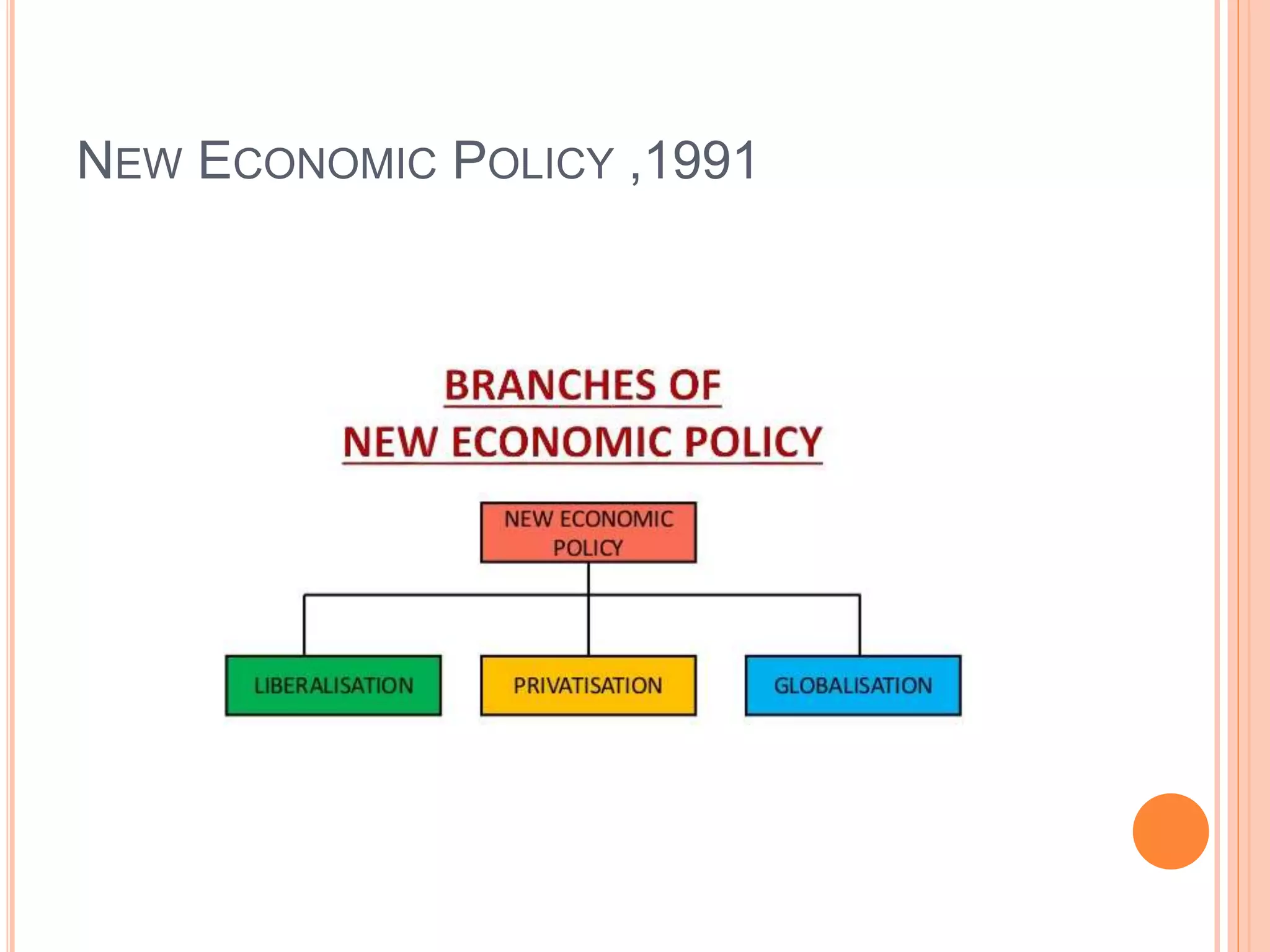
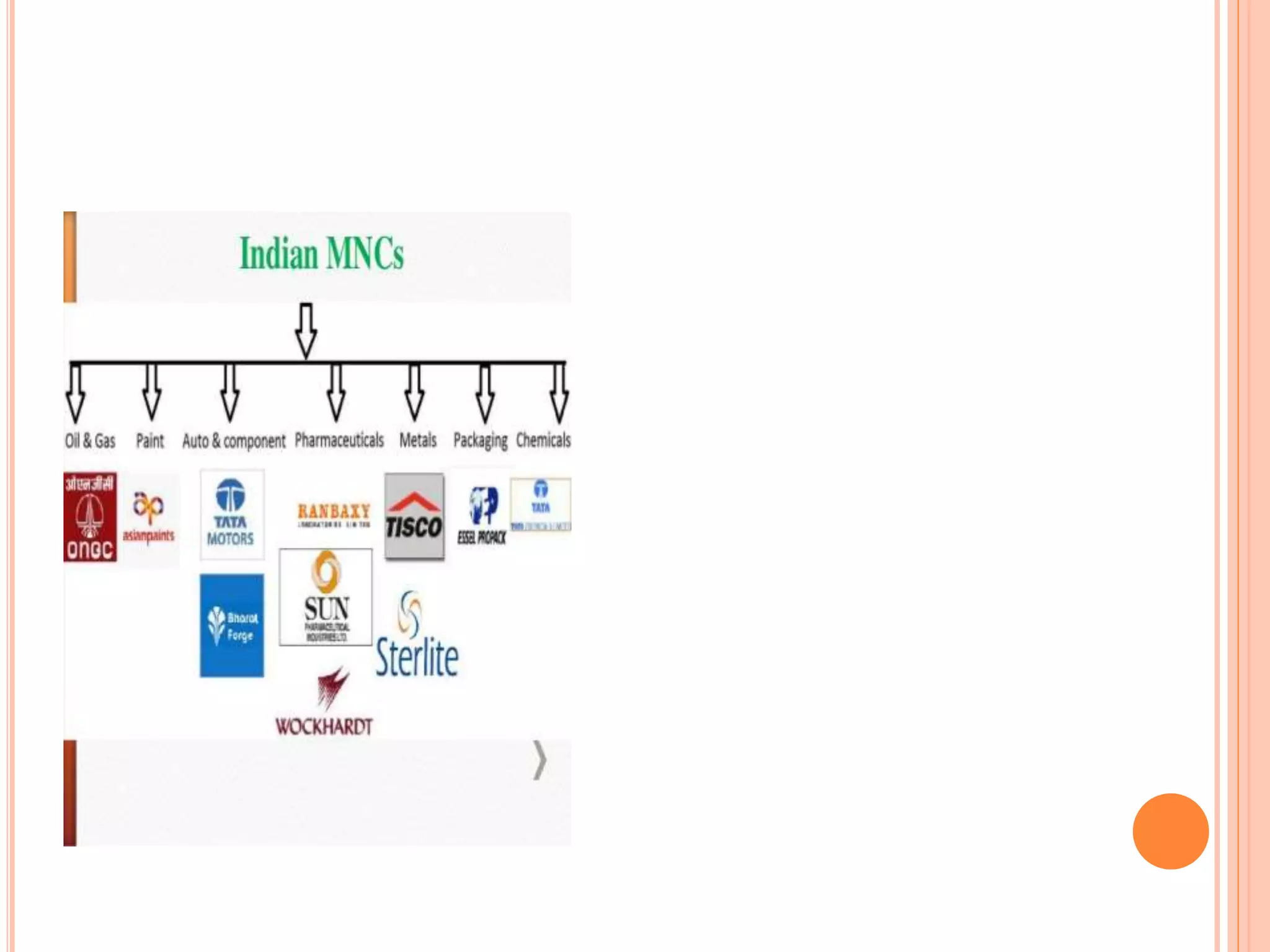
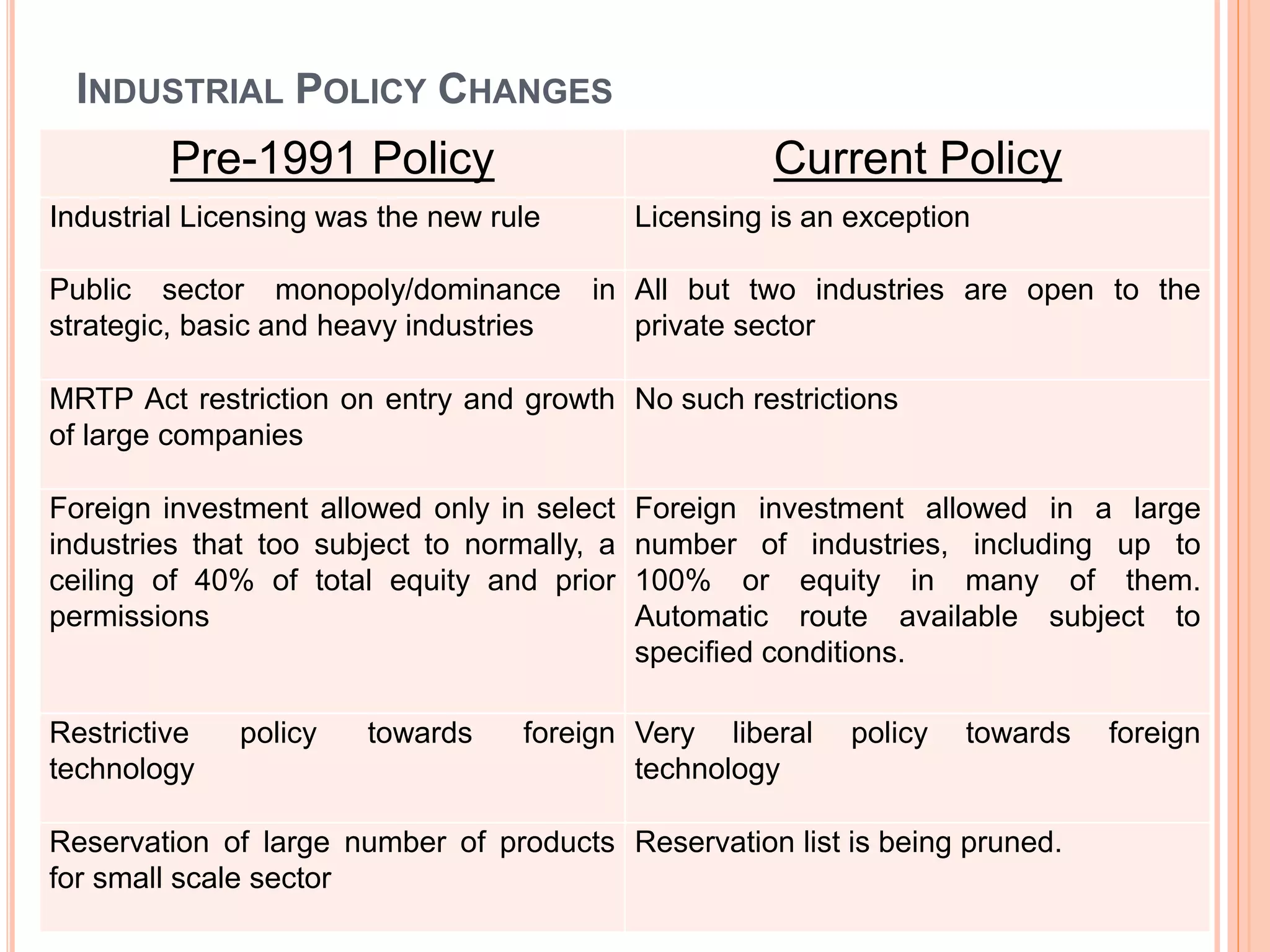
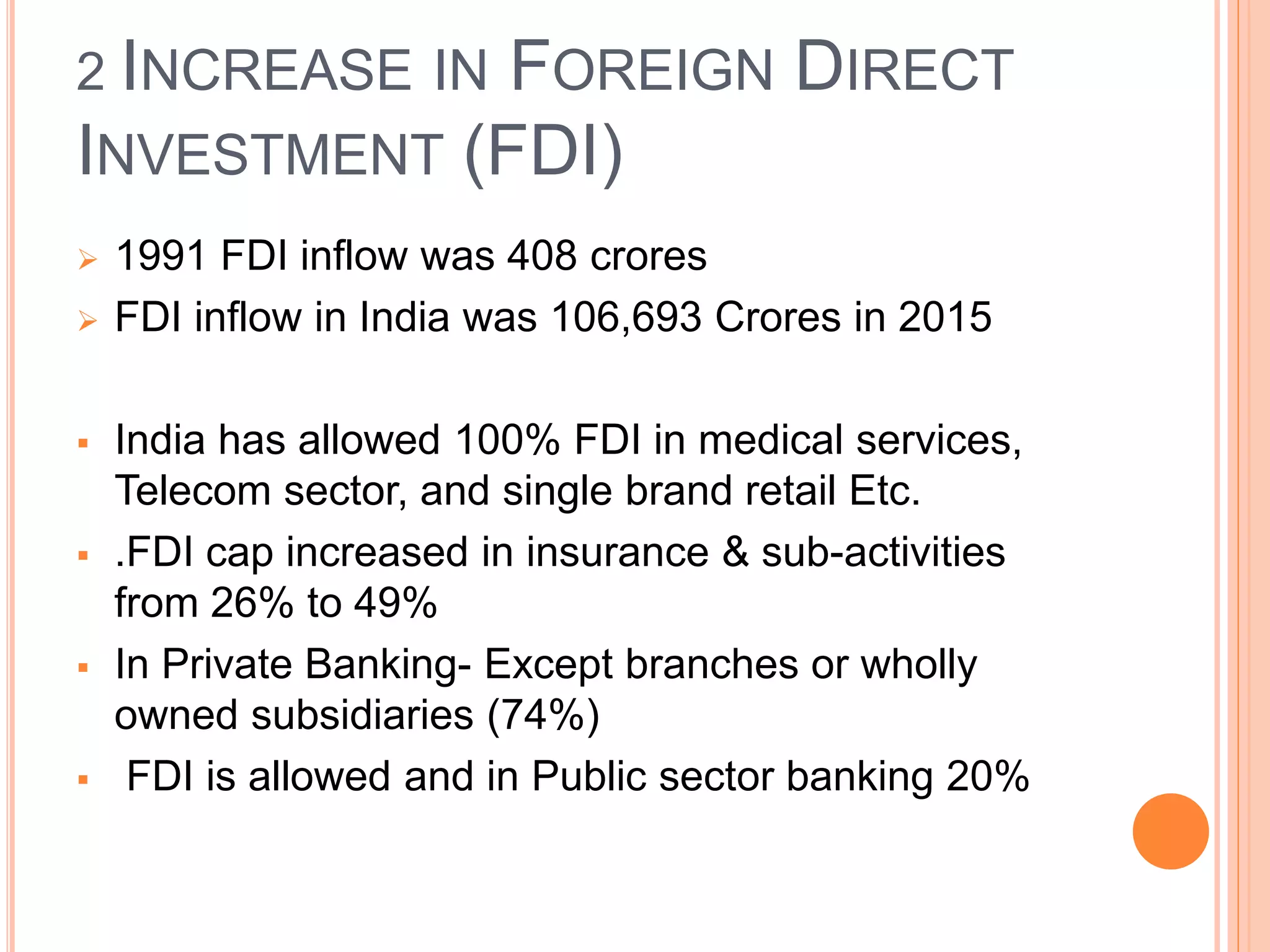
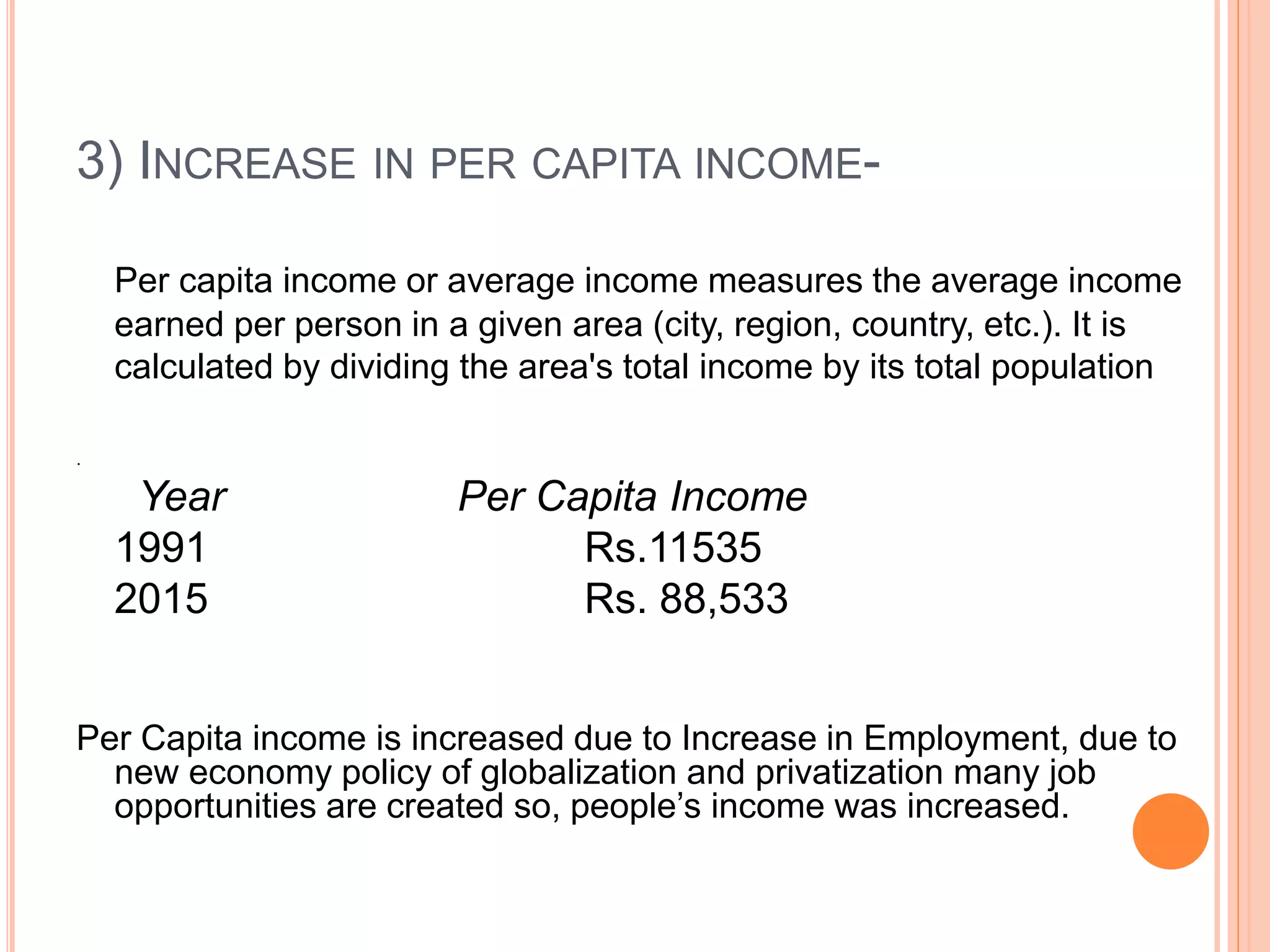
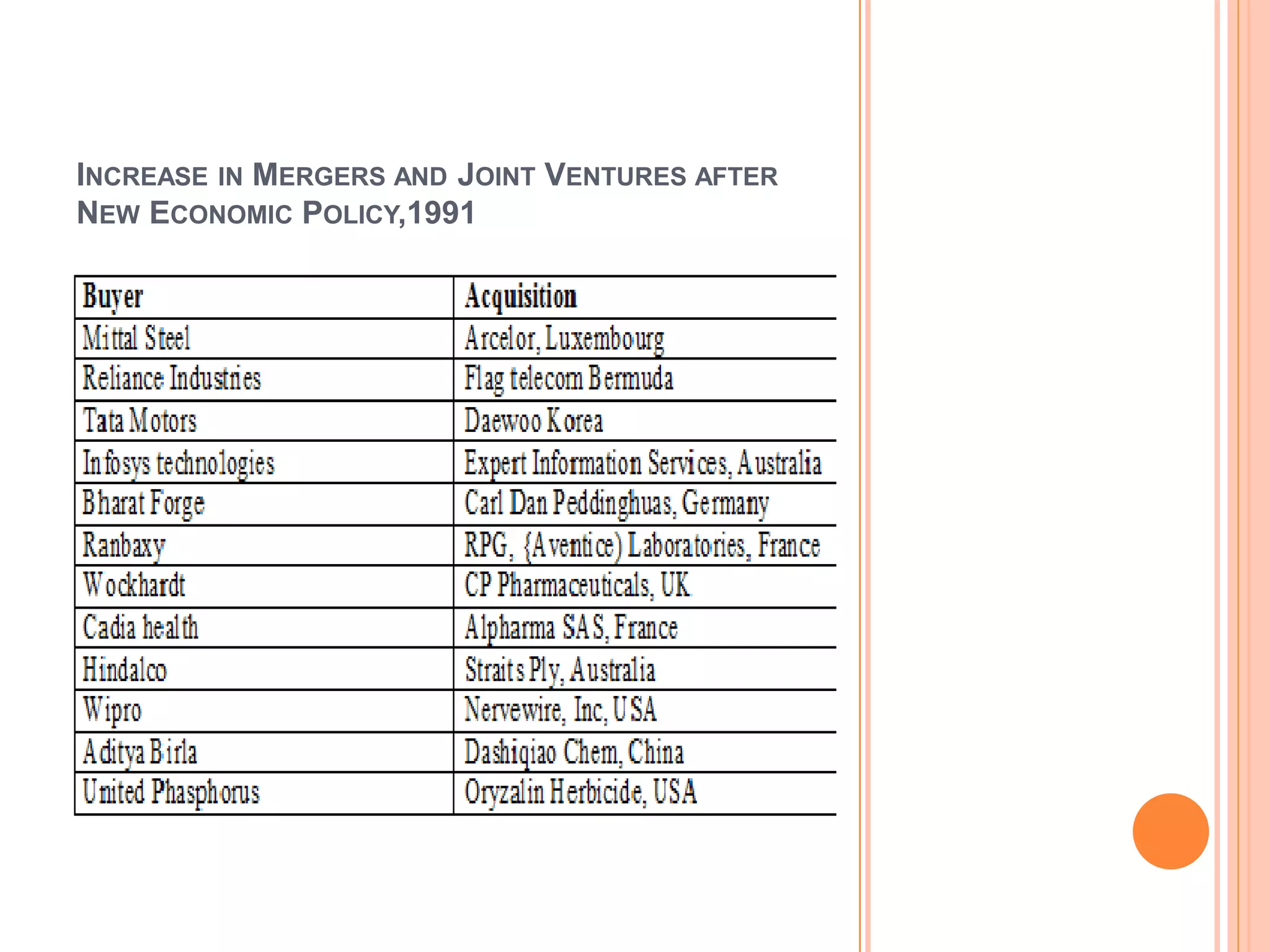
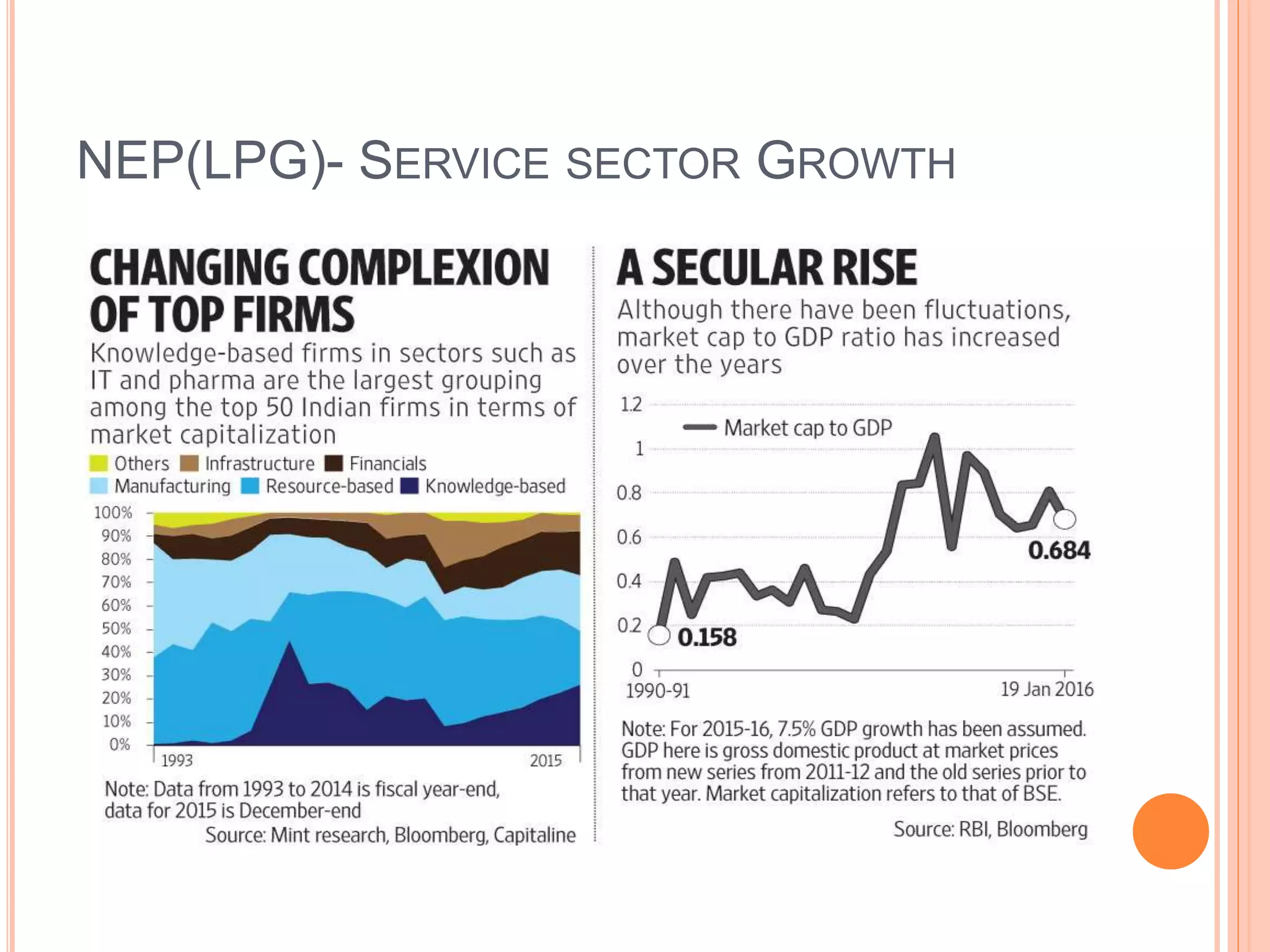
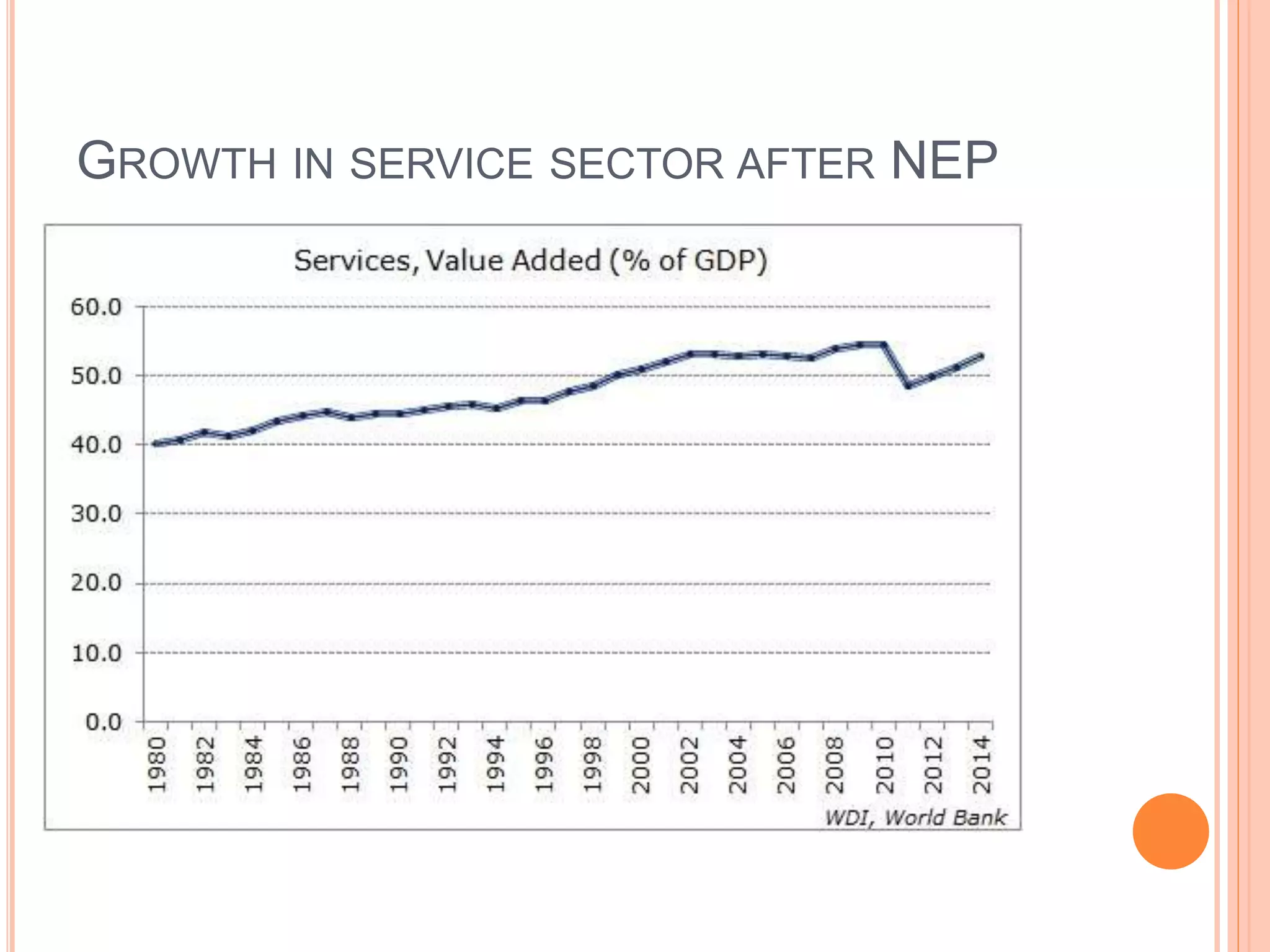
The document discusses the introduction and impact of liberalization, privatization, and globalization (LPG) policies in India beginning in 1991. It notes that LPG was initiated to address declining economic indicators and unemployment. Key aspects of the LPG reforms included abolishing licensing for most industries, liberalizing foreign investment, privatizing state-owned enterprises, and integrating the Indian economy globally. The reforms are credited with increasing India's GDP growth, foreign investment, per capita income, and reducing unemployment over the following decades. Several industries like telecommunications, retail, and automotive significantly expanded due to the new policies.