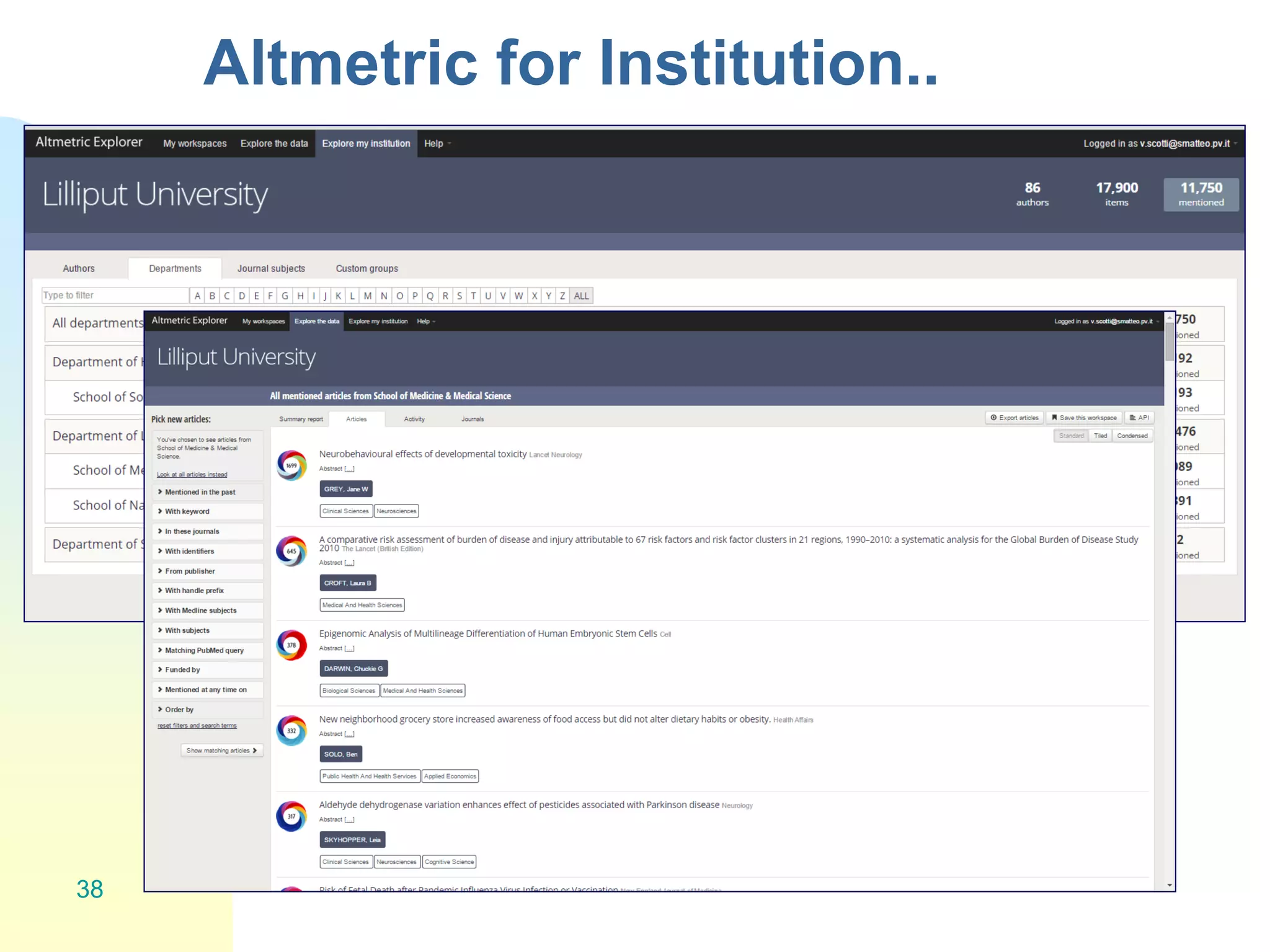
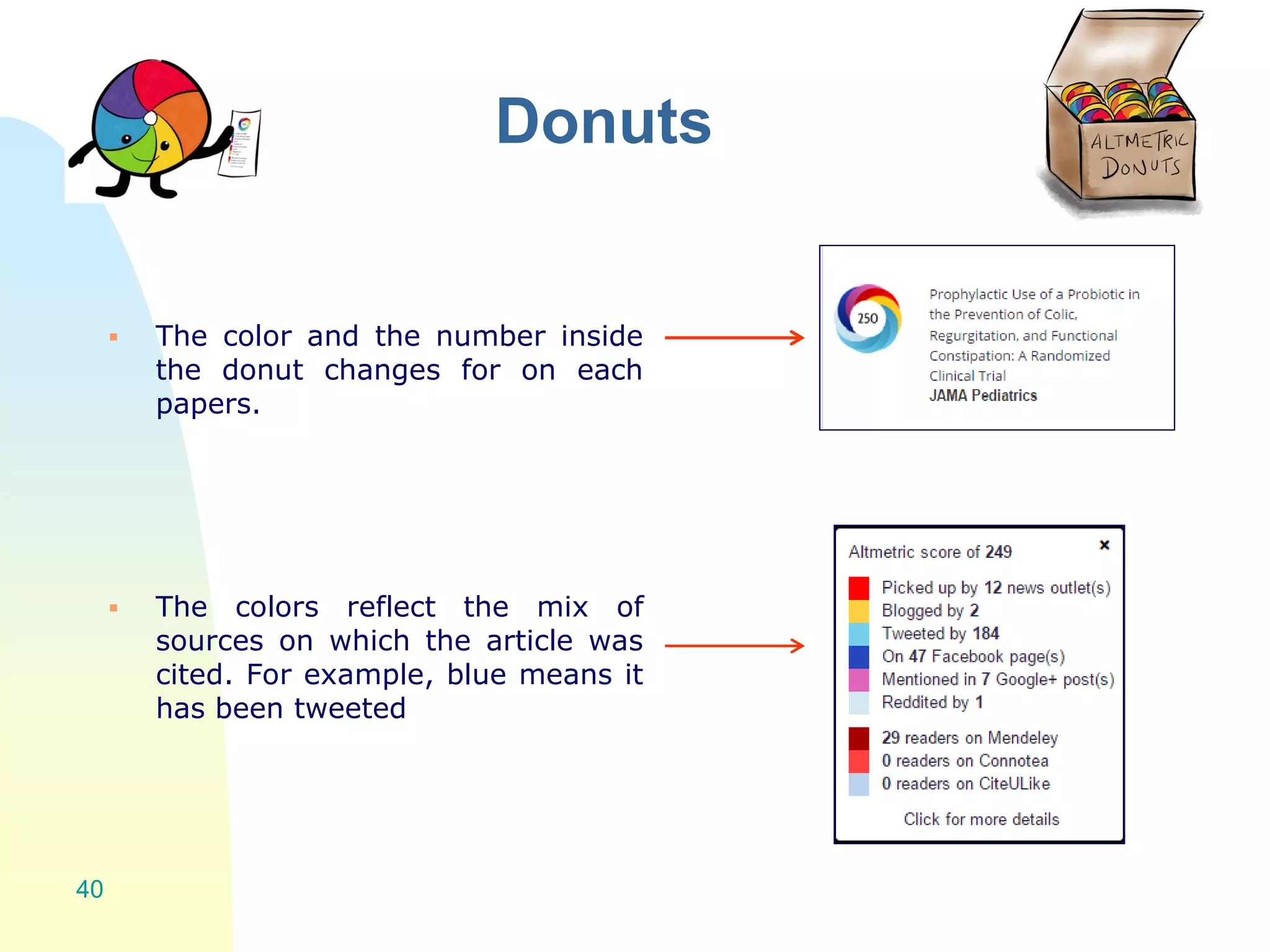
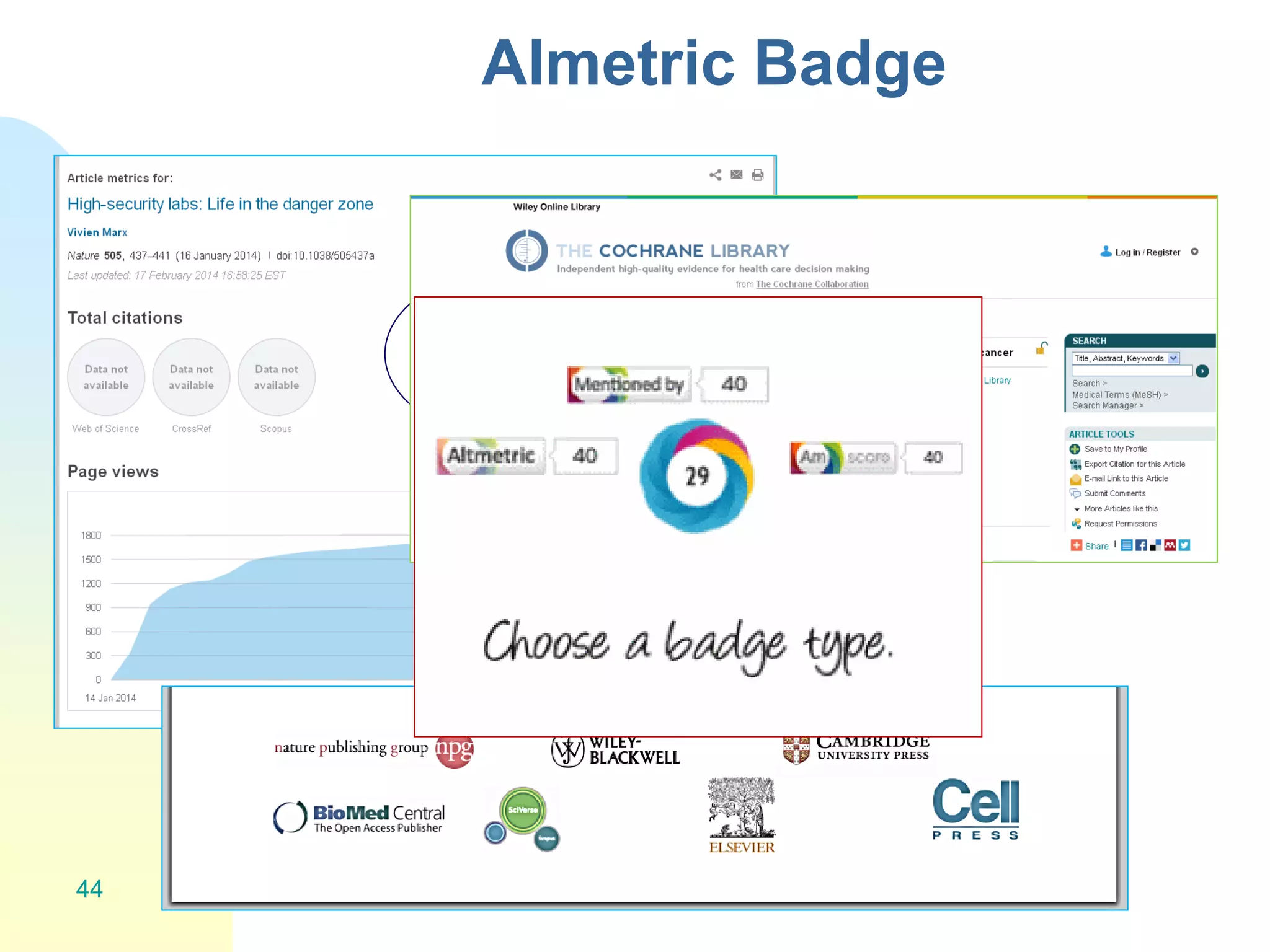
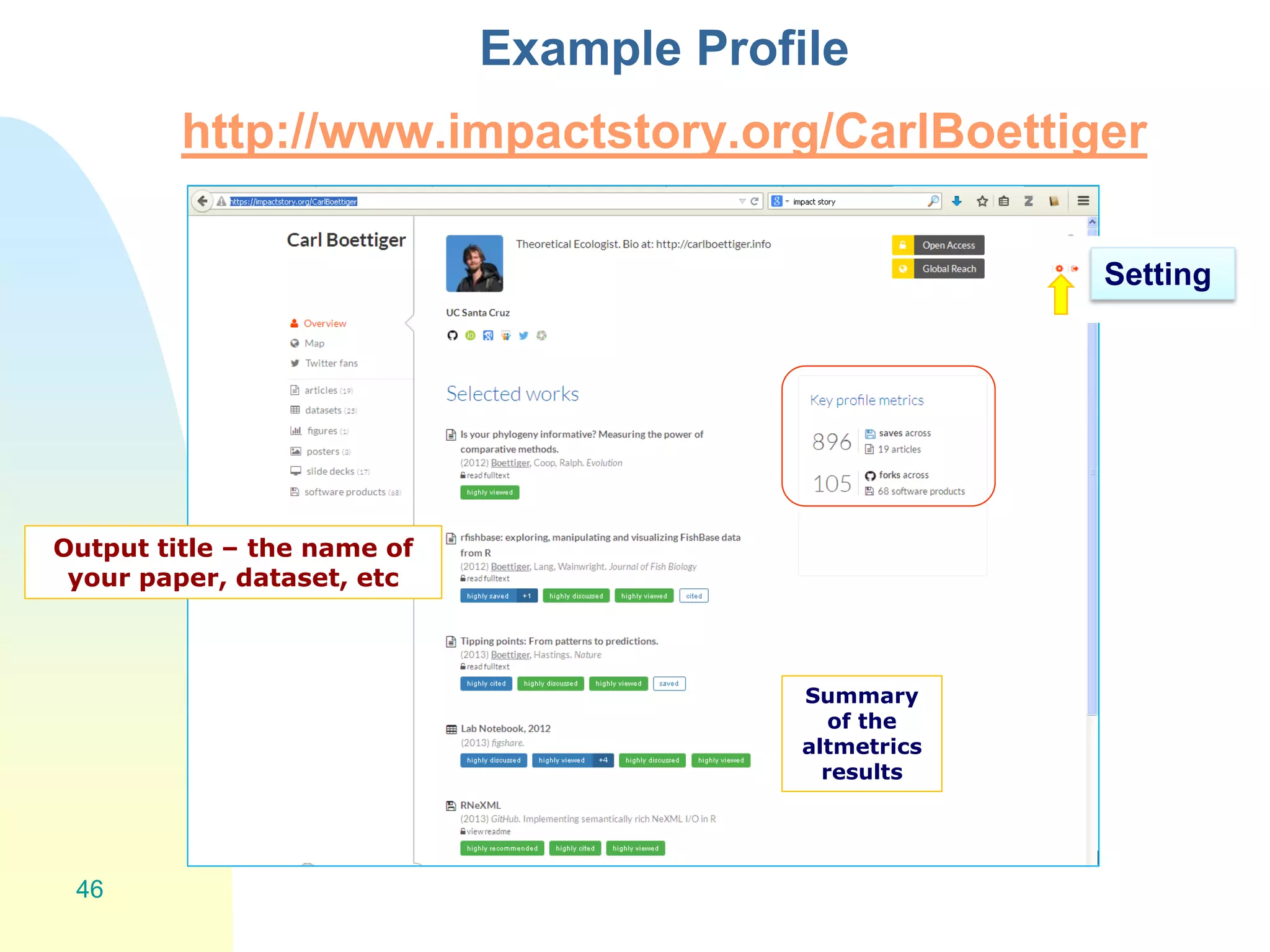
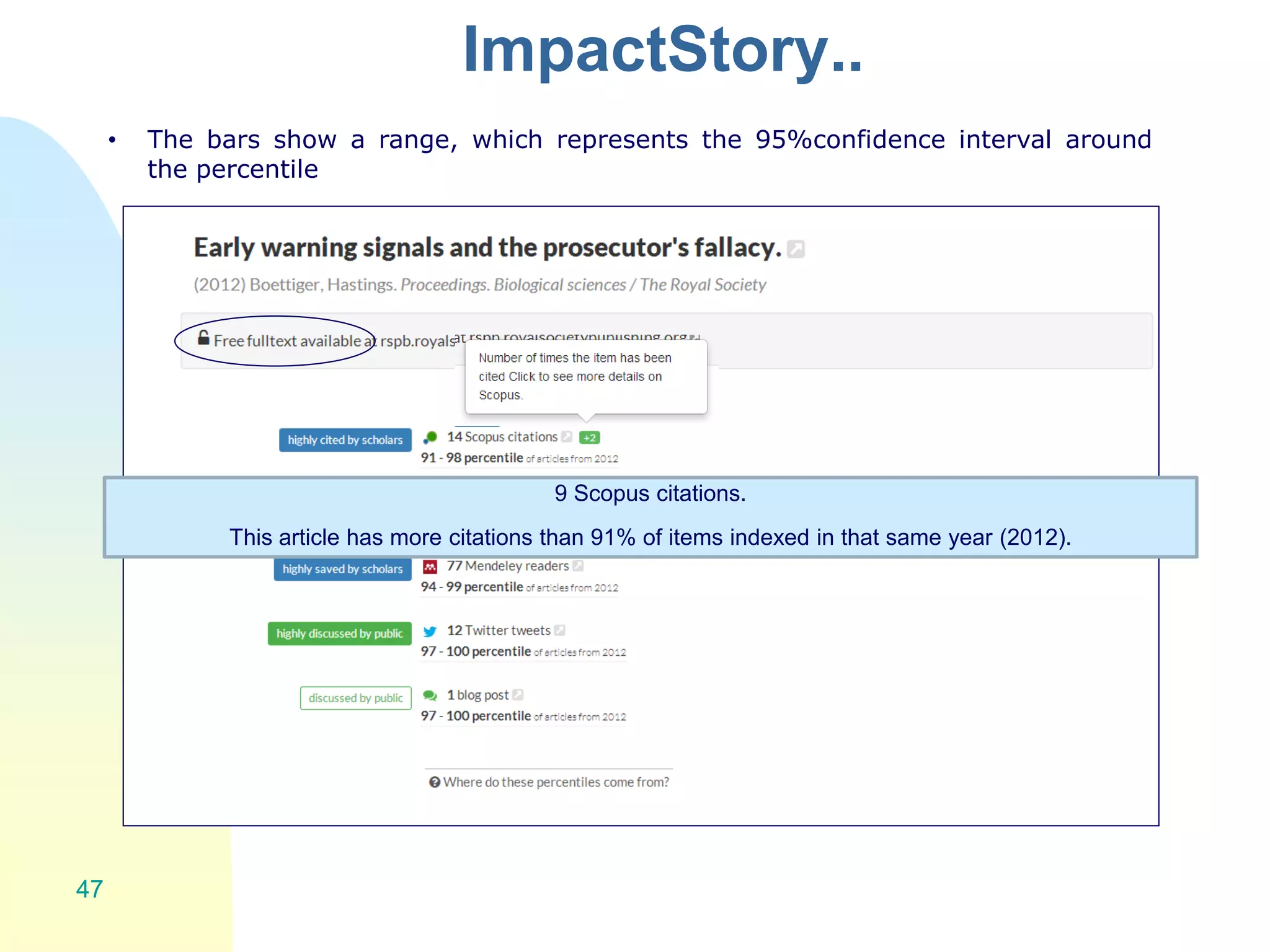
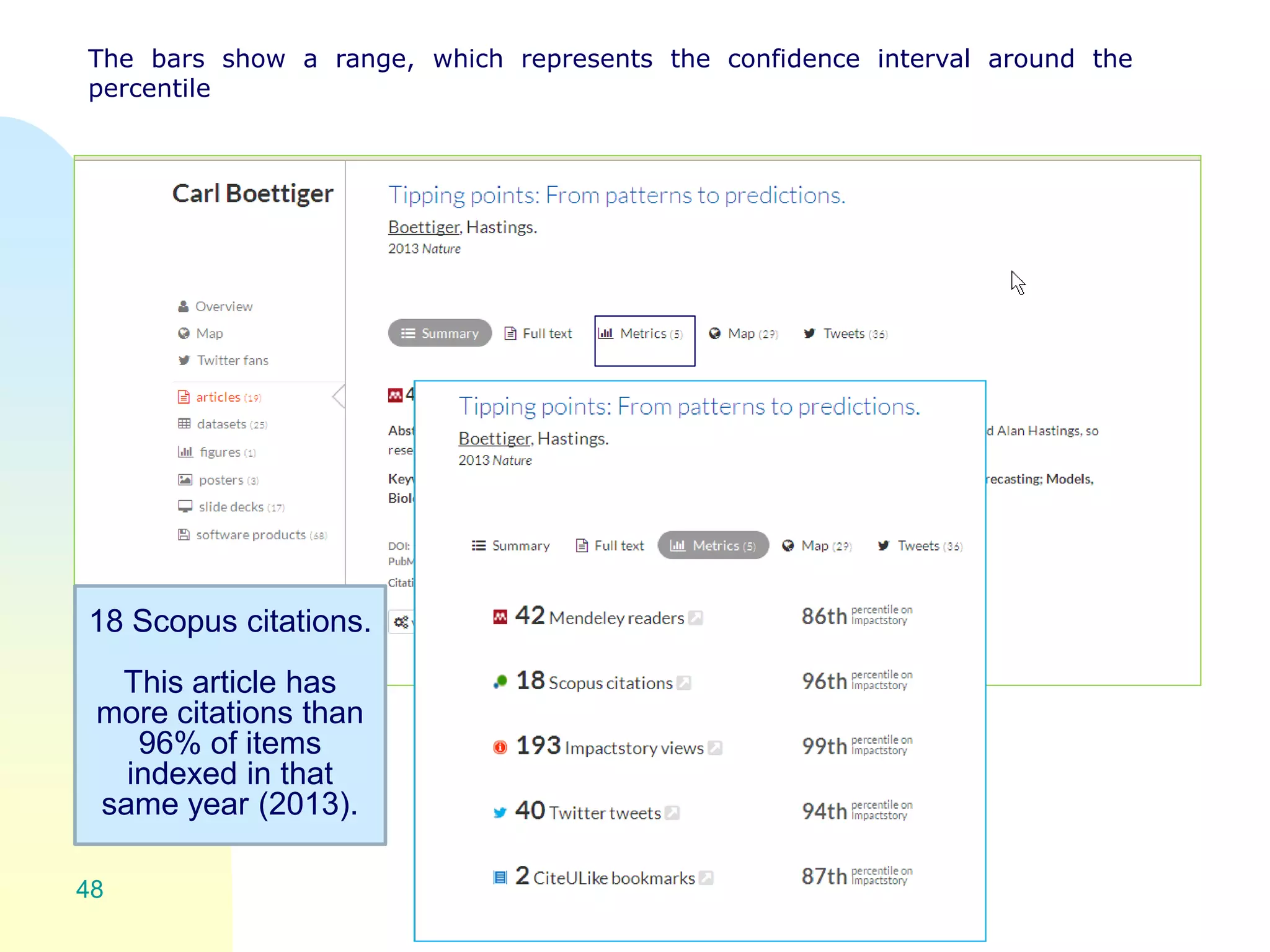
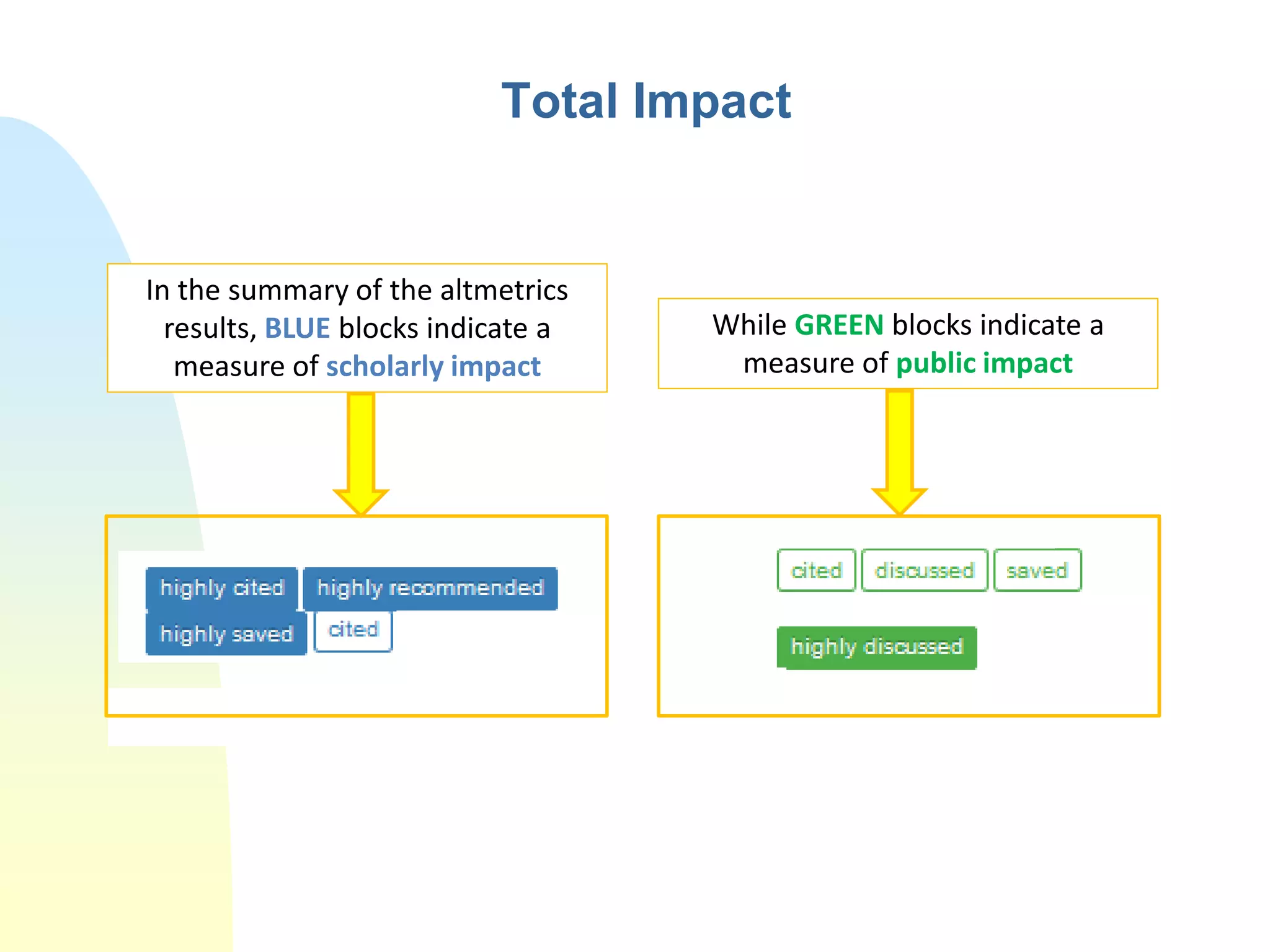
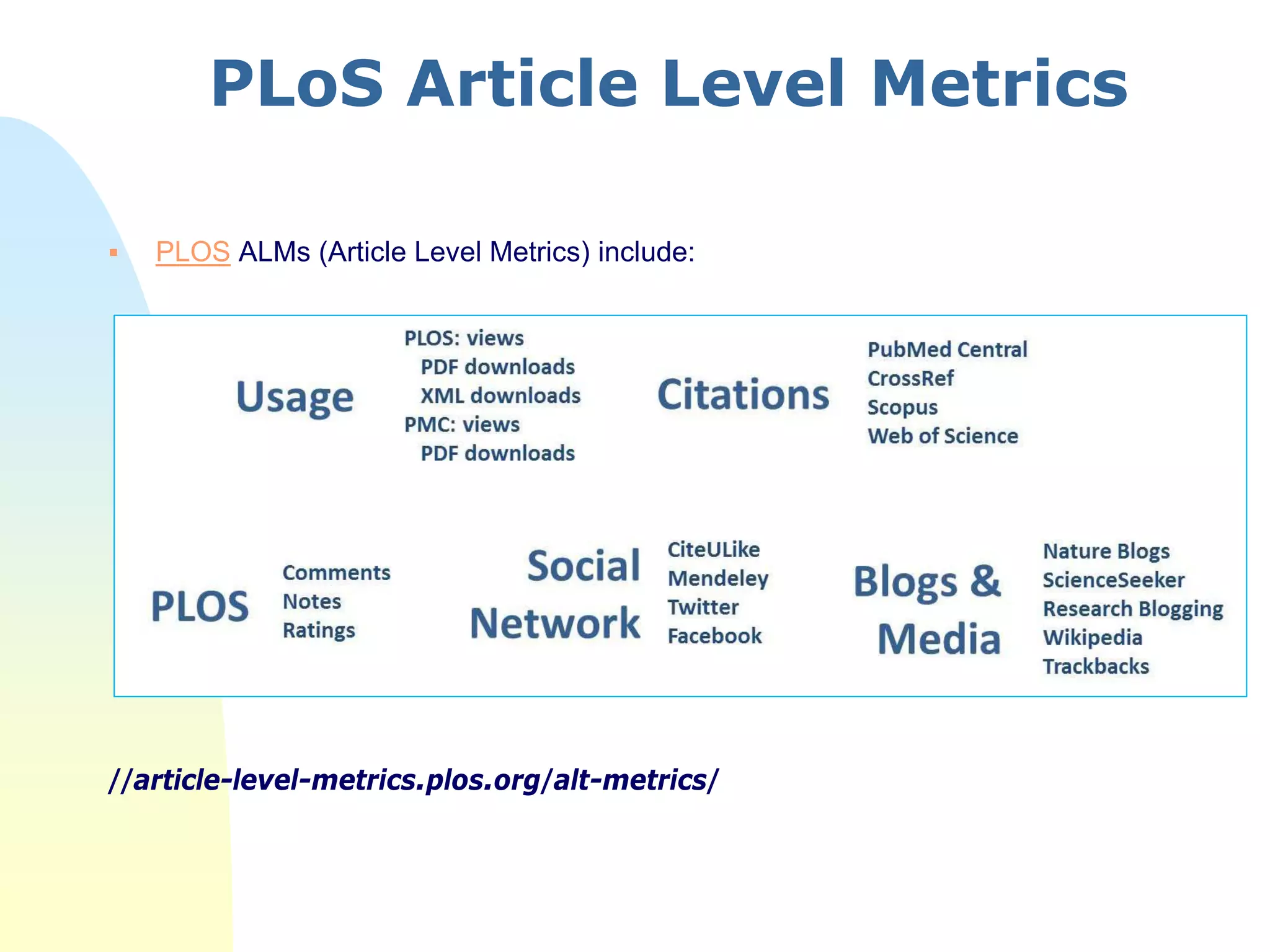
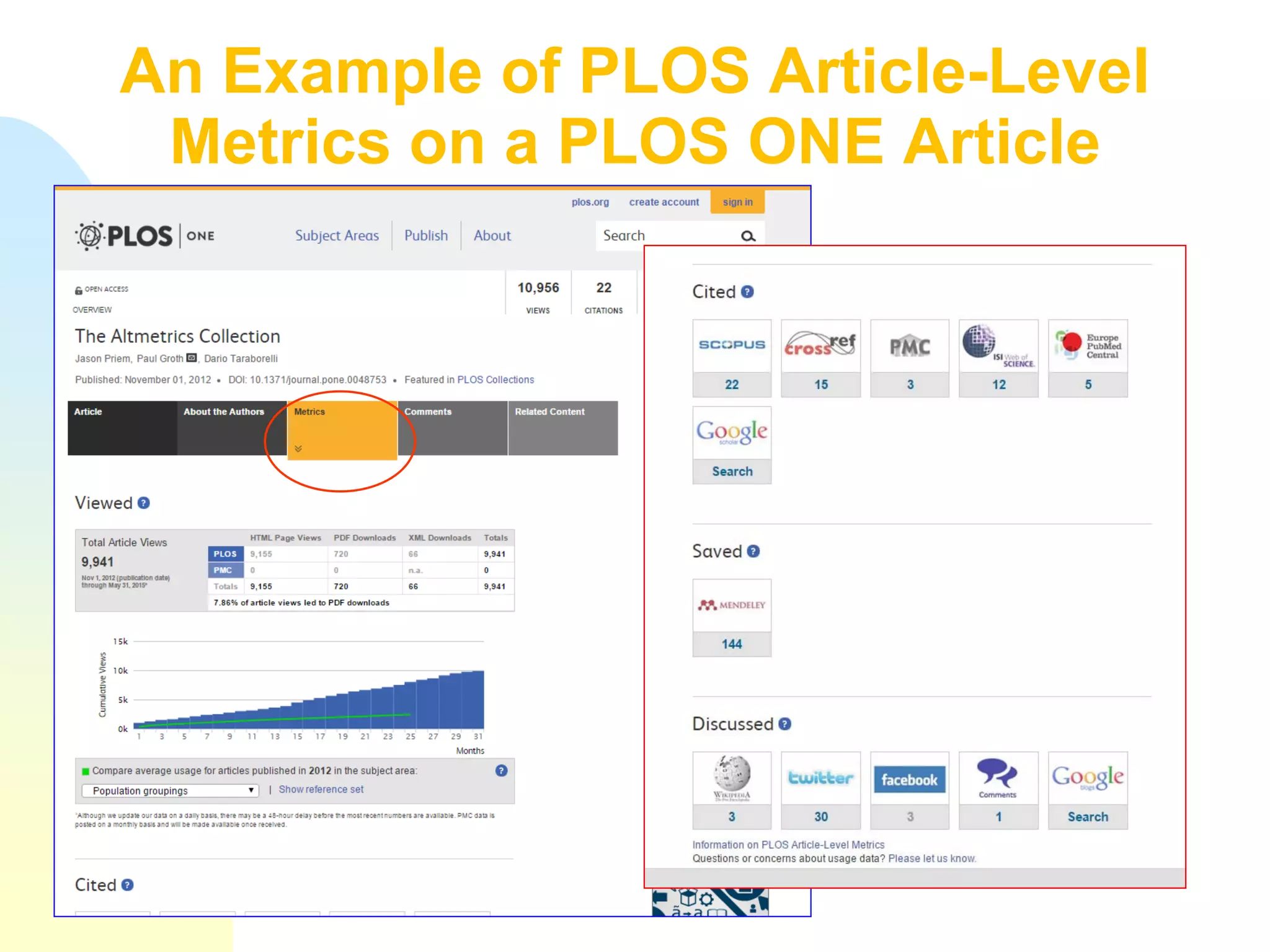
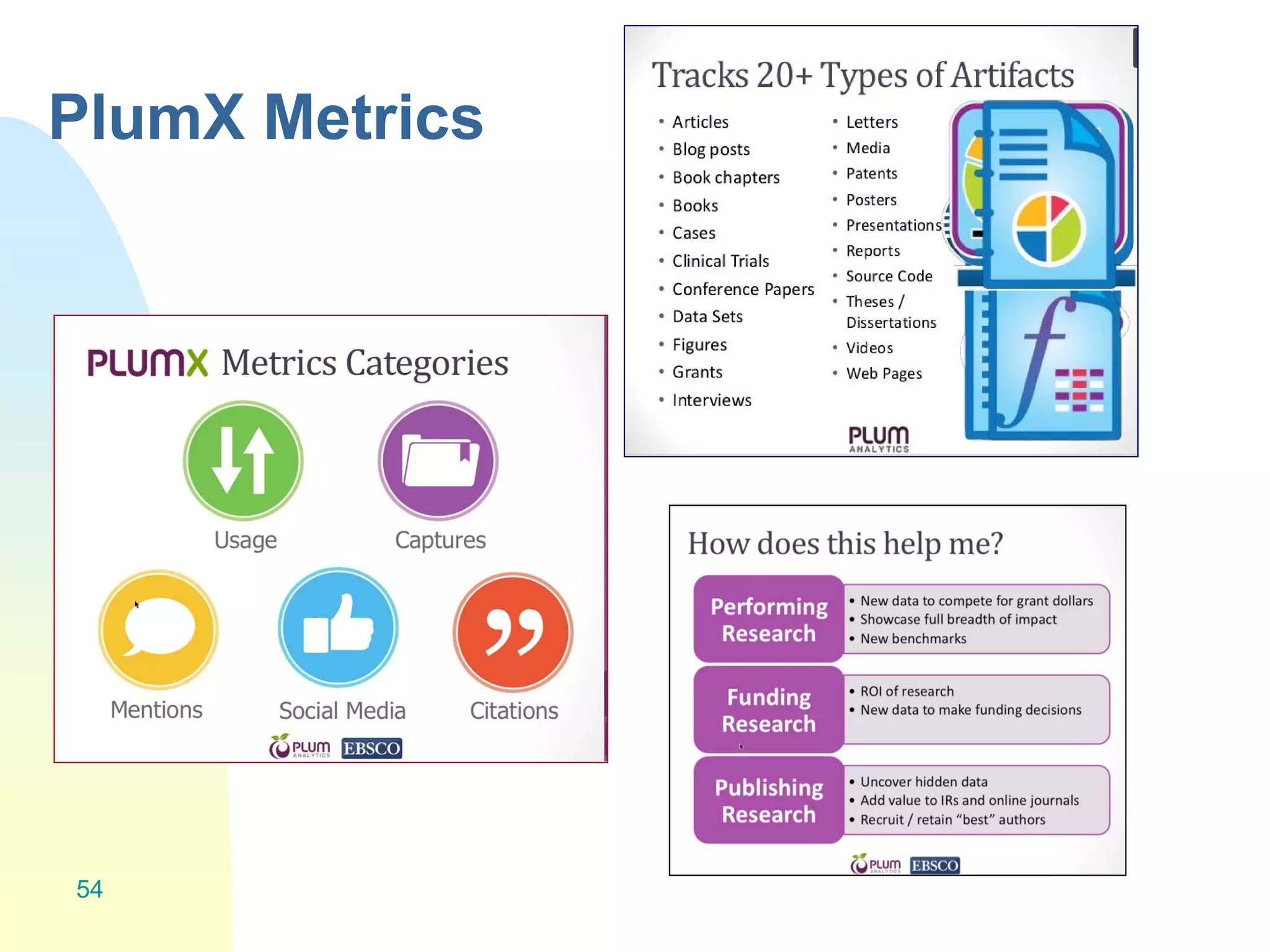
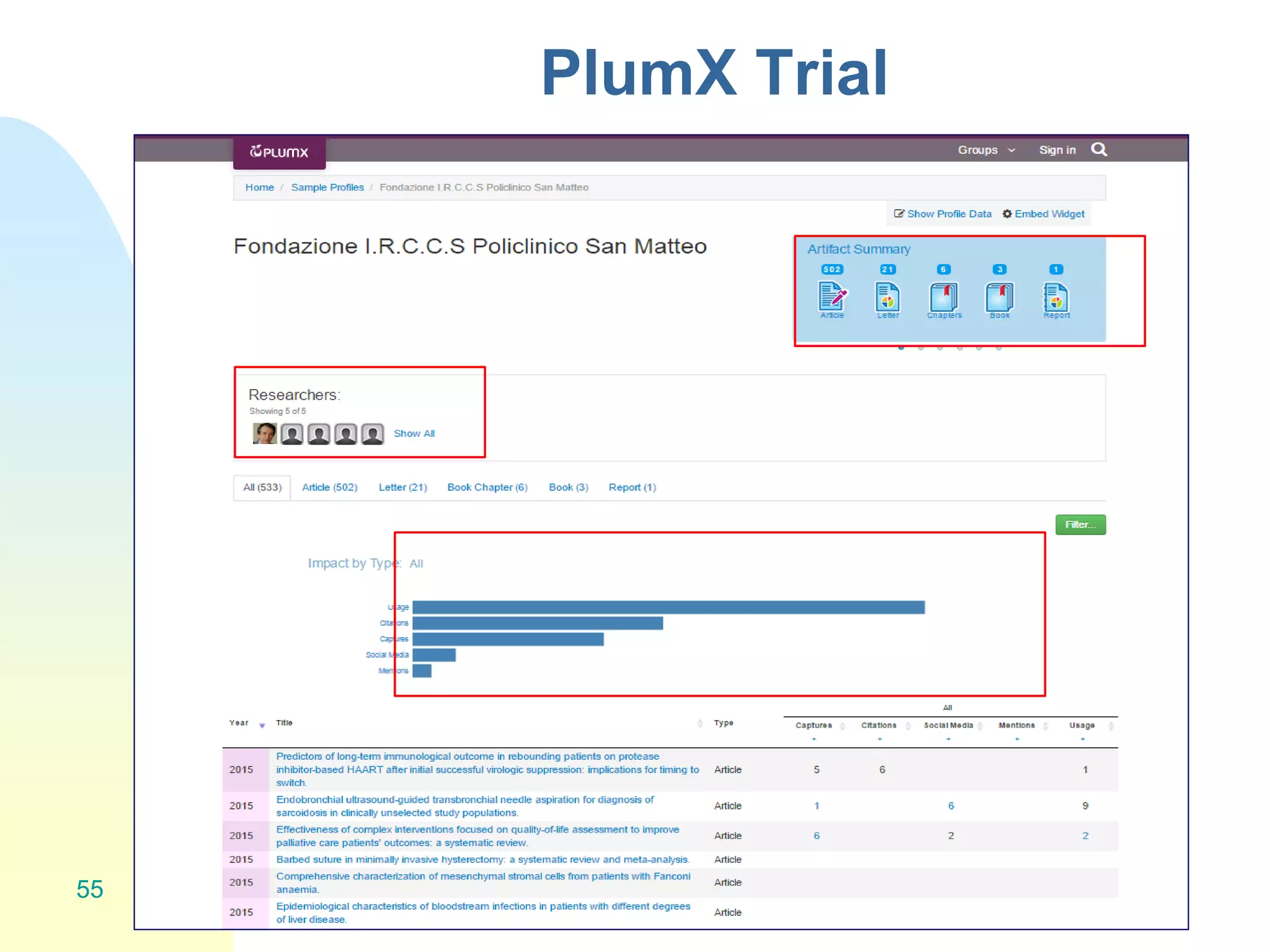
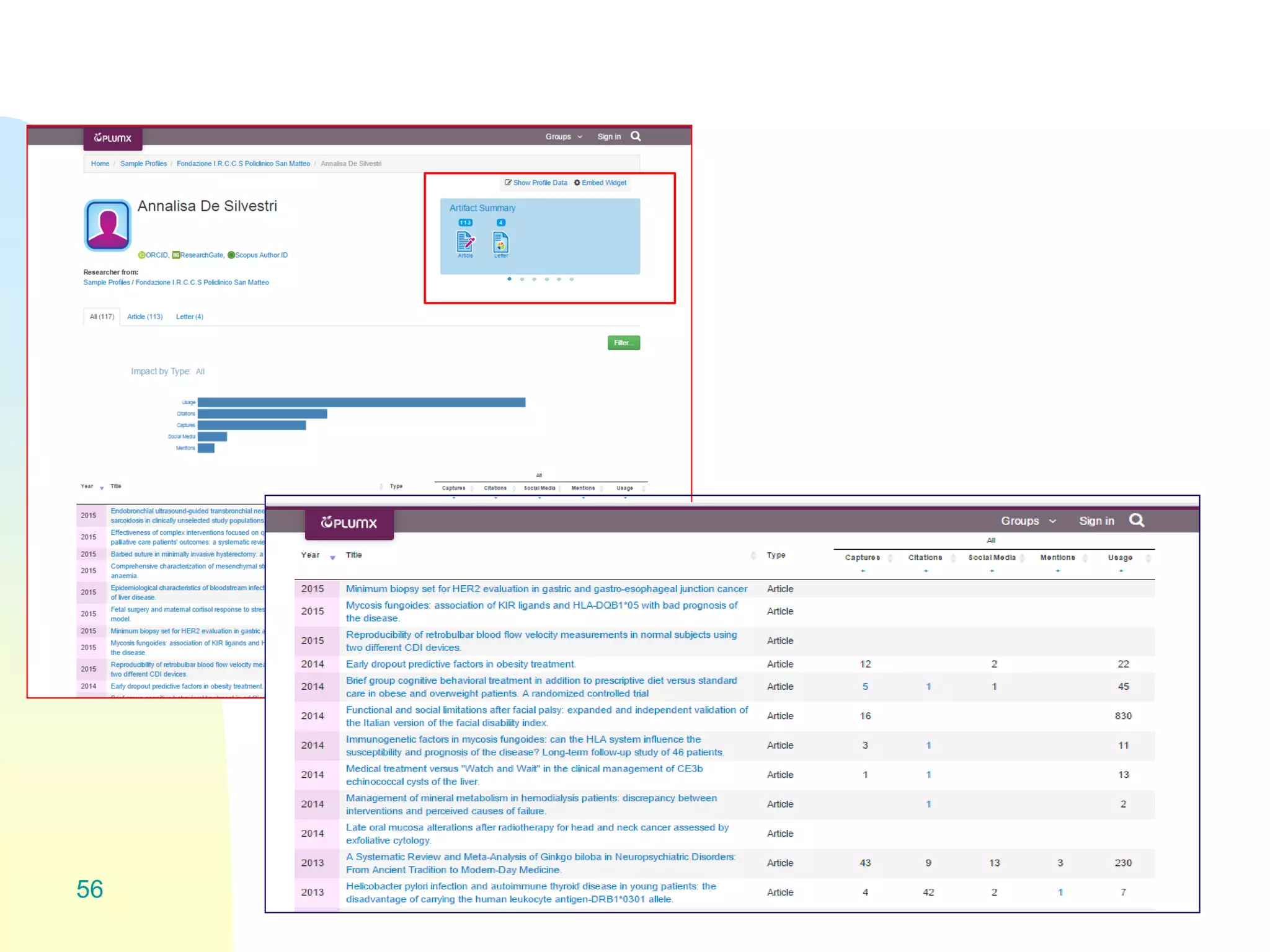
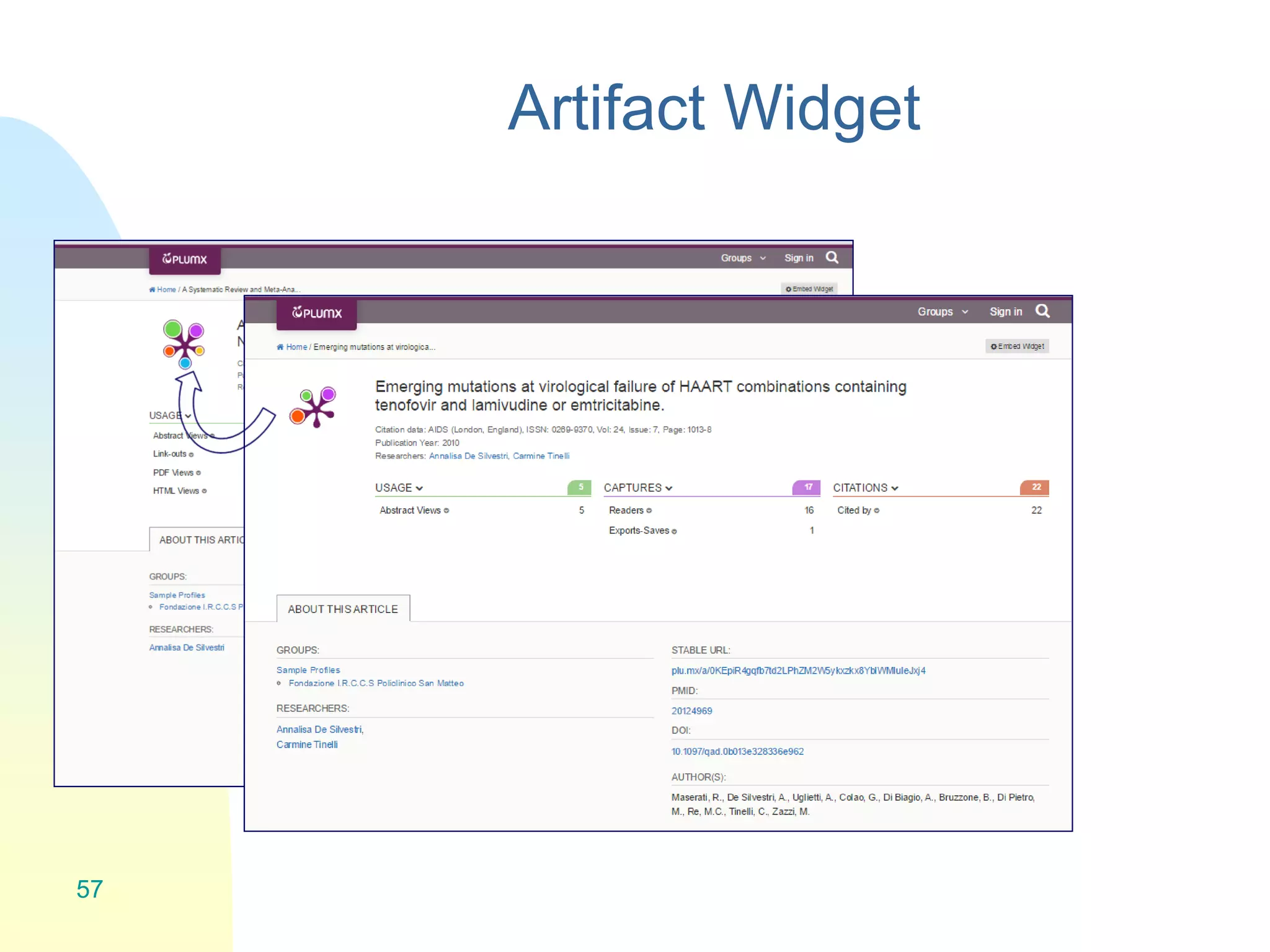
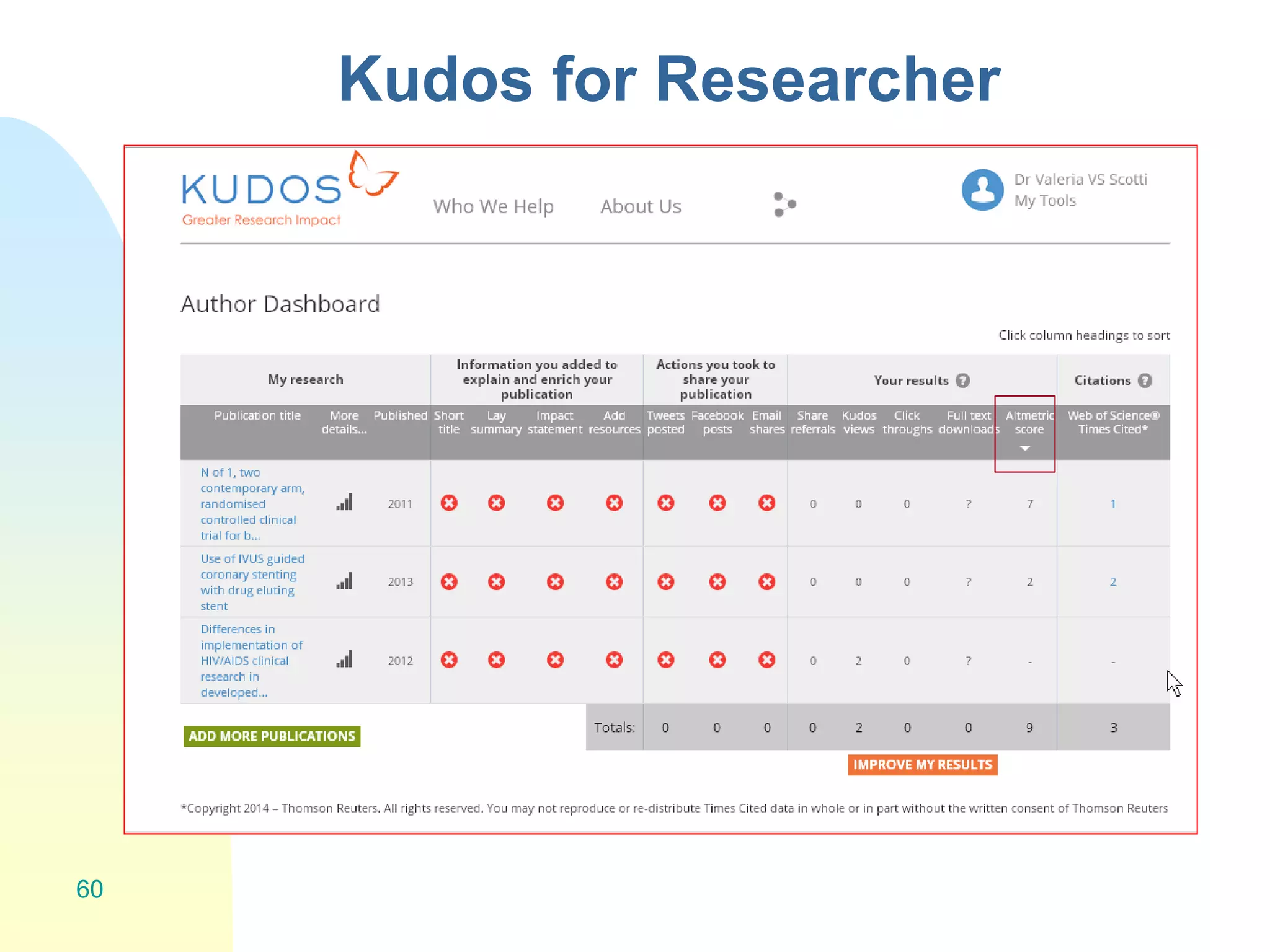
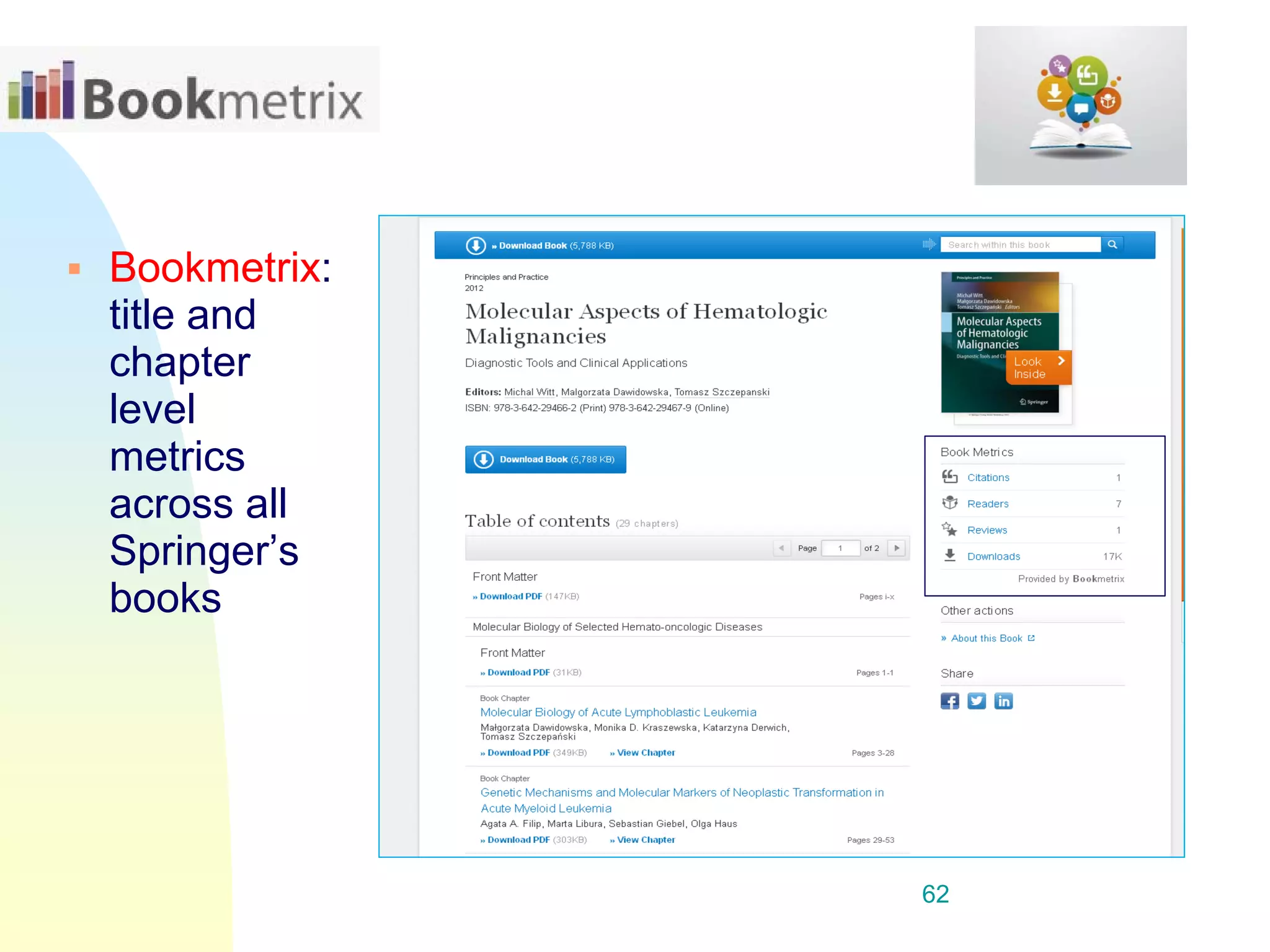
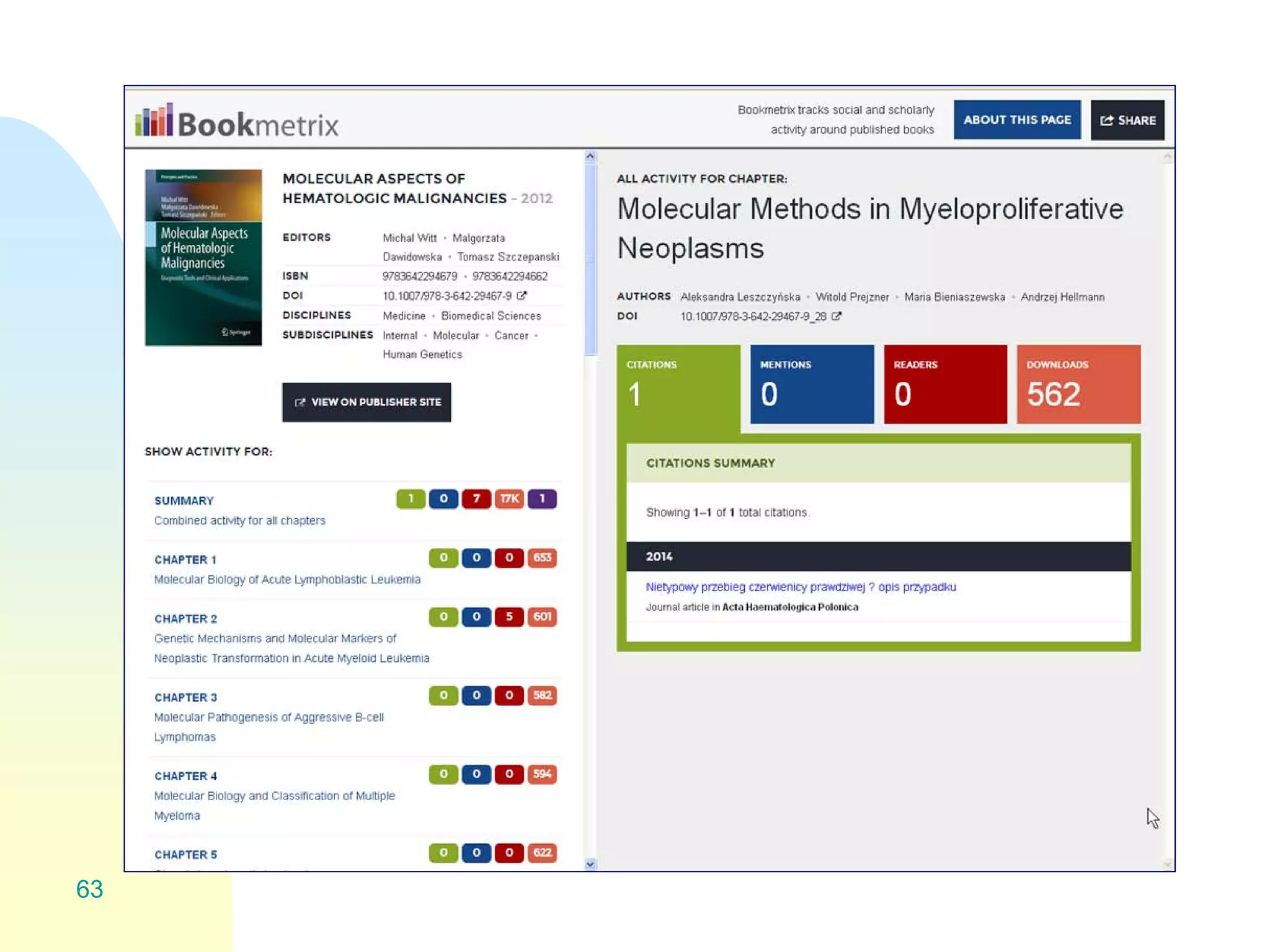
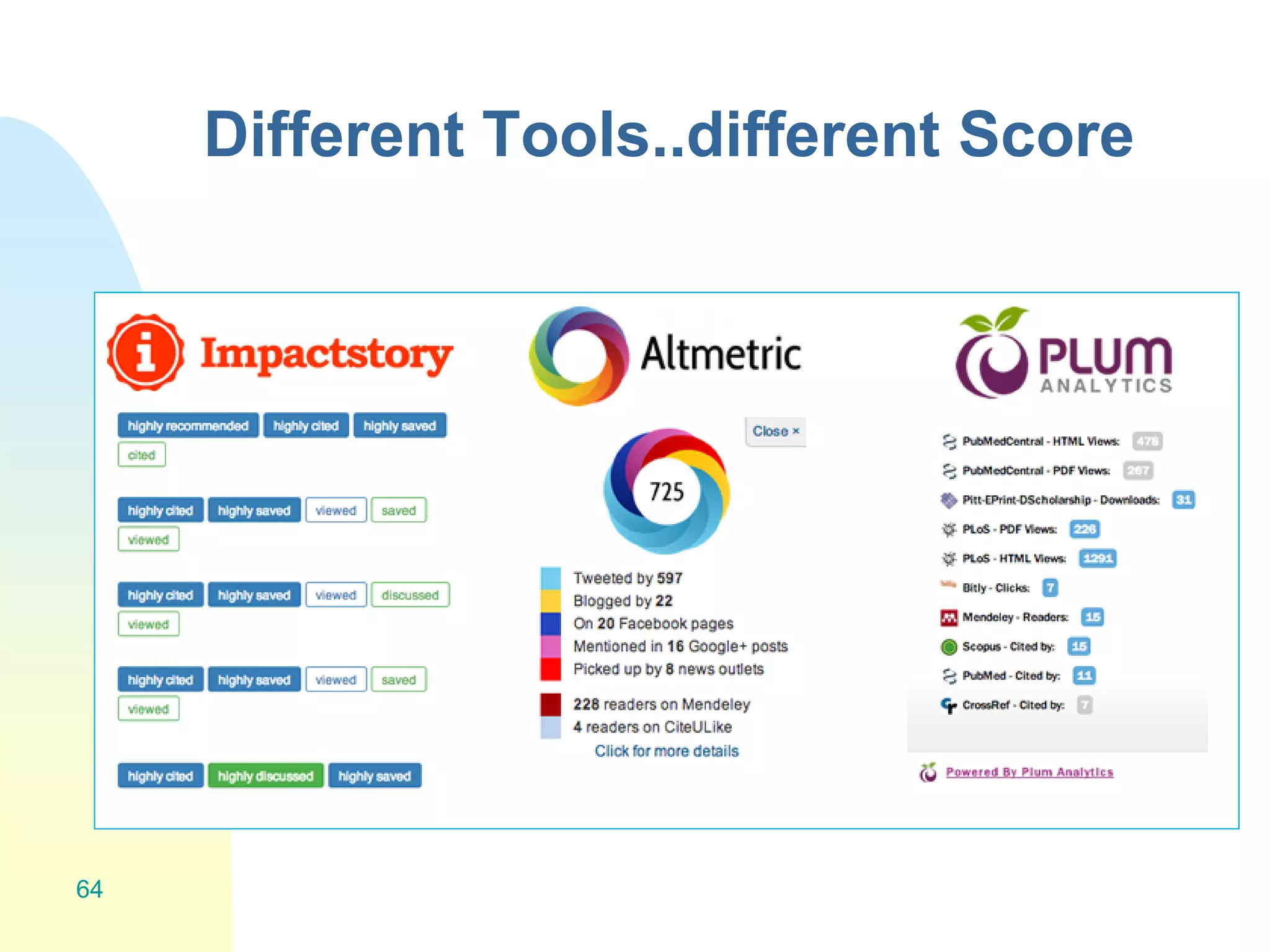
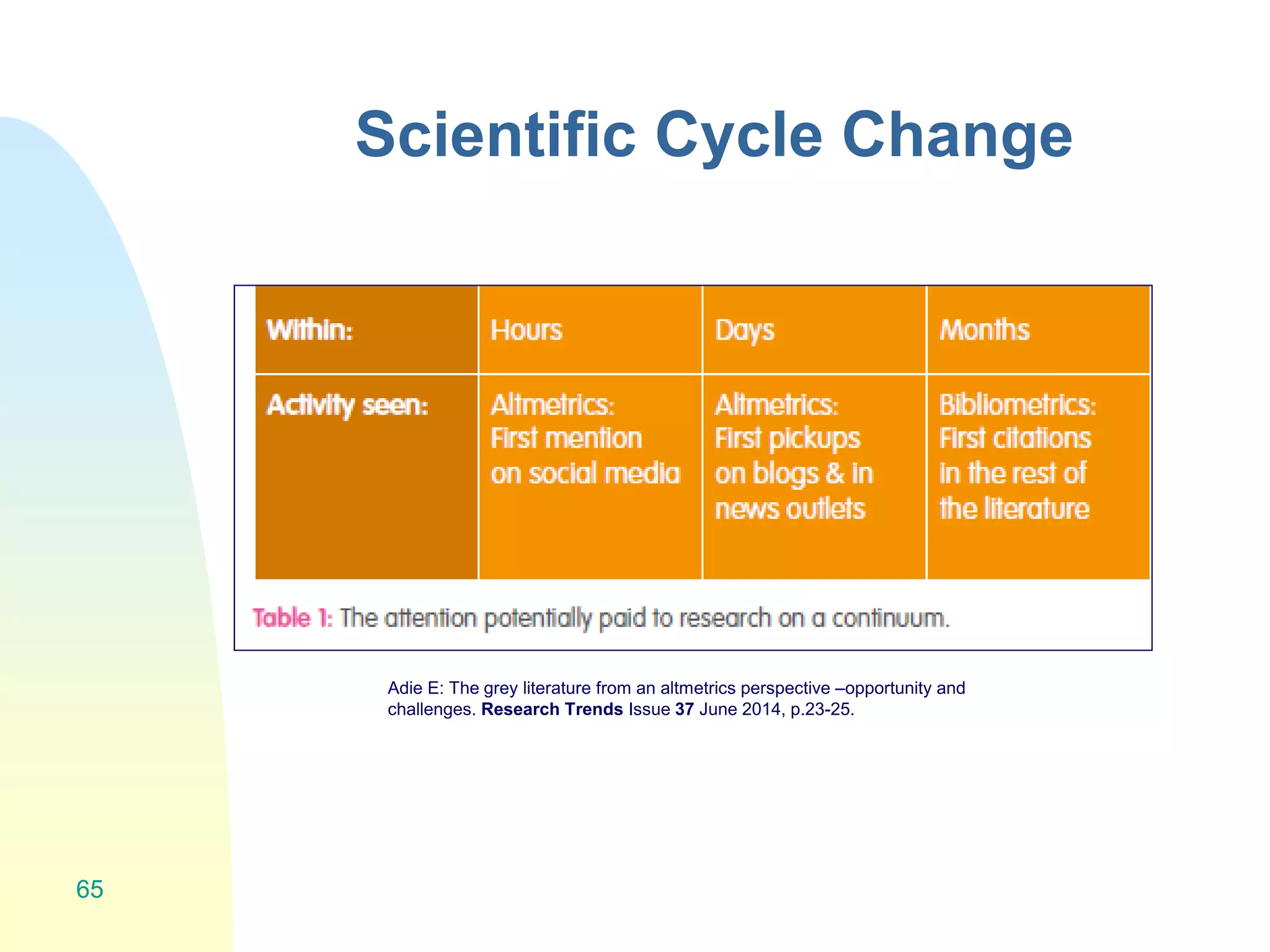
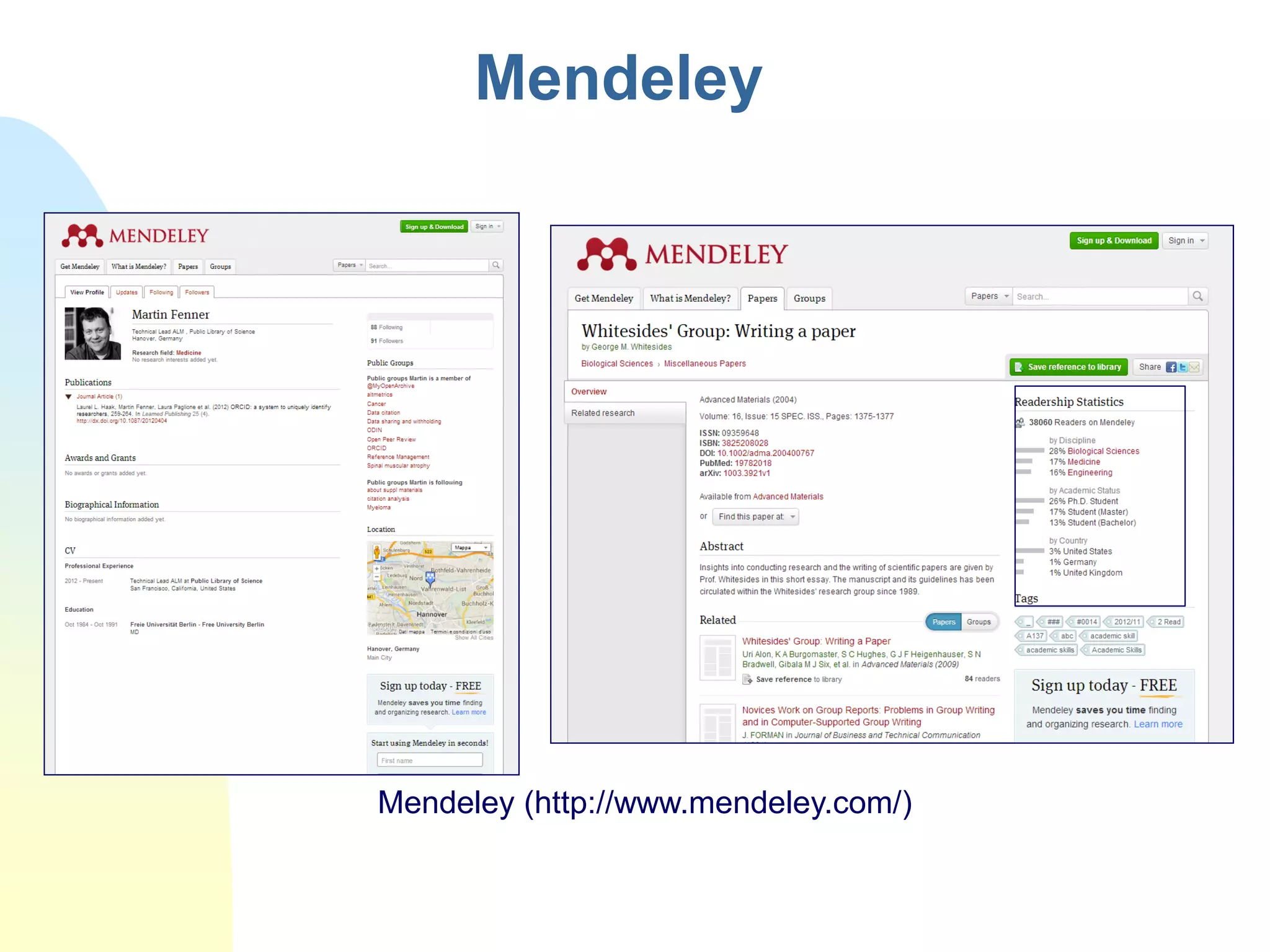
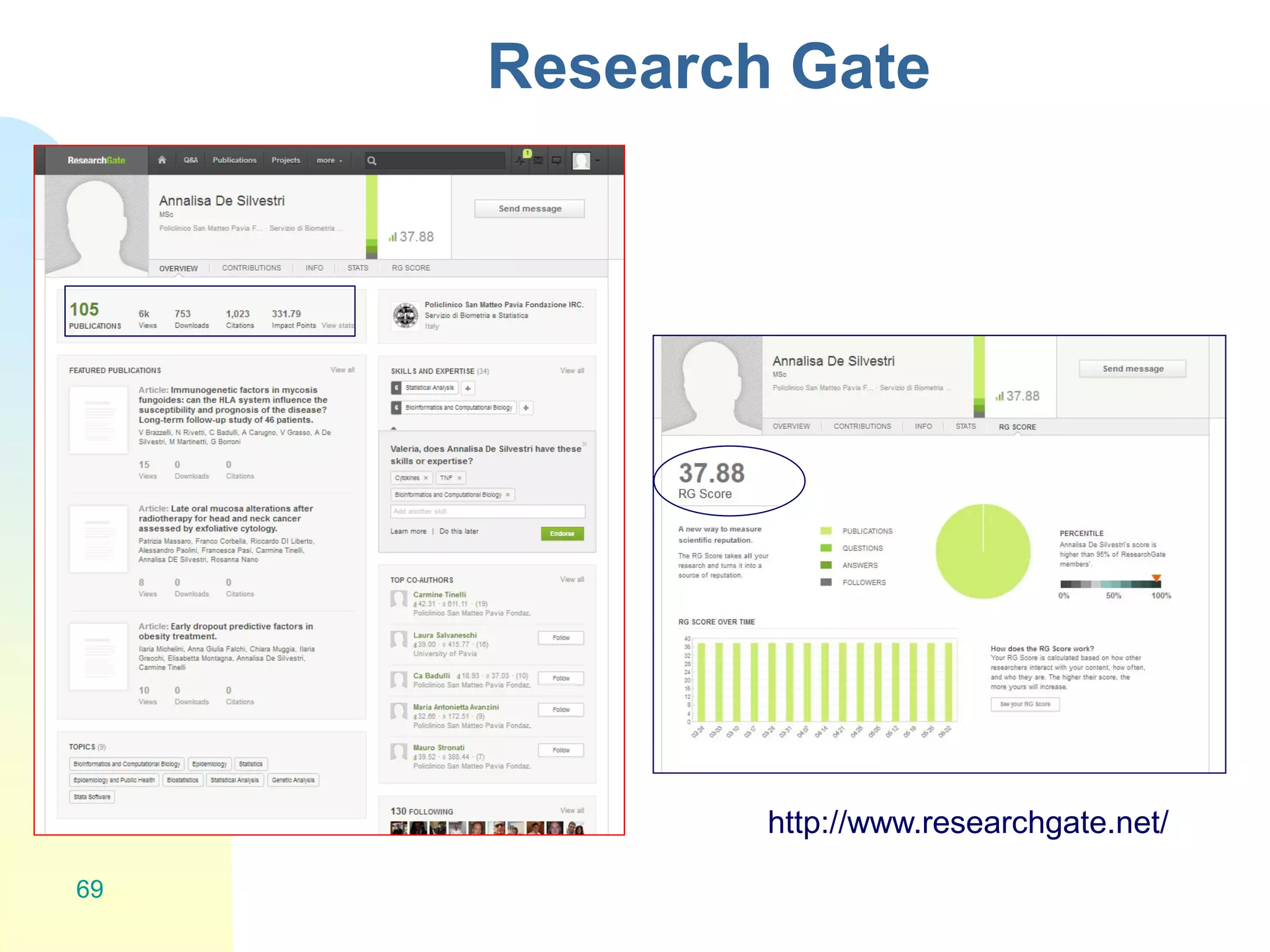
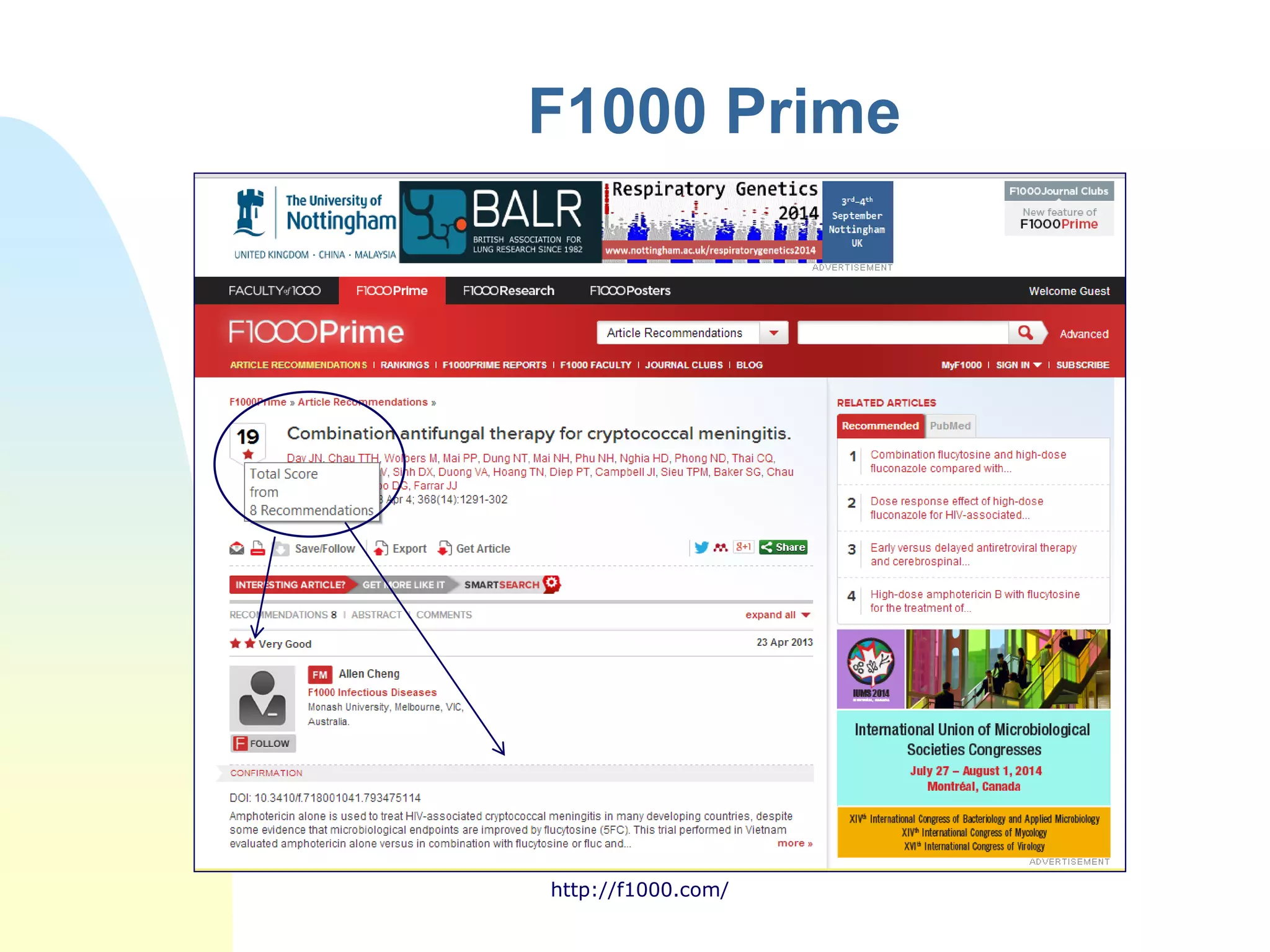
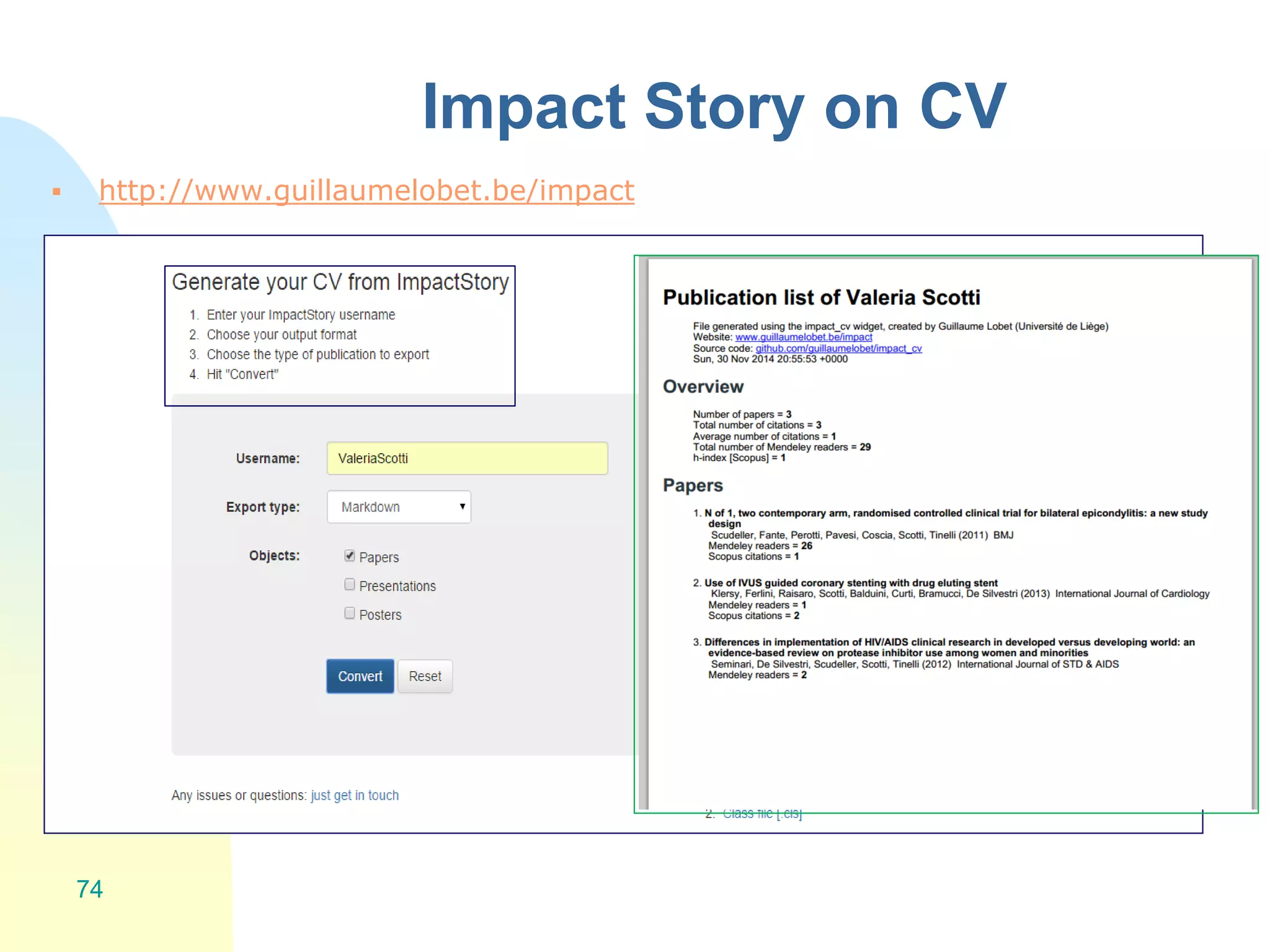
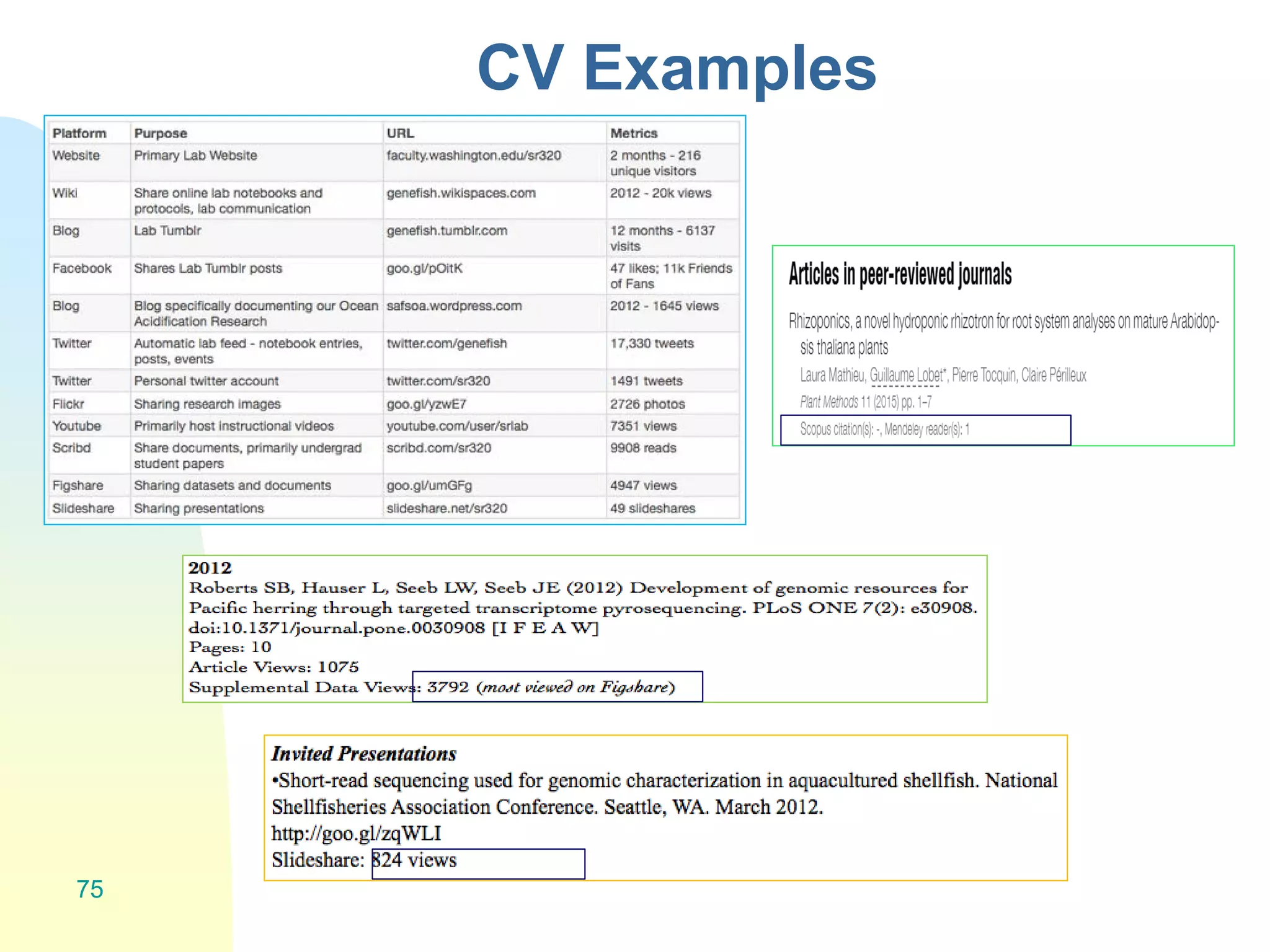
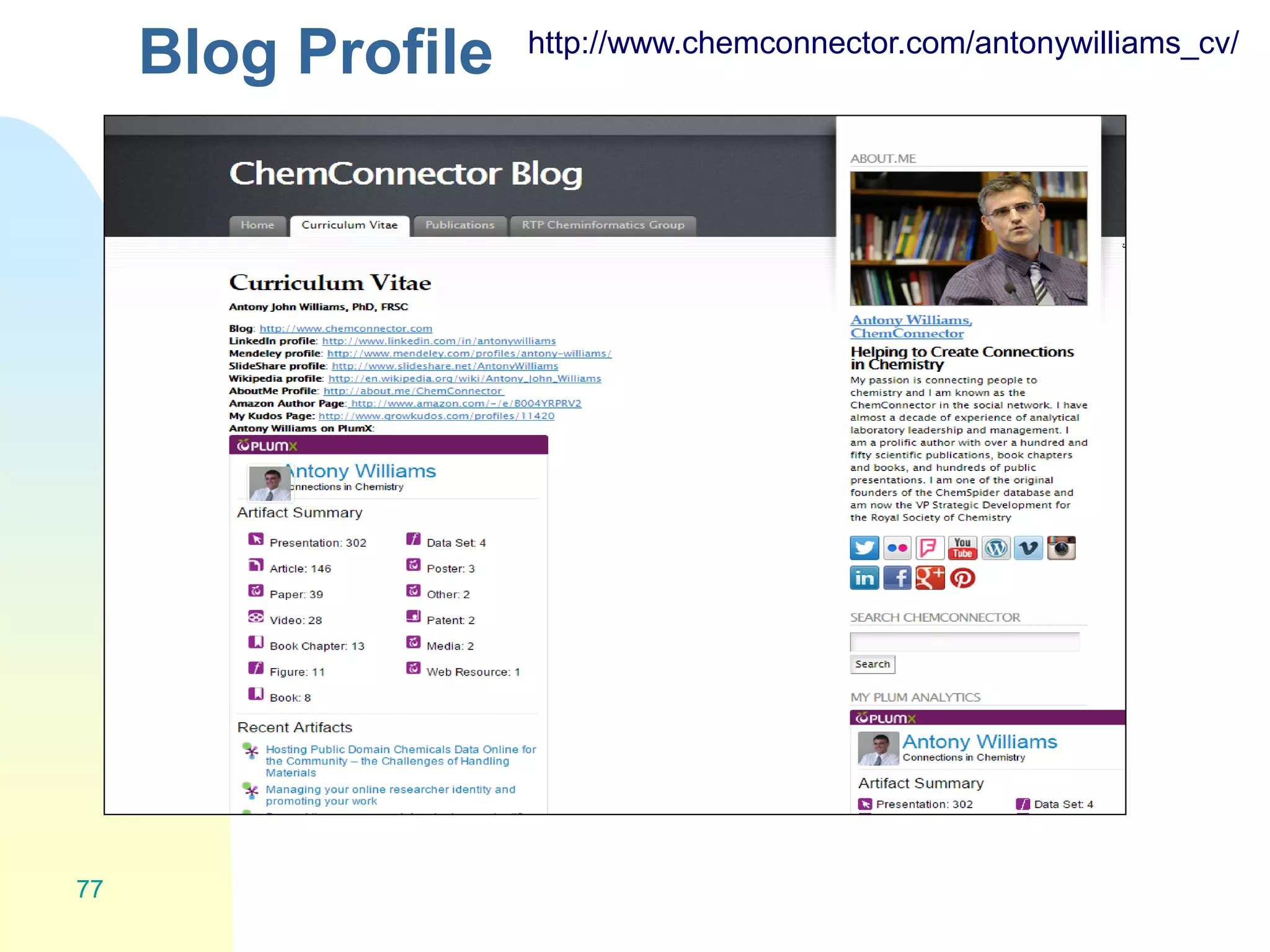
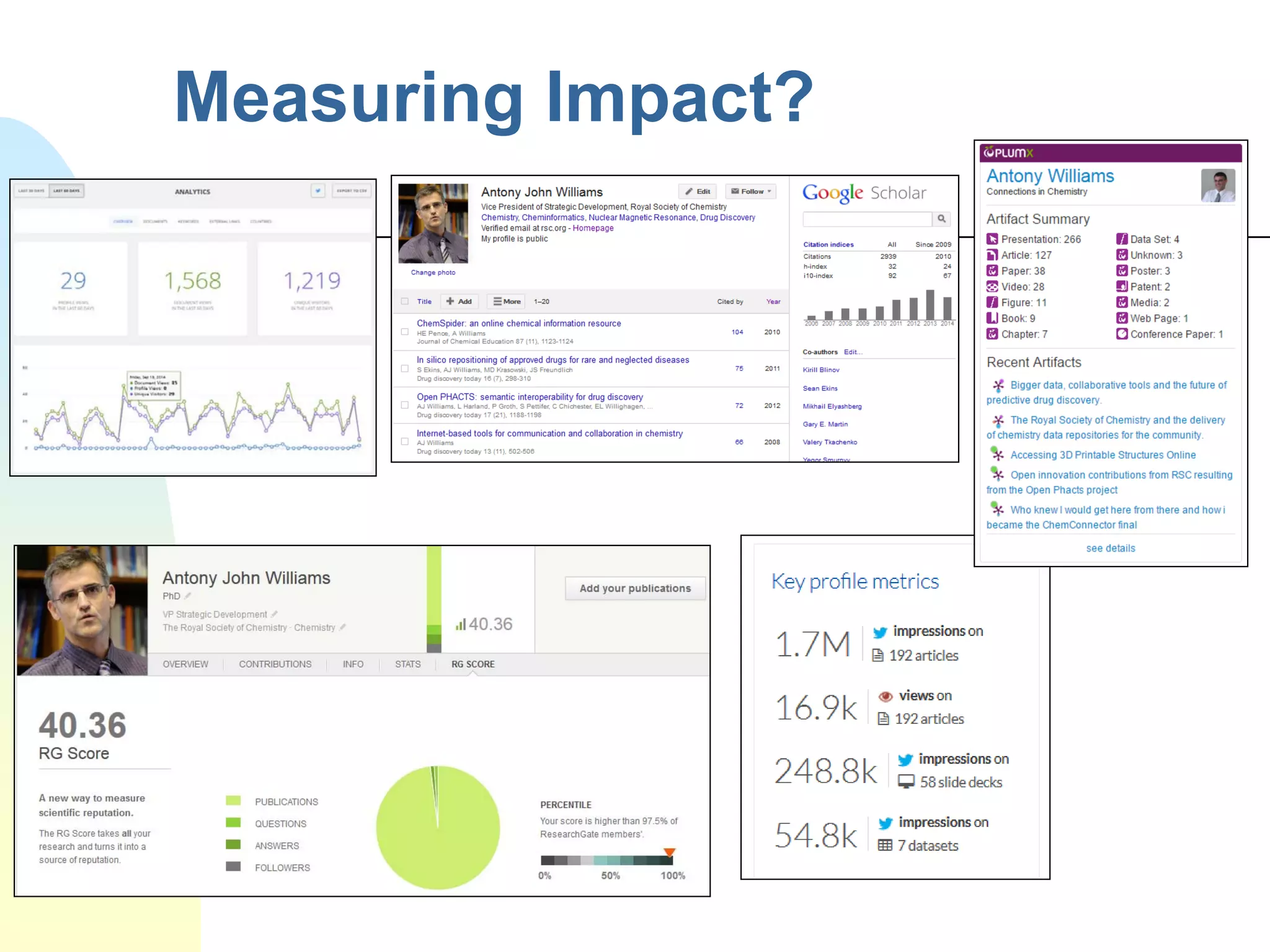
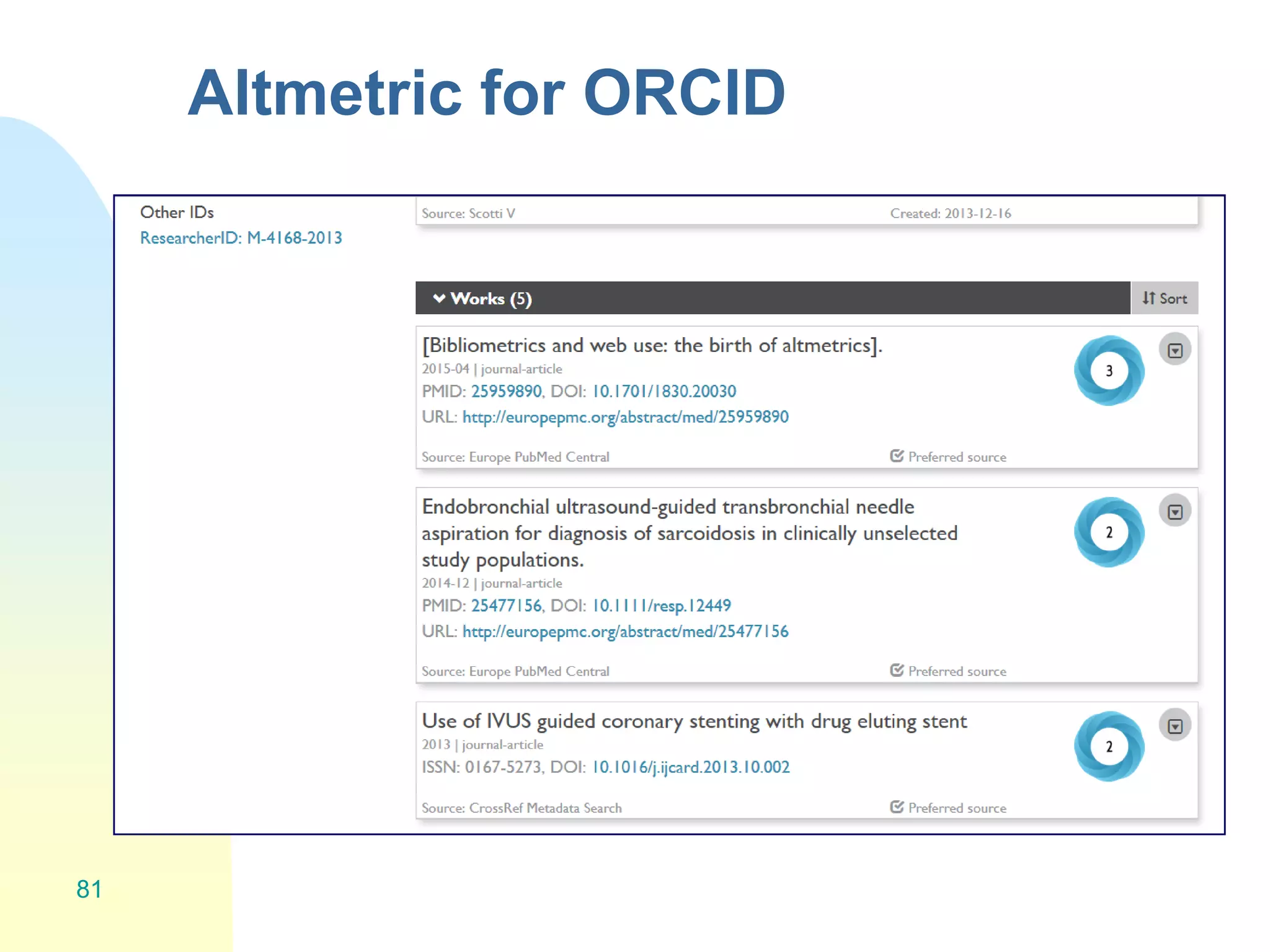
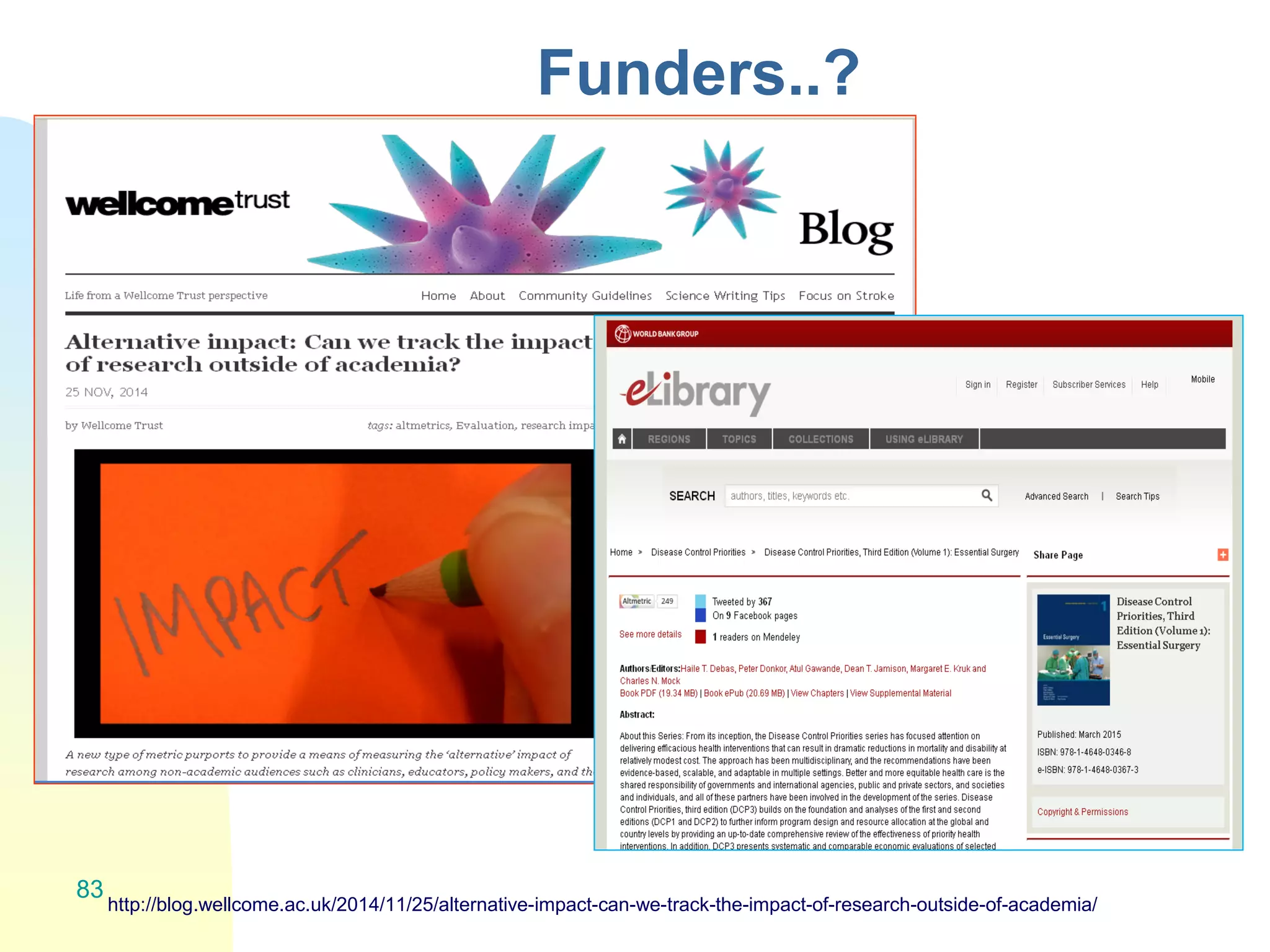
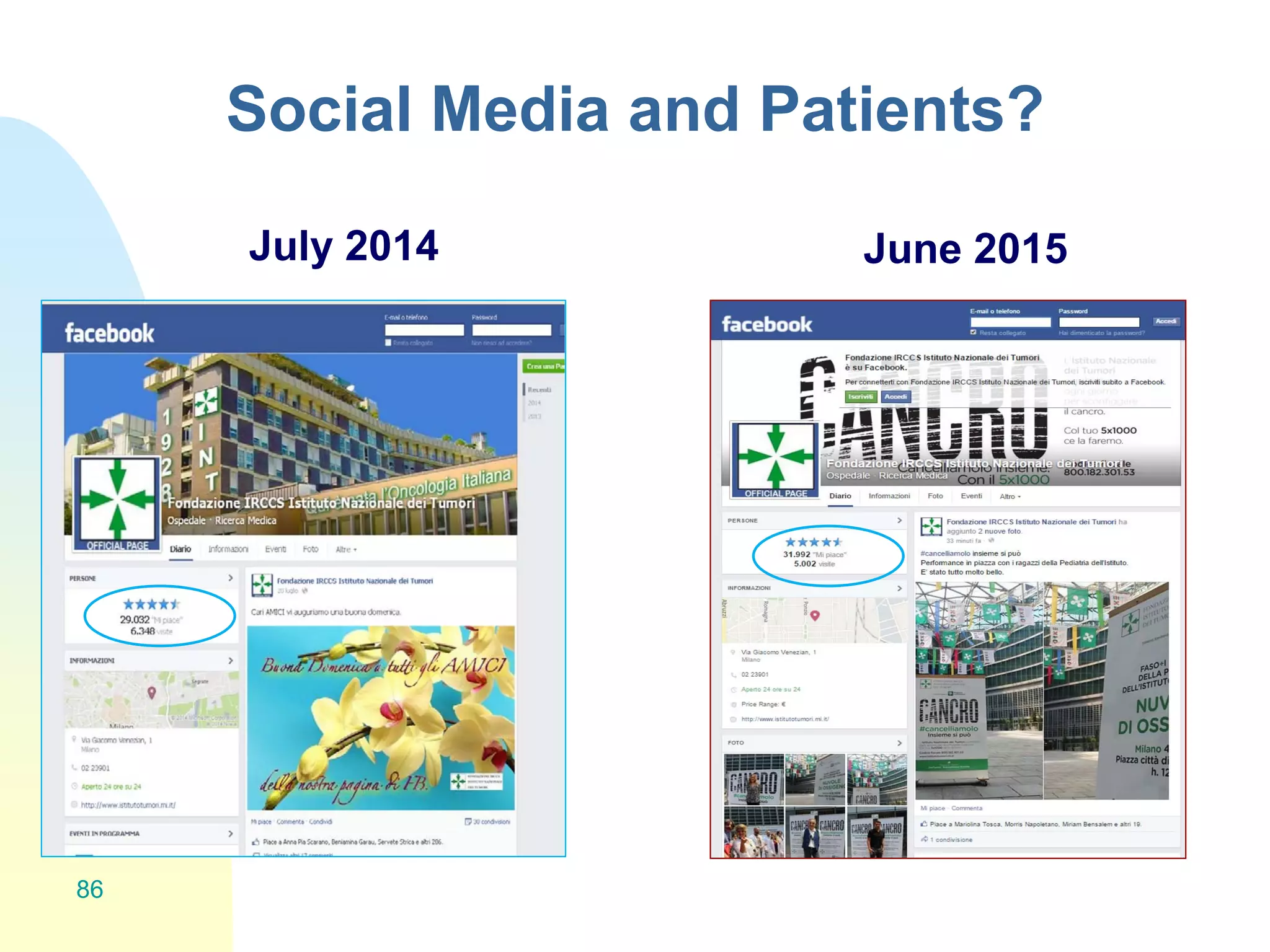
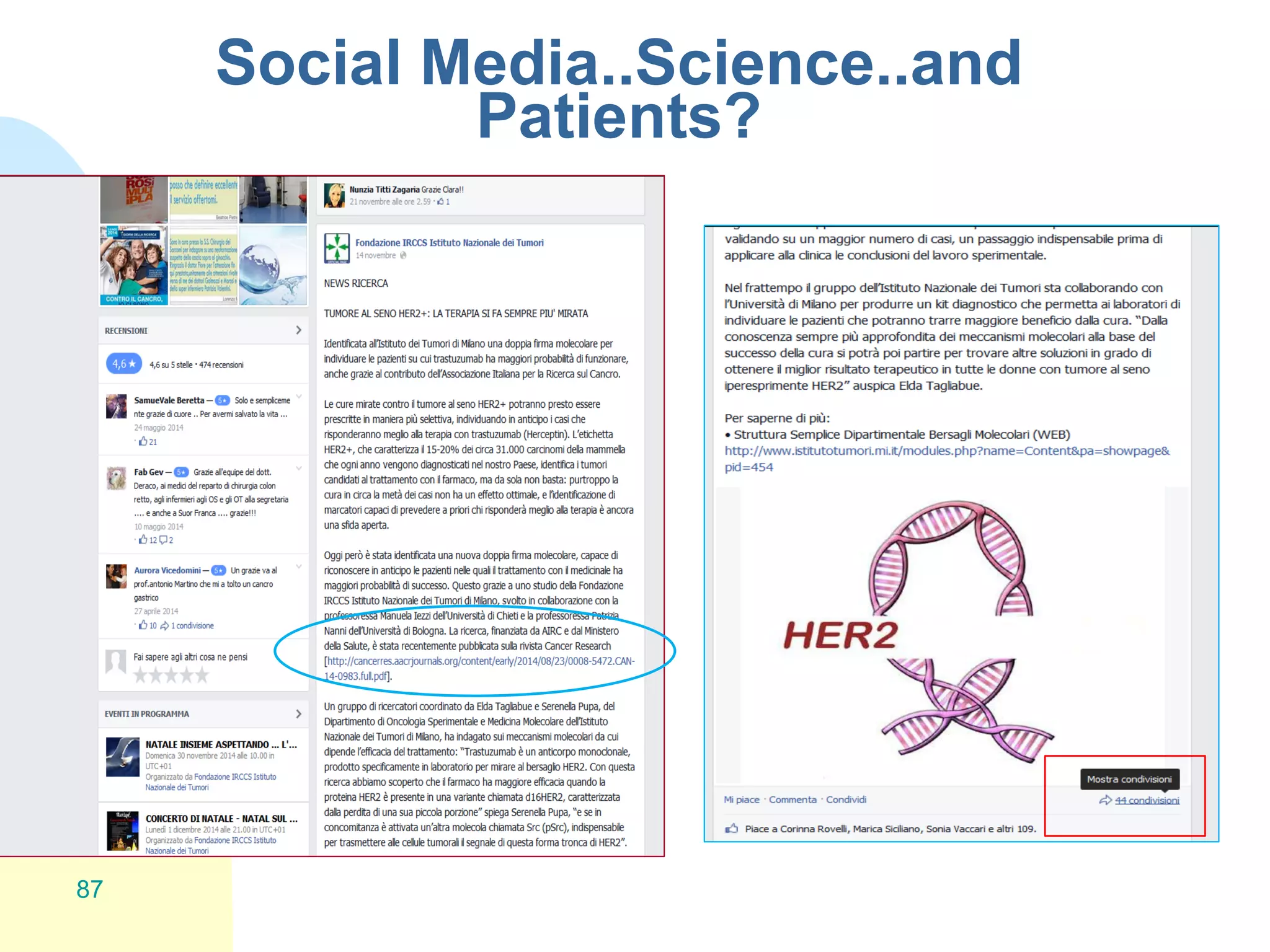
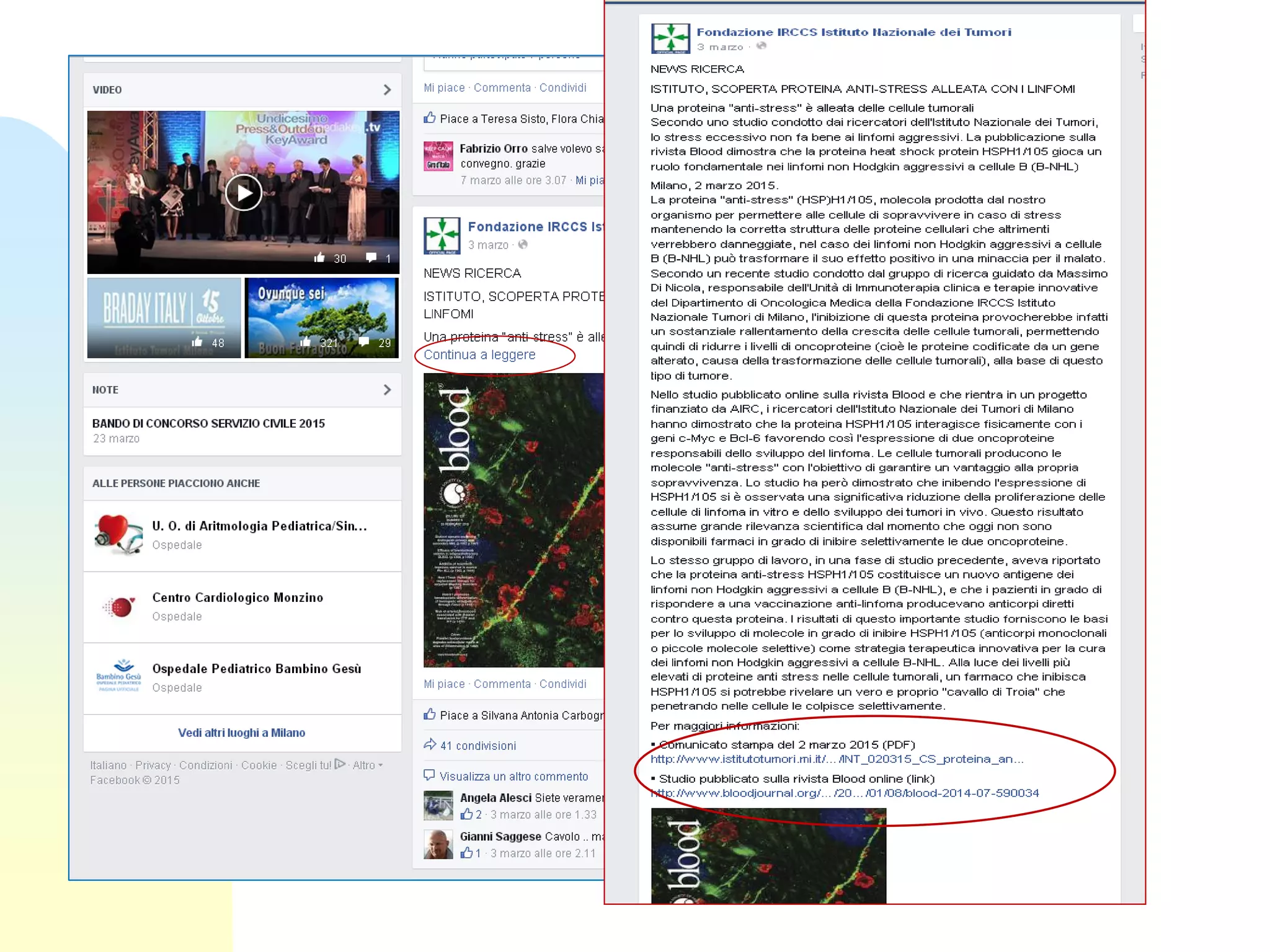
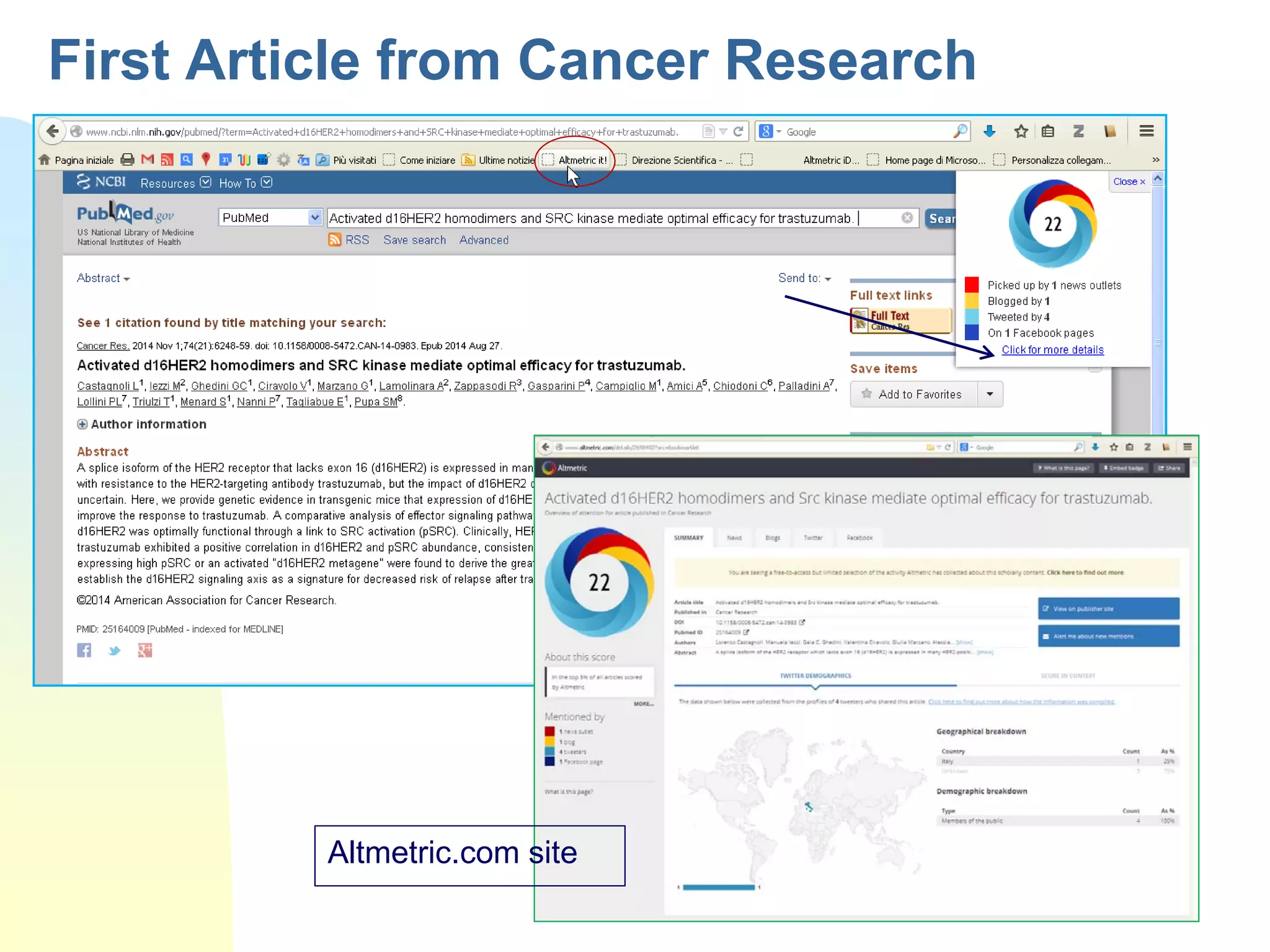
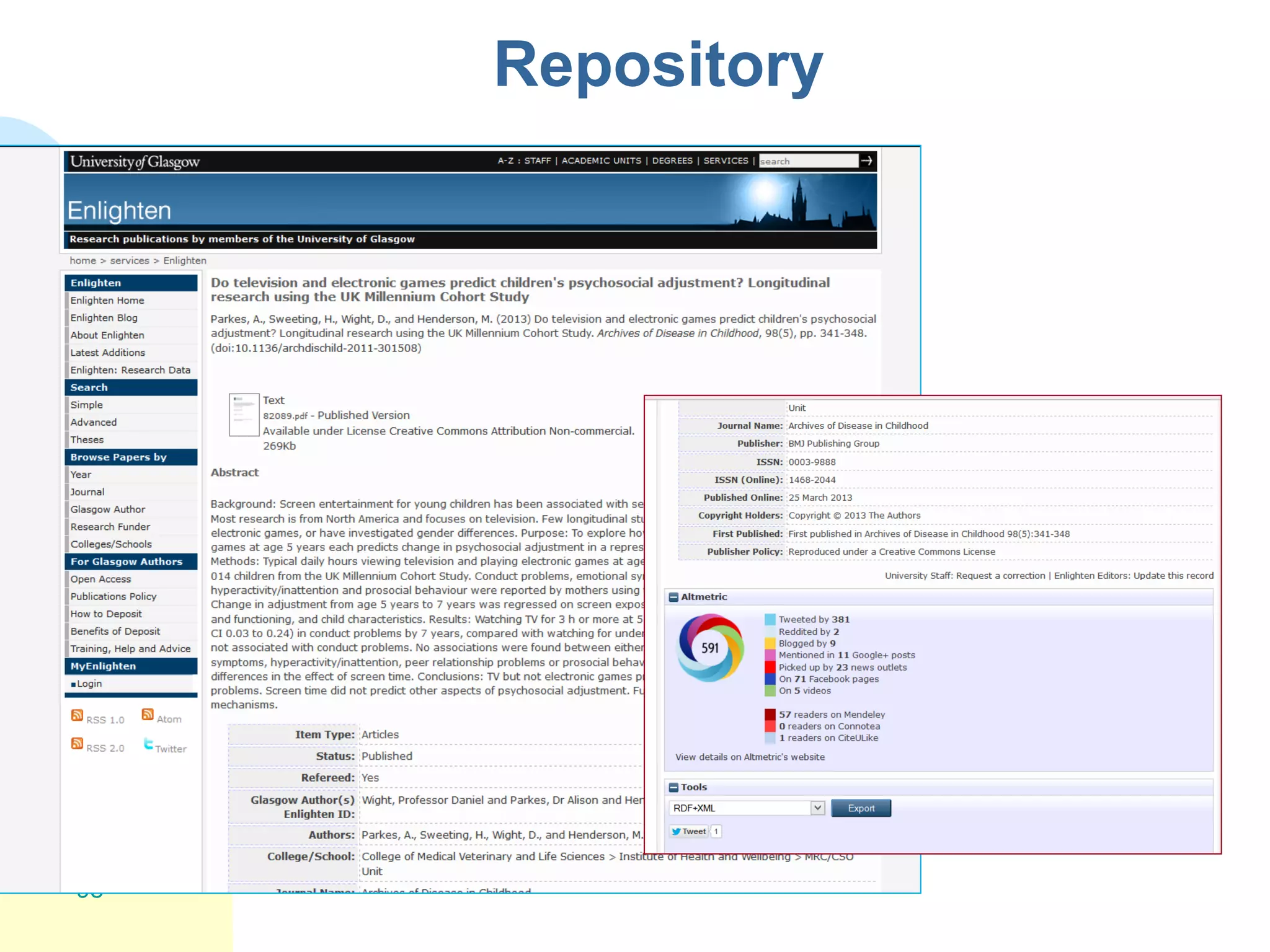
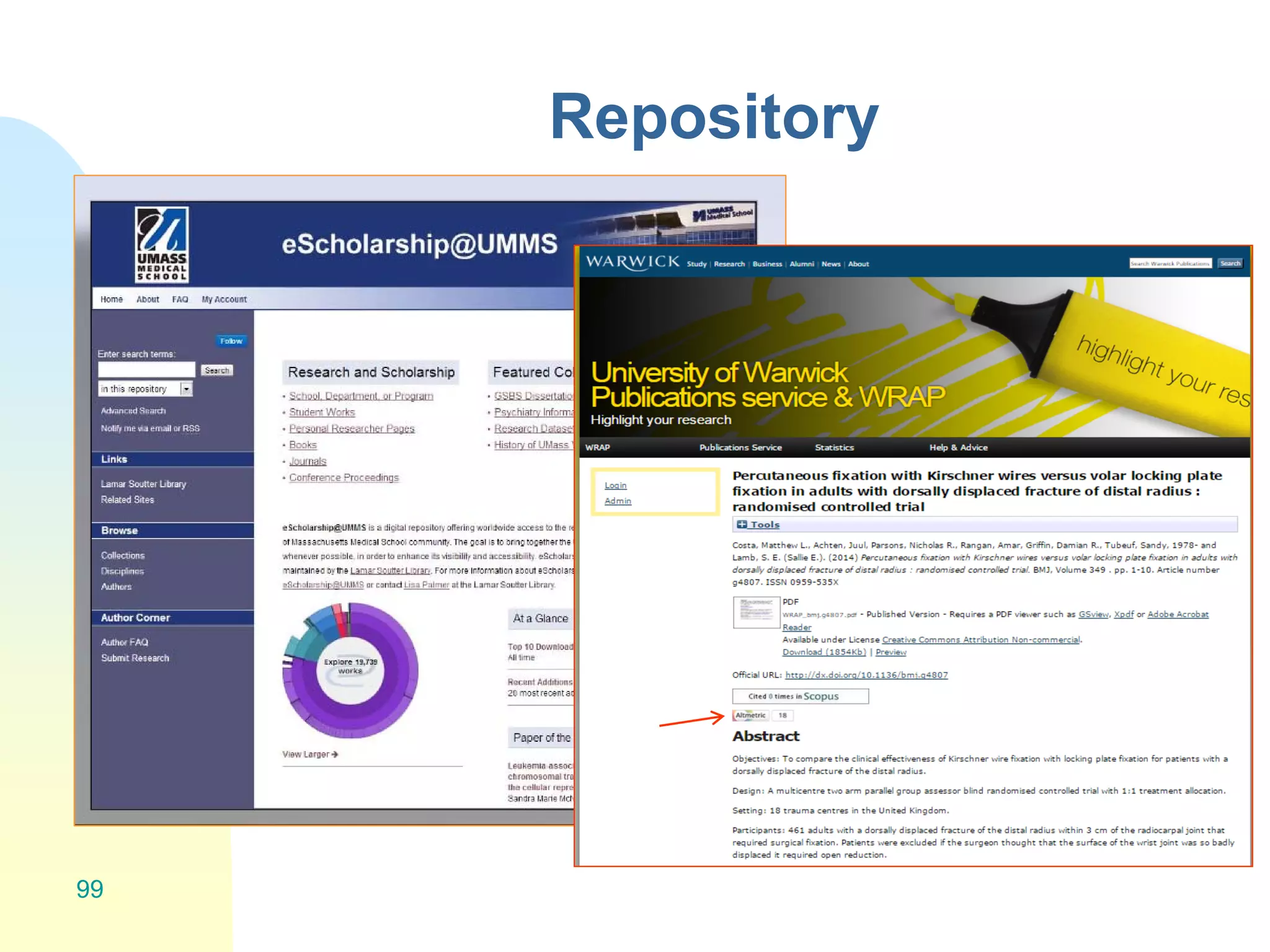
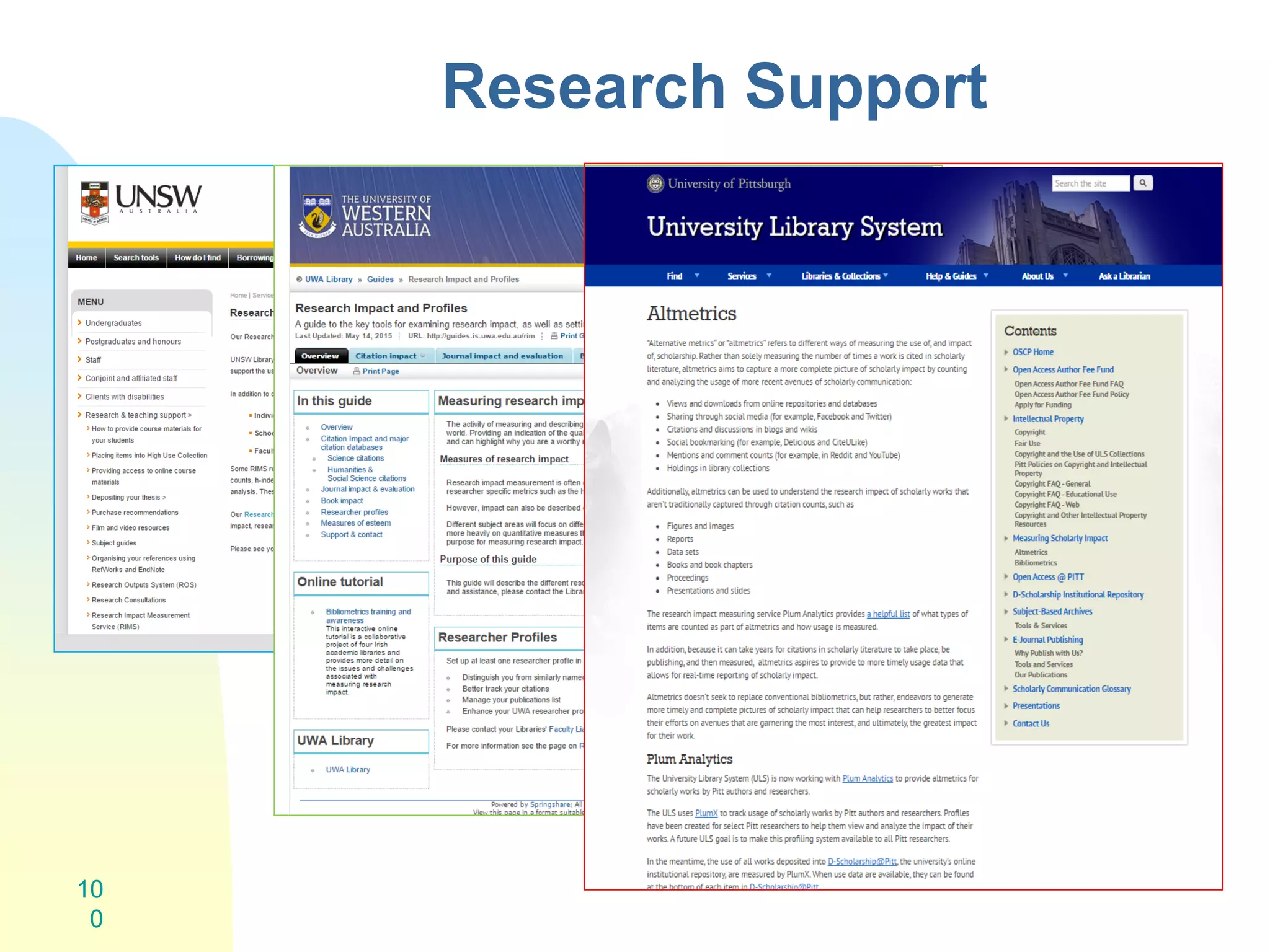
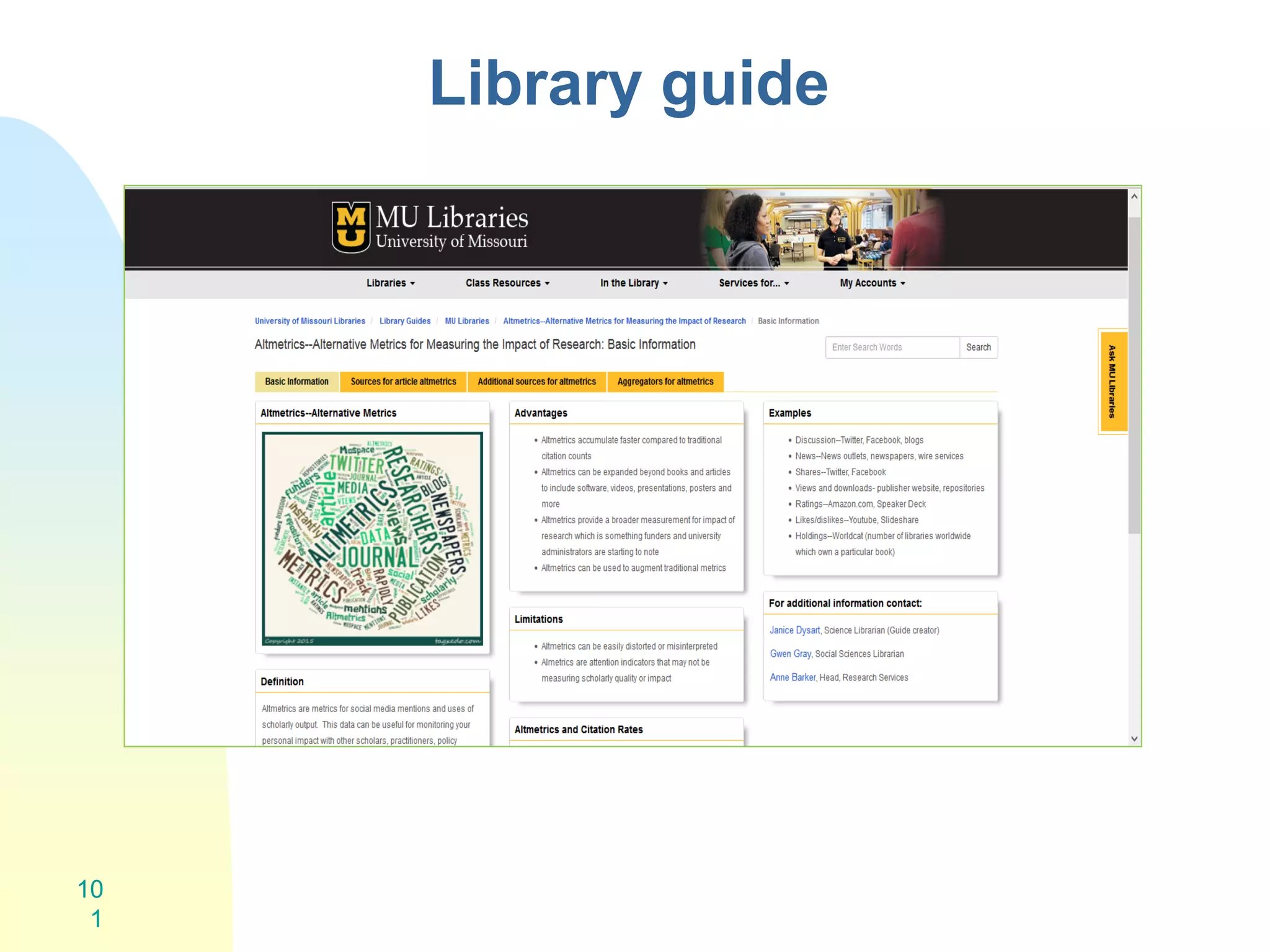
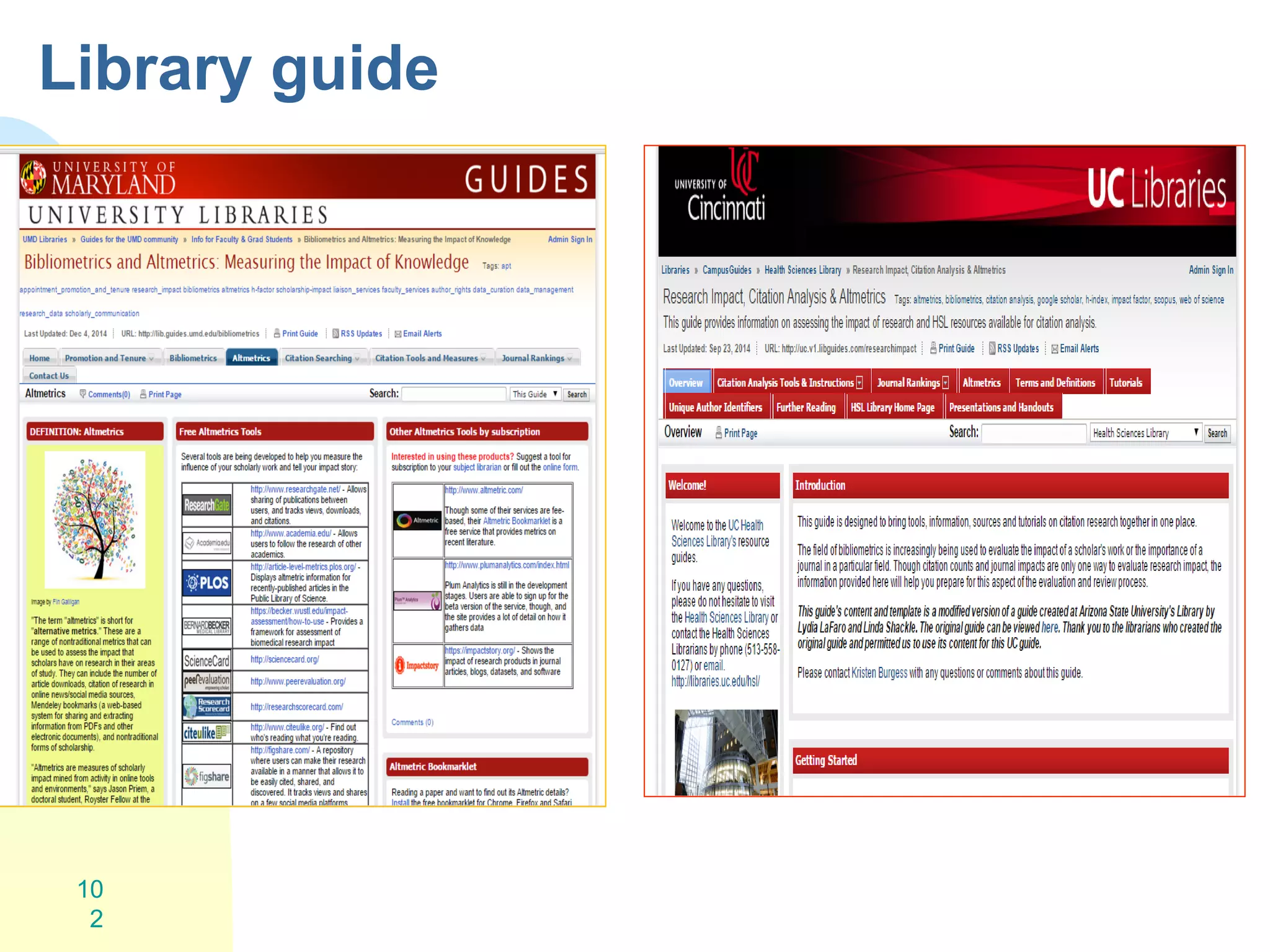
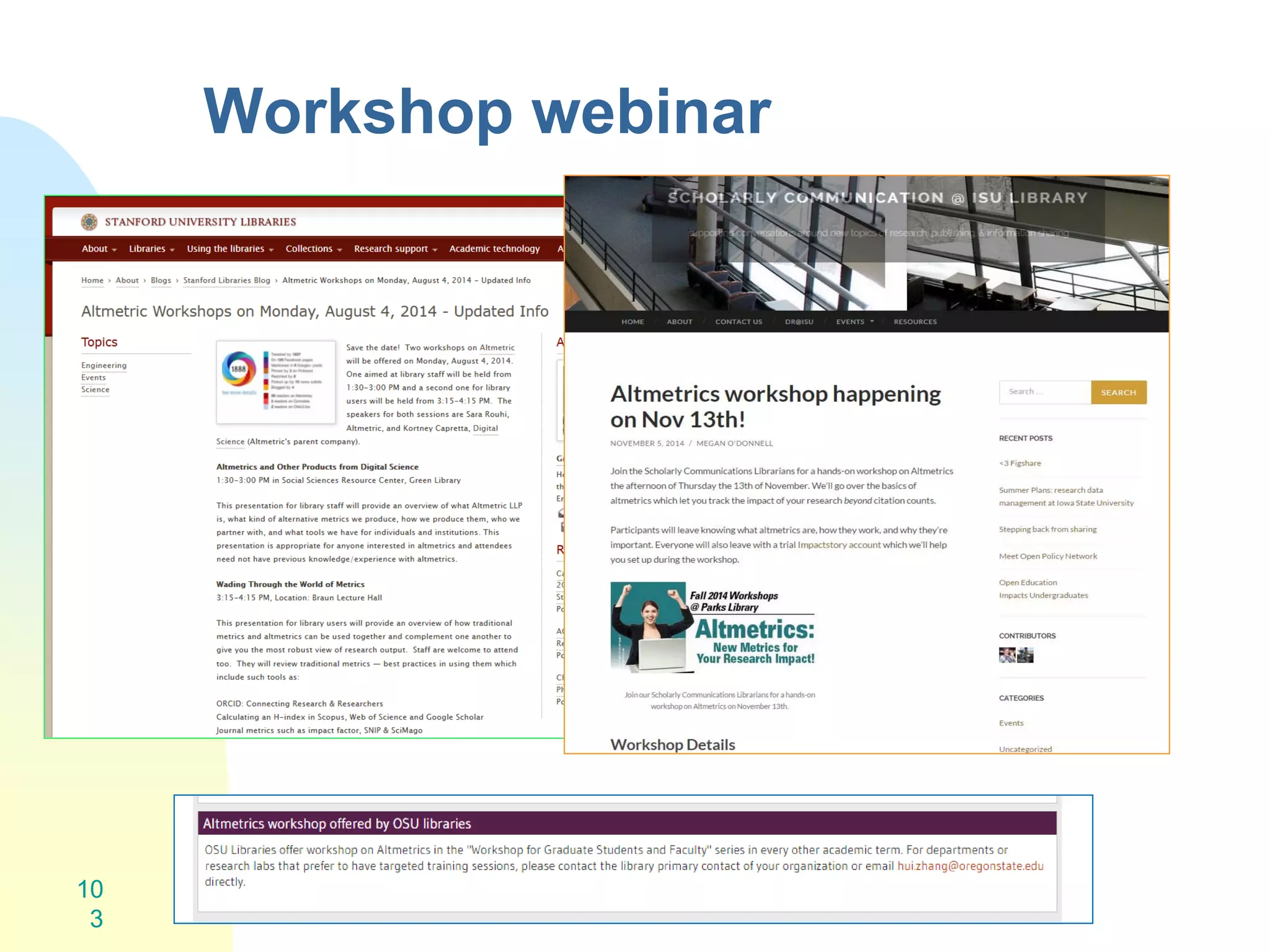
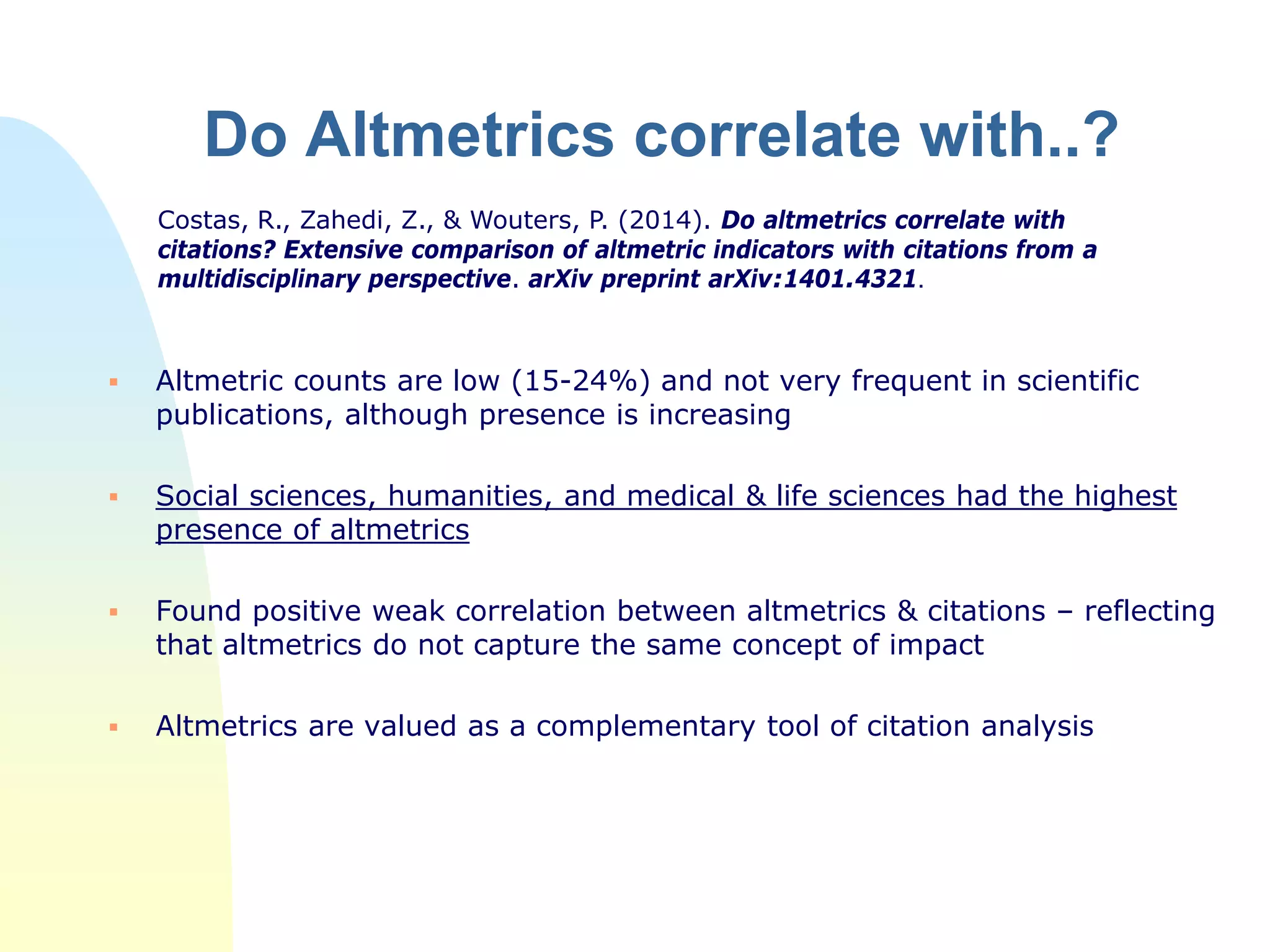
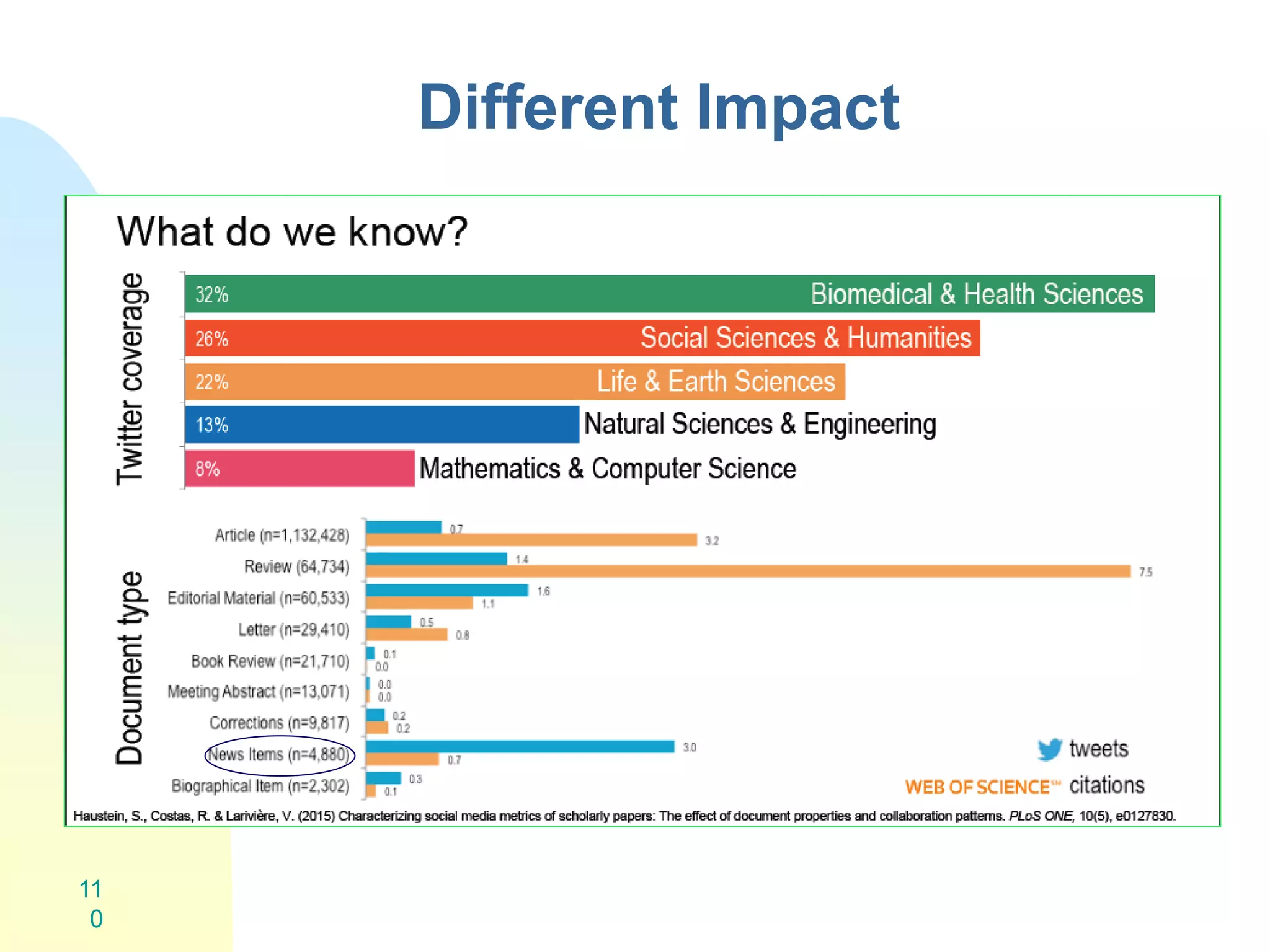
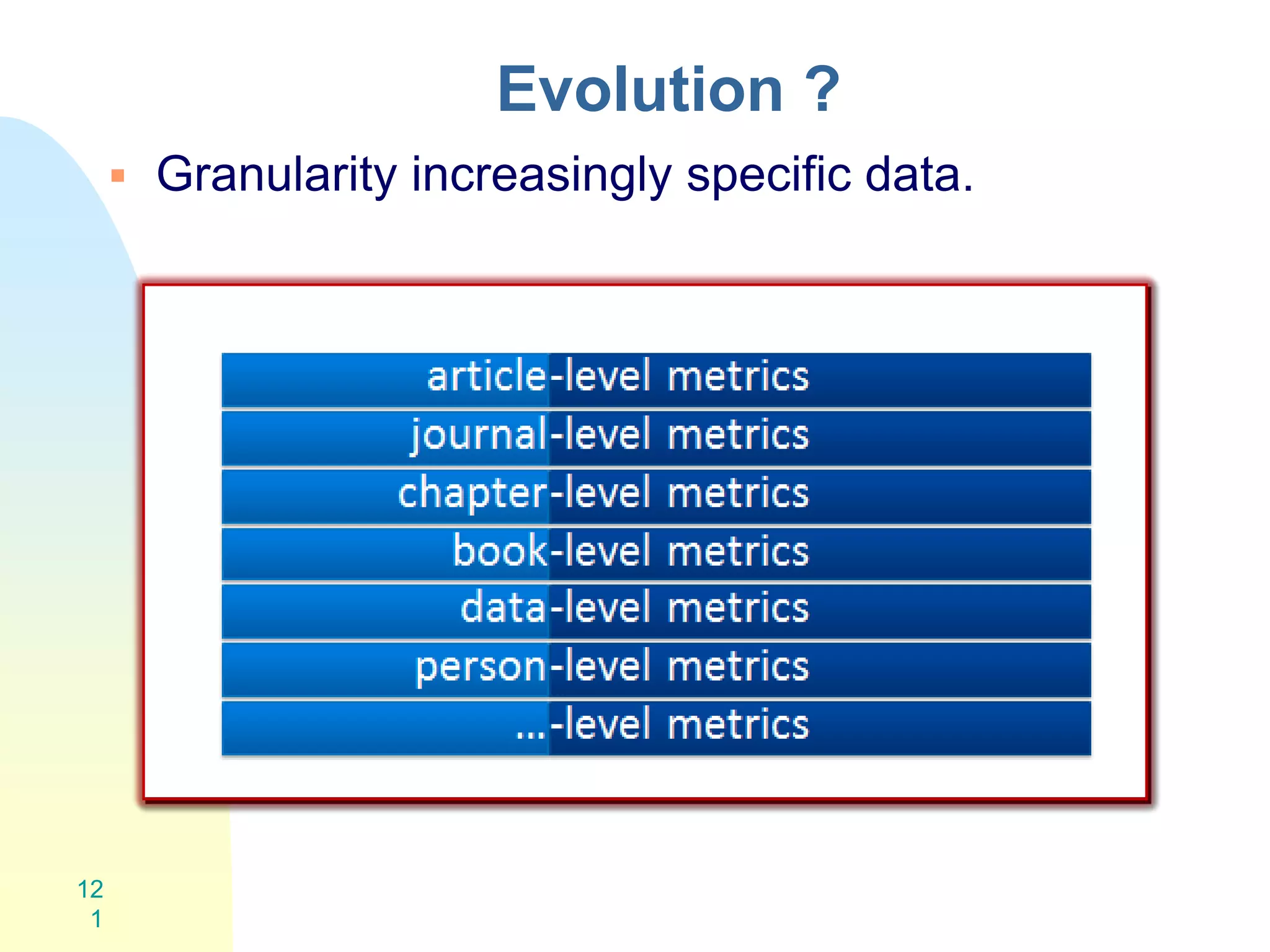
The document discusses the importance of altmetrics in measuring the impact of research publications, highlighting the limitations of traditional bibliometrics and peer review systems. It introduces various altmetrics tools that provide insights into research impact through social media and other digital platforms, advocating for the role of librarians in supporting researchers with these metrics. The document emphasizes the need for a shift towards article-level metrics to better reflect the diverse ways research can influence scholarship and public engagement.