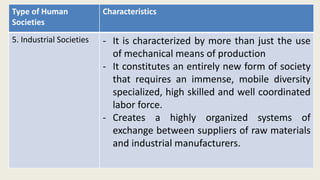
Hunting and gathering societies were the earliest form of human society and subsisted by foraging for foods. Horticultural societies began cultivating fields using human and tool labor in either subsistence farming which only produced enough for families, or surplus farming for storage. Pastoral societies relied on herding domesticated animals. Agricultural societies used plows and irrigation, forming social classes and states. Industrial societies used machinery across specialized labor and organized exchange systems. Post-industrial societies are knowledge and service based with computer and information industries dominating the economy.