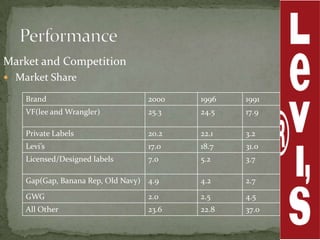
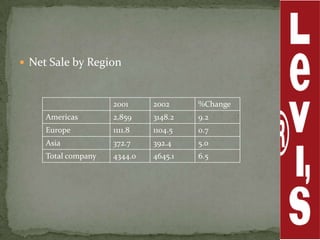
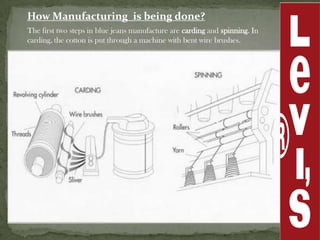
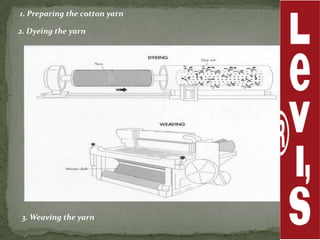
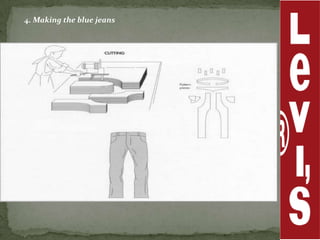
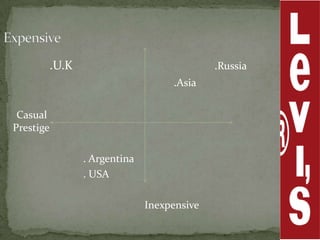
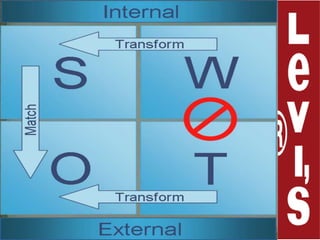
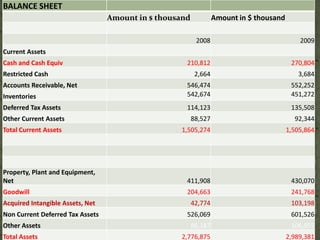
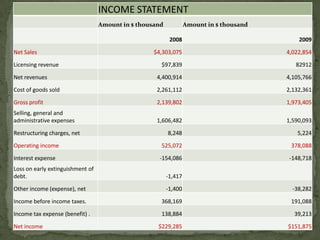
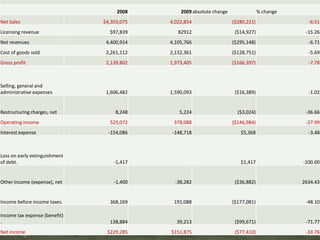
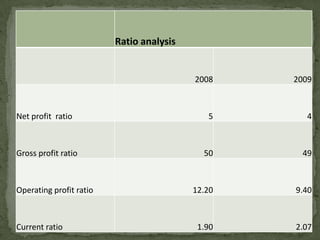
Levi Strauss & Co. is one of the largest apparel manufacturers globally, known for its jeans and brands like Levi's and Dockers, with a commitment to sustainability and responsible commercial success. Founded in 1853, the company revolutionized the denim market by introducing riveted jeans in 1873, which led to its prominence and historic sales surpassing $1 billion by 1974. The company continues to innovate and has implemented various marketing strategies to maintain its status as an American icon while expanding into global markets.