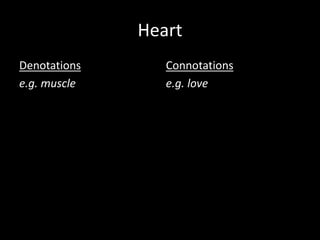
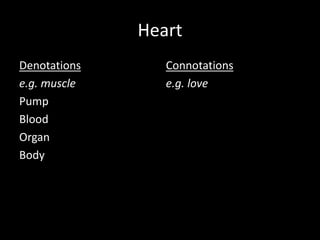
The document discusses the concepts of denotation and connotation as they relate to the word "heart." It explains that the denotation of heart is a muscle, pump, blood, organ, and body, while the connotations include love, feelings, romance, and sweet. The document also explores how mise-en-scene, which means "putting into the scene," analyzes the setting, costumes, actors, lighting, and positioning of objects and people in media to understand how meaning is constructed.