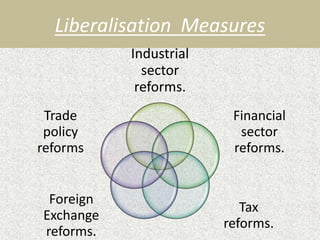
The document discusses the rationale for India's economic reforms in 1991 that introduced Liberalization, Privatization, and Globalization (LPG model). It provides background on the economic crisis India was facing in 1991 with high inflation, large fiscal deficit, and foreign exchange crisis. This led India to take loans from IMF and World Bank who mandated reforms like liberalizing and opening the economy. The 1991 New Economic Policy introduced reforms across industries, finance, trade, and more to boost growth. Key aspects of the reforms included liberalizing licenses, privatizing public sector units, and integrating India more into the global economy.