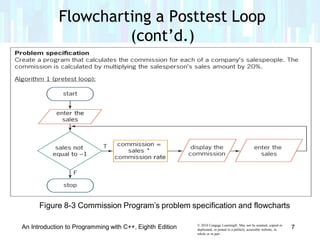
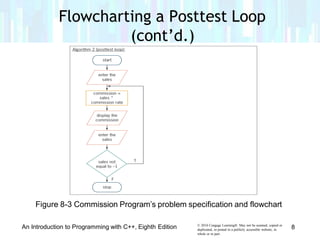
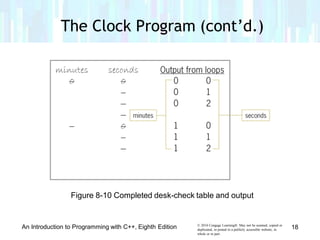
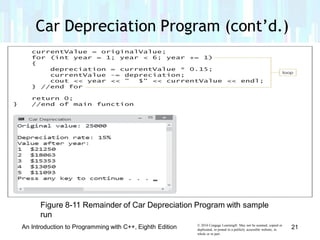
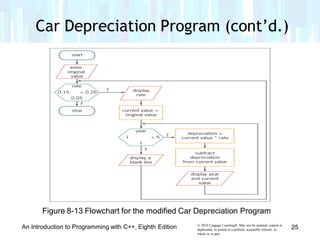
The document discusses repetition structures in C++ programming, including posttest and pretest loops. It covers coding posttest loops using do-while statements, nesting loops, and examples like a clock program and car depreciation programs. Key points are that pretest loops evaluate the condition before processing statements while posttest loops evaluate after, do-while is used for posttest loops, and loops can be nested with the inner loop contained in the outer loop.