Semiotic film theory analyzes how meaning is conveyed through signs and codes in cinema. Films use various visual elements like lighting, shot composition, and juxtaposition of images to signify ideas beyond their literal meaning. Structuralist film theory emphasizes how simple combinations of shots can create additional implied meanings through cultural codes and conventions. Semiotic analysis involves examining signs like characters, props, and backgrounds to understand their denotations and cultural connotations, and how they relate through paradigmatic and syntagmatic relationships to construct meaning.











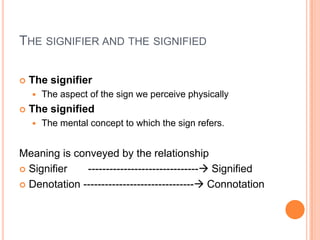


![codes"The way we watch television and the way we perceive [everyday] reality are fundamentally similar, in that both are determined by conventions or codes. Reality is itself a complex system of signs interpreted by members of the culture in exactly the same way as are films and television programmes. (Fiske)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semiotics-100315004516-phpapp02/85/Semiotics-15-320.jpg)




