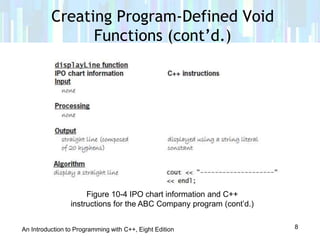
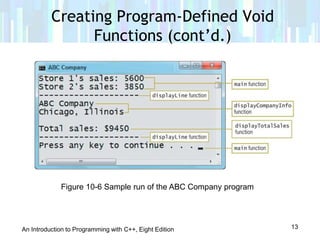
This document provides an introduction to void functions in C++ programming. It discusses how to create and call void functions, as well as how to pass information to void functions through references. Specifically, it notes that void functions perform tasks without returning values, and how to define void functions without return data types or return statements. It also explains how passing by reference allows void functions to modify variable values in the calling function's memory space.