This document provides lesson materials on the concept of representation for a media studies exam preparation. It includes two lessons on representation, with the second focusing on planning an essay question applying representation to a coursework production. The lessons define representation, discuss its importance, and provide examples of how it can be analyzed in media texts. Key theories and theorists on representation such as Laura Mulvey, Richard Dyer, and David Buckingham are outlined. Students are guided in identifying representational concepts in their own work and planning a structured essay applying representation theory.






![Example Exam Question
(b) Apply the concept of representation to one
of your coursework productions. [25]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson5-6representation-q1byear13mediastudies2016v7-160513140428/85/Lesson-5-Representation-7-320.jpg)








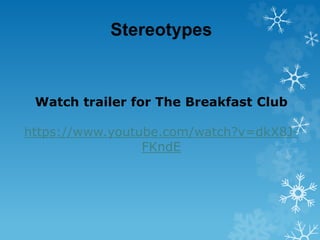











![SECTION A: Theoretical Evaluation of Production
1 (b) In question 1(b) you must write about one of your media
productions.
(b) Apply the concept of representation to one of your coursework
productions. [25]
Example Exam Question
How might you now go about planning for
this question?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson5-6representation-q1byear13mediastudies2016v7-160513140428/85/Lesson-5-Representation-28-320.jpg)
![(b) Apply the concept of representation to one of your coursework
productions. [25]
Now using your lesson plan attempt
the question:
….You have 30 mins
Good luck!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson5-6representation-q1byear13mediastudies2016v7-160513140428/85/Lesson-5-Representation-30-320.jpg)
