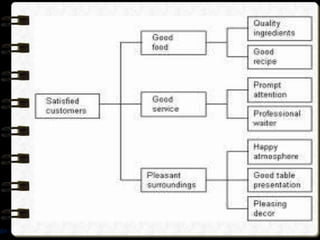
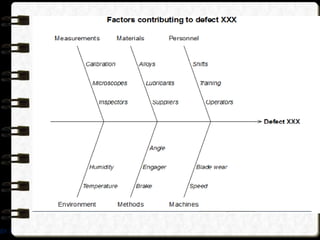
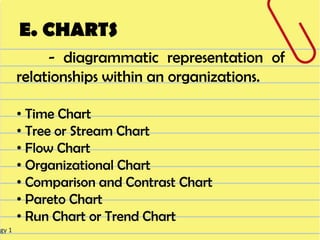
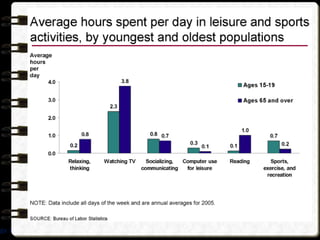
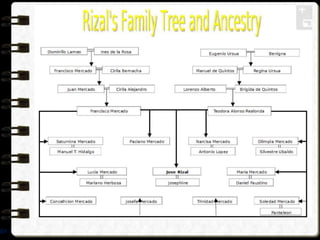
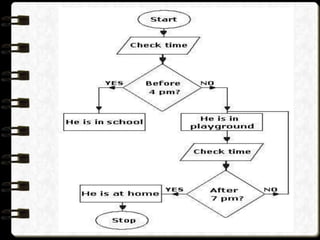
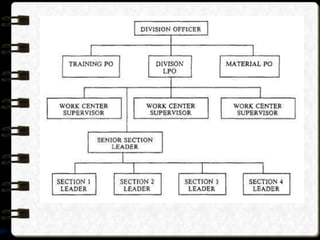
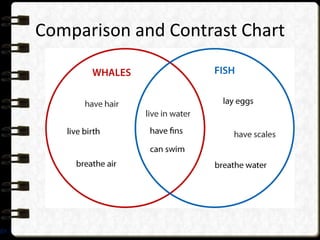
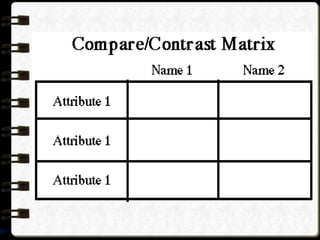
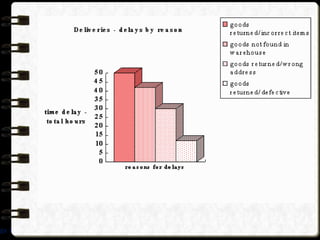
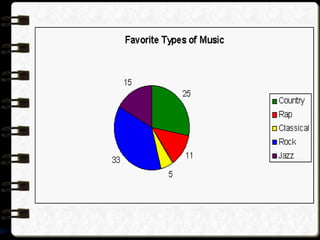
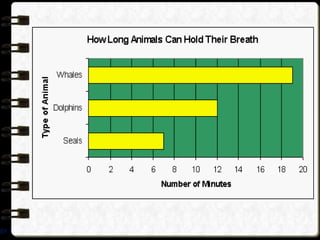
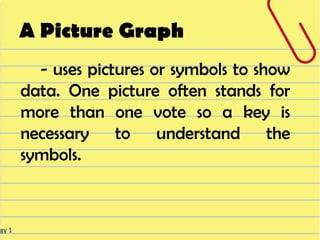
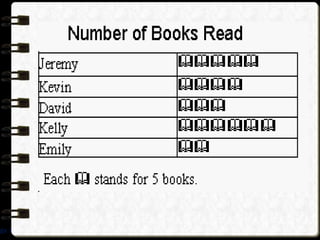
The document discusses different visual symbols that can be used for teaching, including drawings, cartoons, diagrams, charts, and graphs. It provides examples and descriptions of each type of visual symbol, such as how drawings can illustrate lectures, how cartoons can convey messages metaphorically, and how diagrams can show relationships and arrangements. Maps are also included as a kind of visual symbol that can represent spatial relationships.