This document provides examples and explanations of concepts related to classifying and ordering different types of numbers:
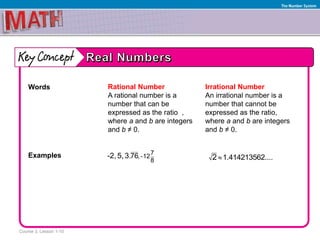
1) It defines rational and irrational numbers, and provides examples of each. Rational numbers can be expressed as ratios of integers, while irrational numbers cannot.
2) Exercises are included for classifying numbers as rational or irrational, comparing irrational numbers on a number line, and ordering sets of numbers from least to greatest.
3) Answering "Why is it helpful to write numbers in different ways?" the document explains that not all numbers can be written the same way, like irrational numbers that cannot be expressed as integers. Being able to classify numbers facilitates understanding and operations involving different types of numbers.