The document summarizes key concepts from a 5th grade math unit on number theory, including:
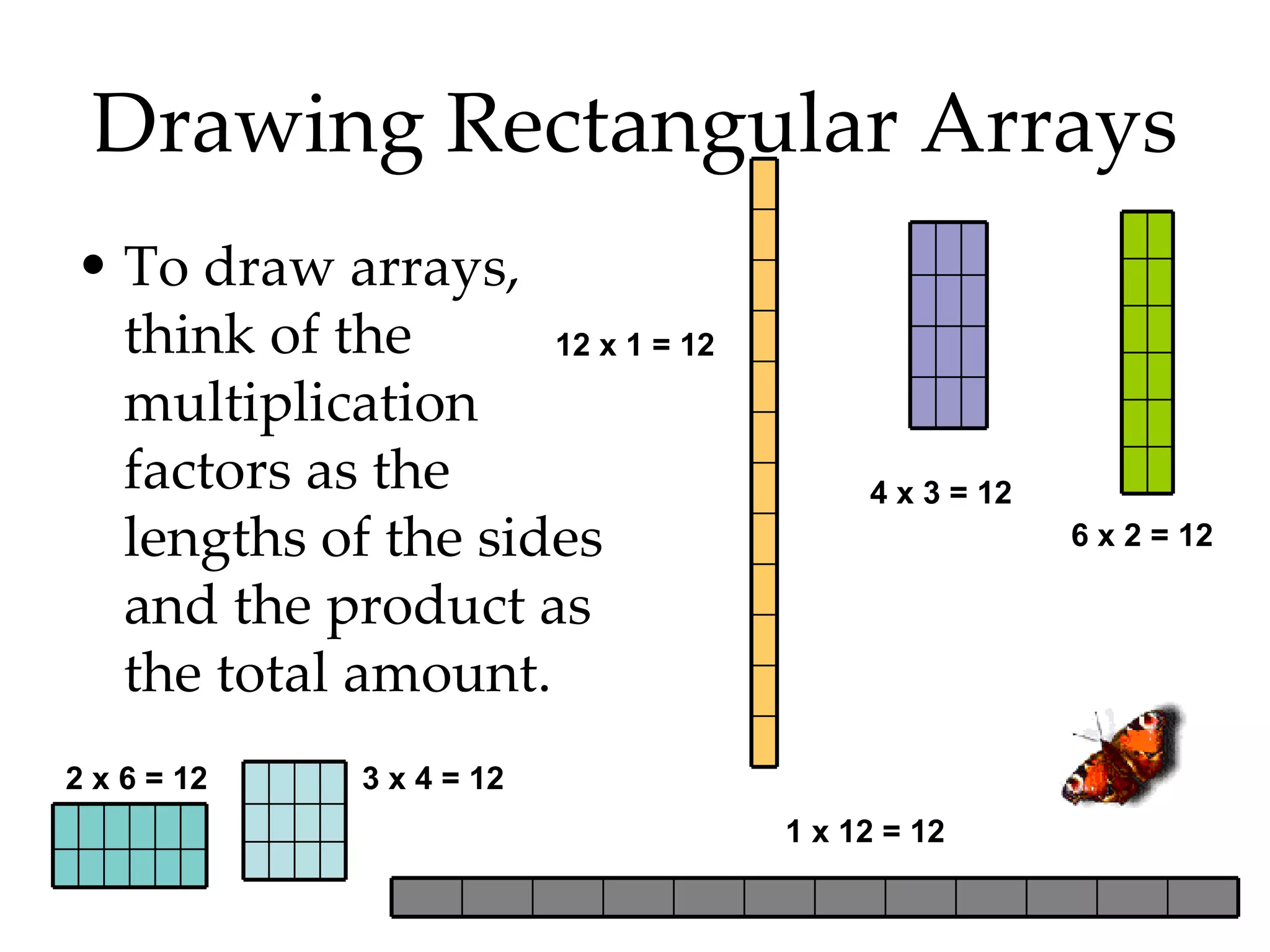
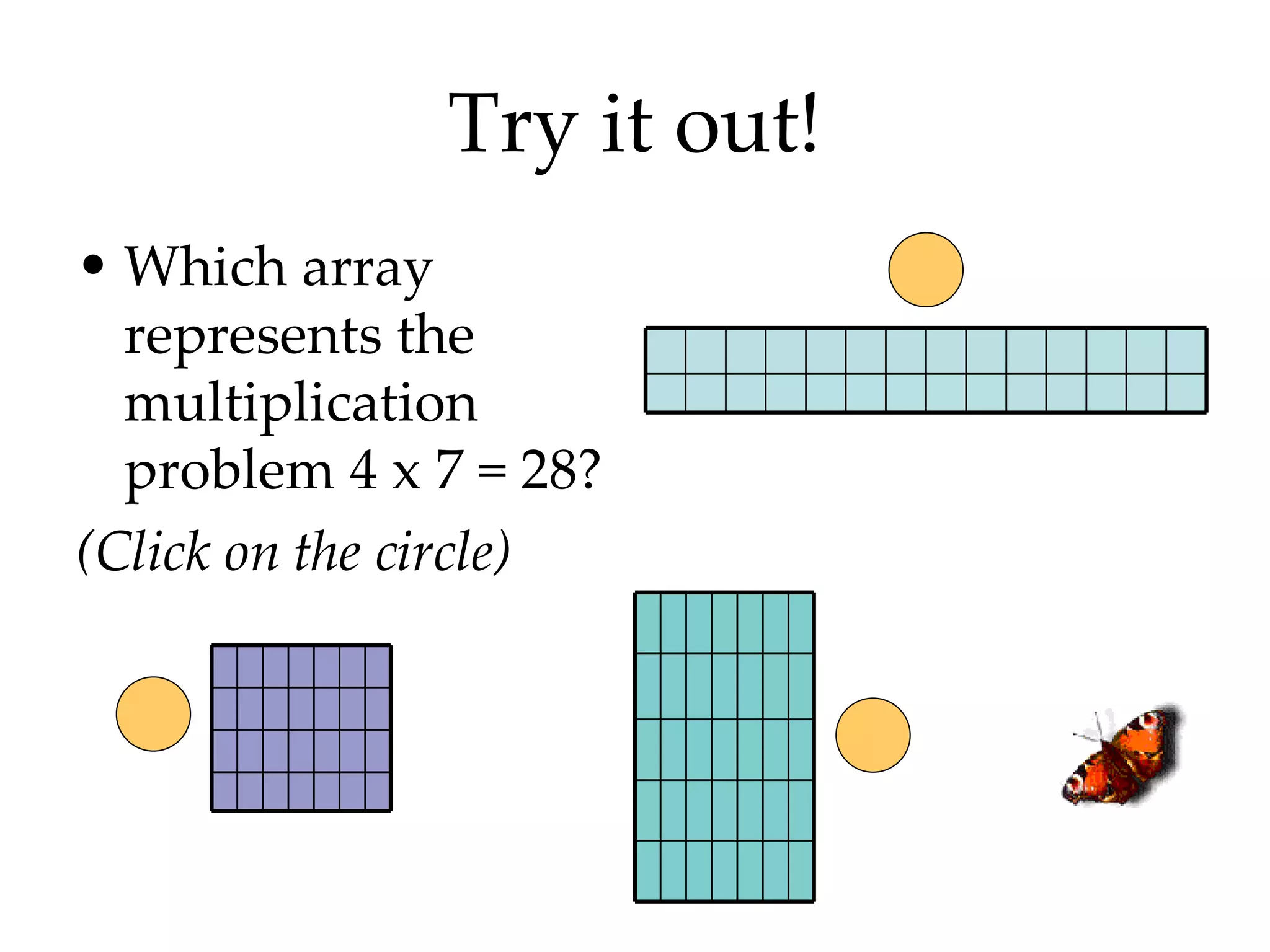
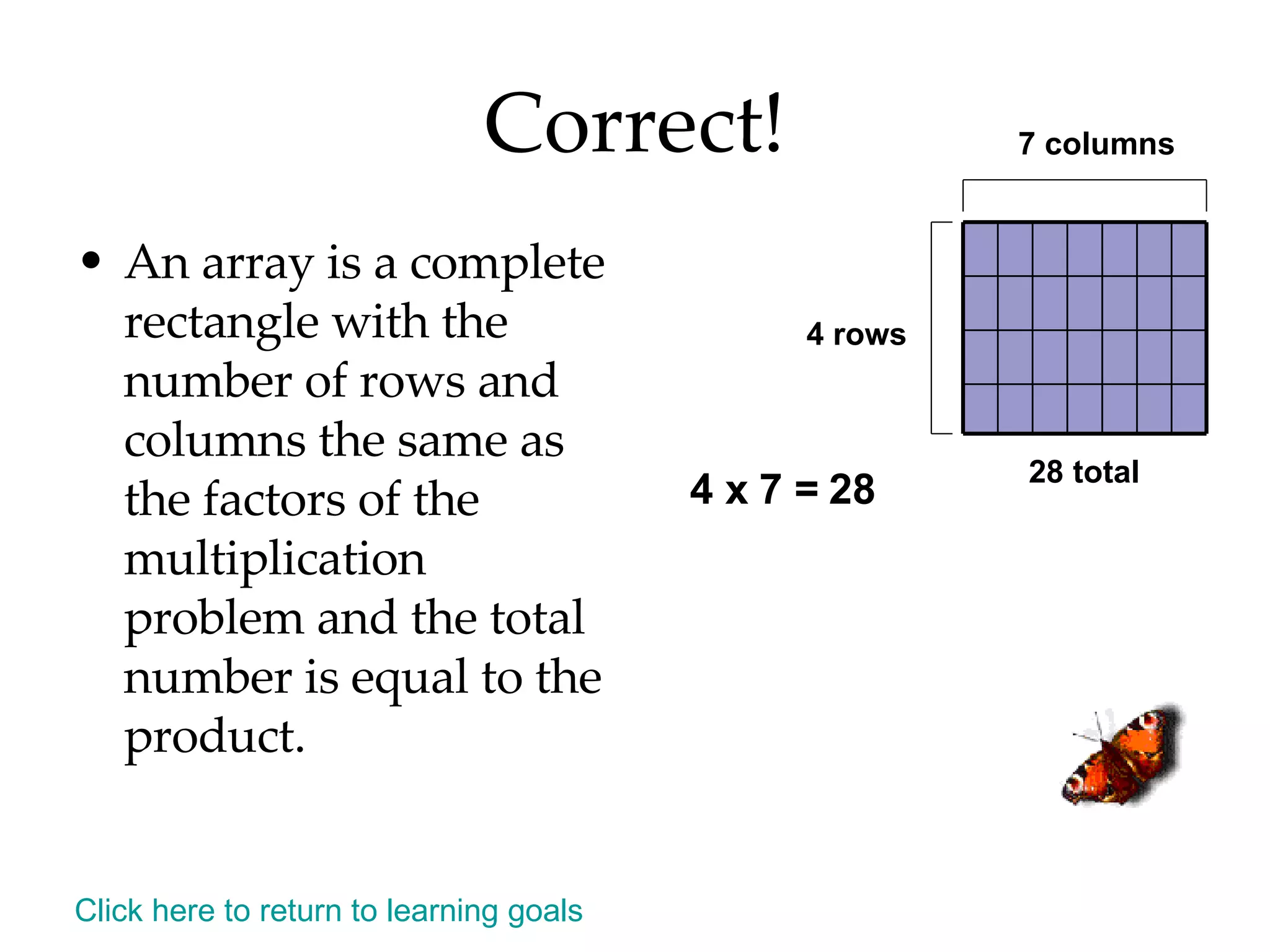
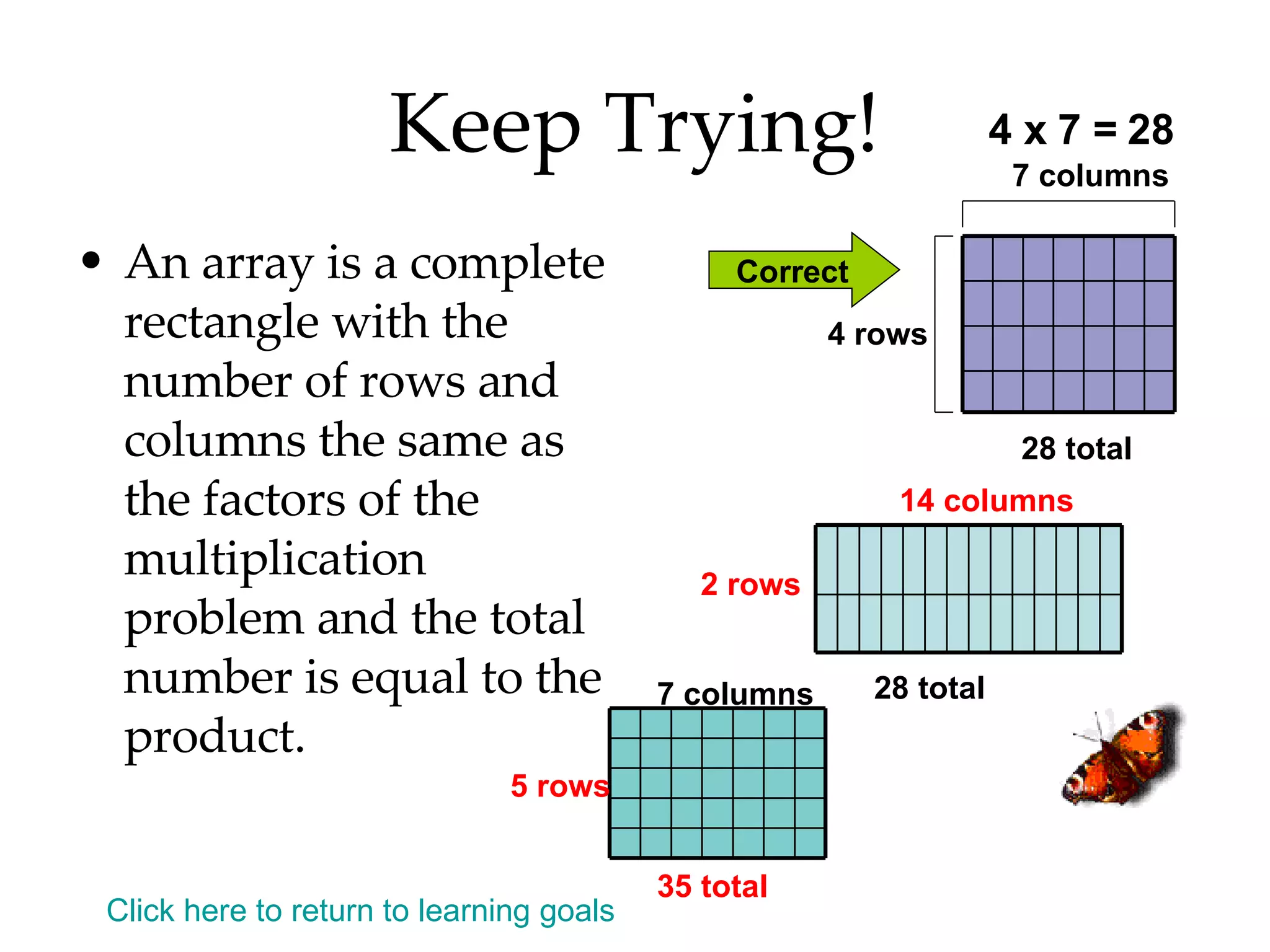
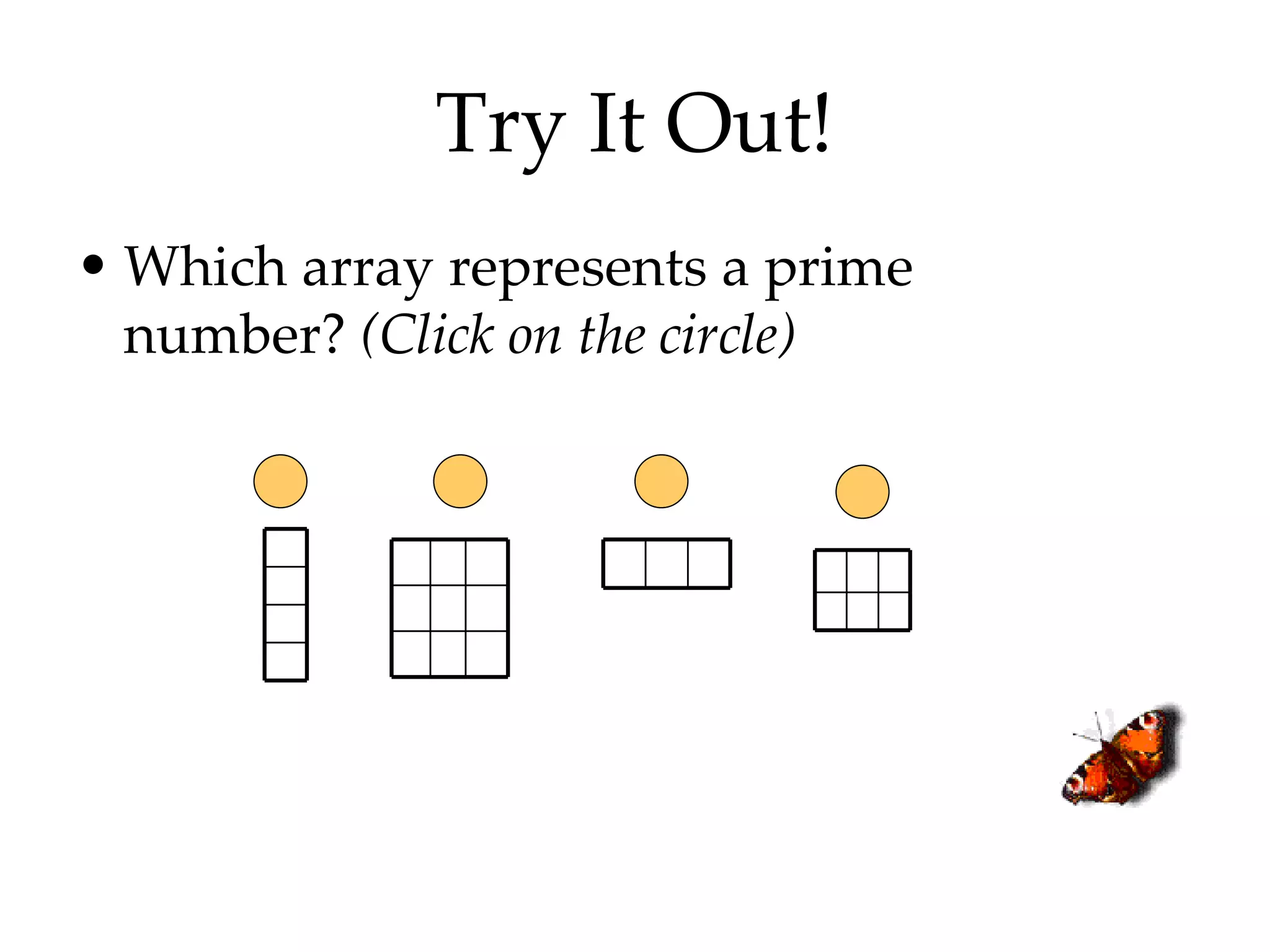
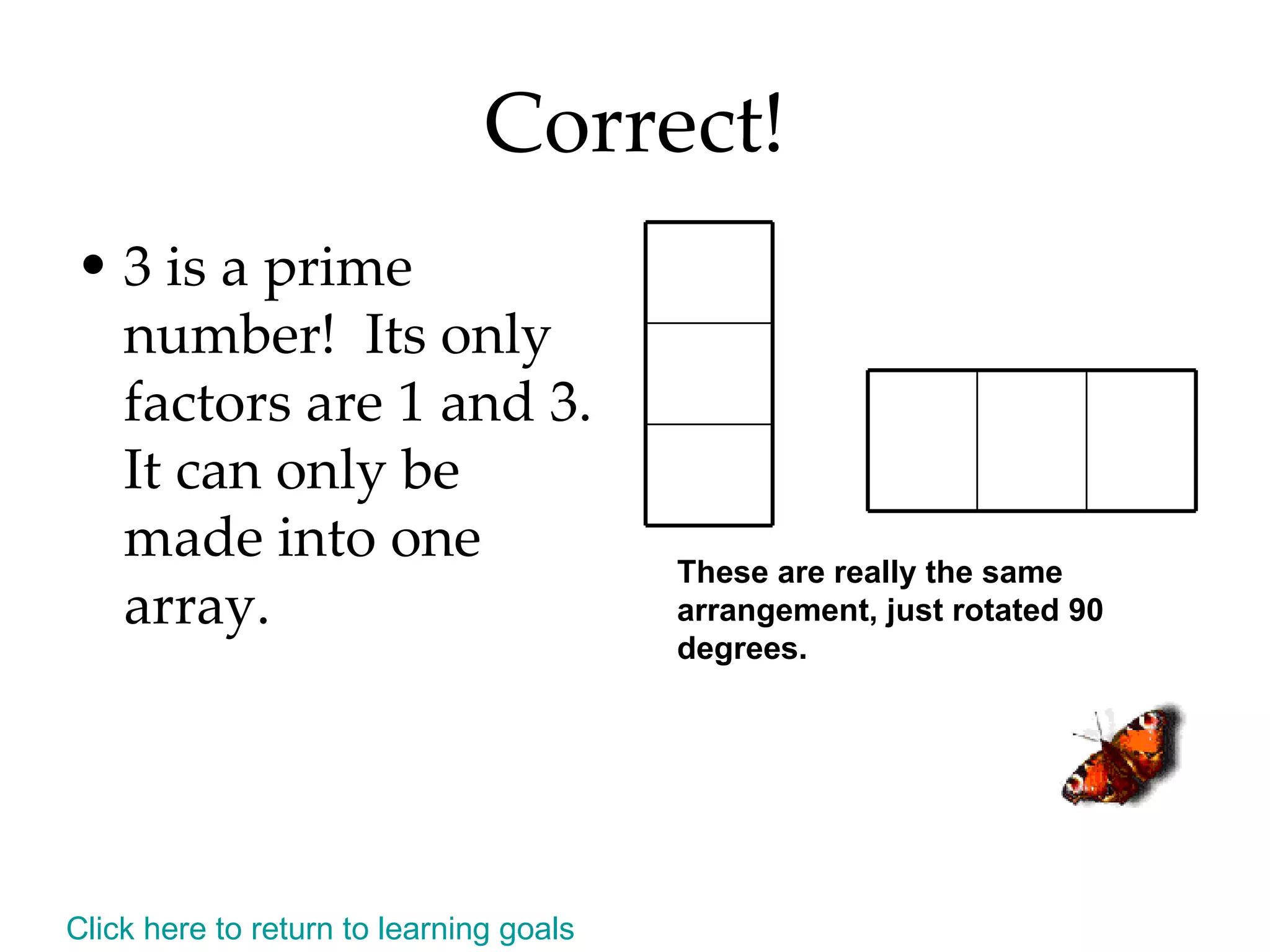
- Identifying even and odd numbers and using arrays to represent multiplication
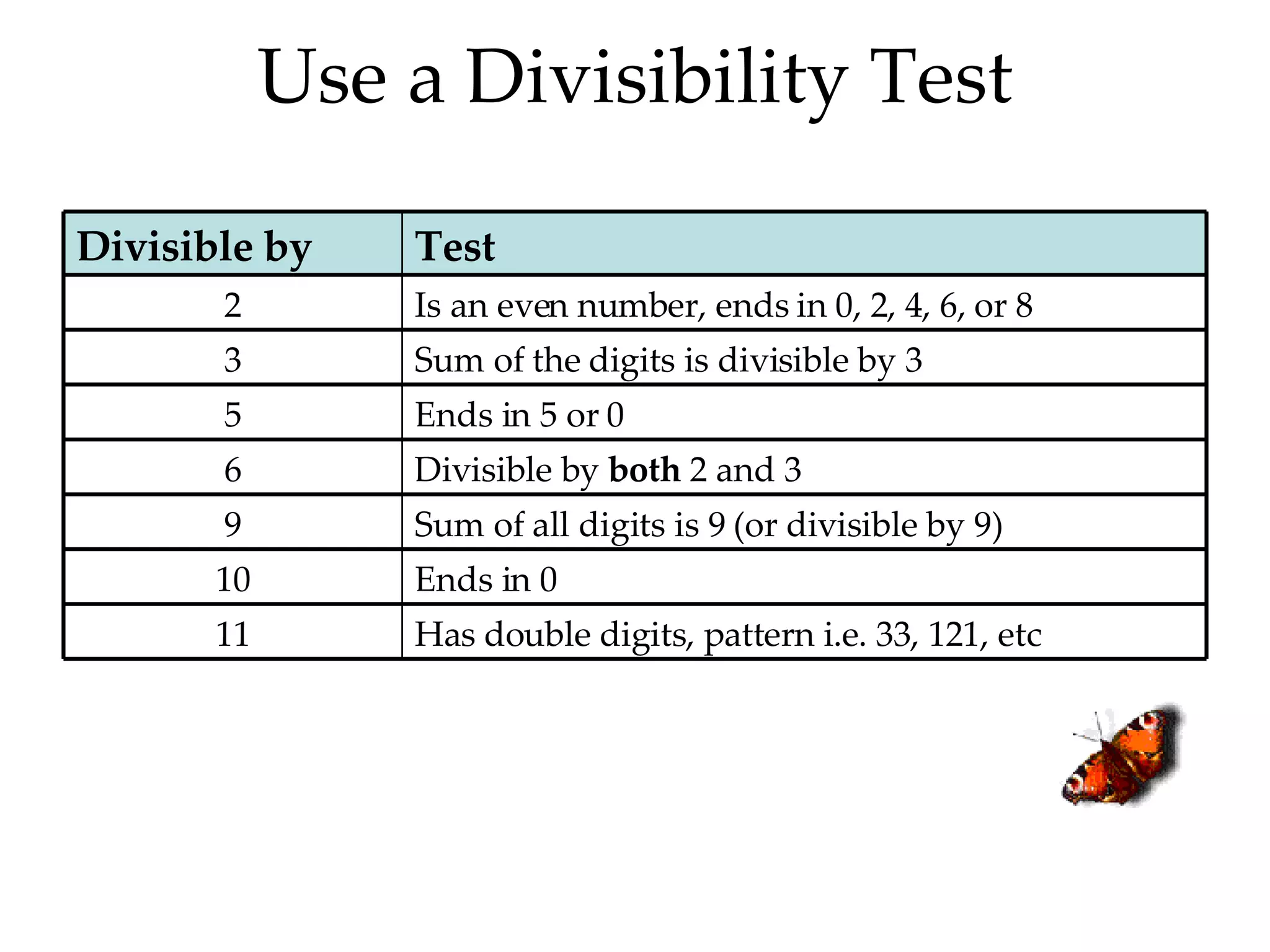
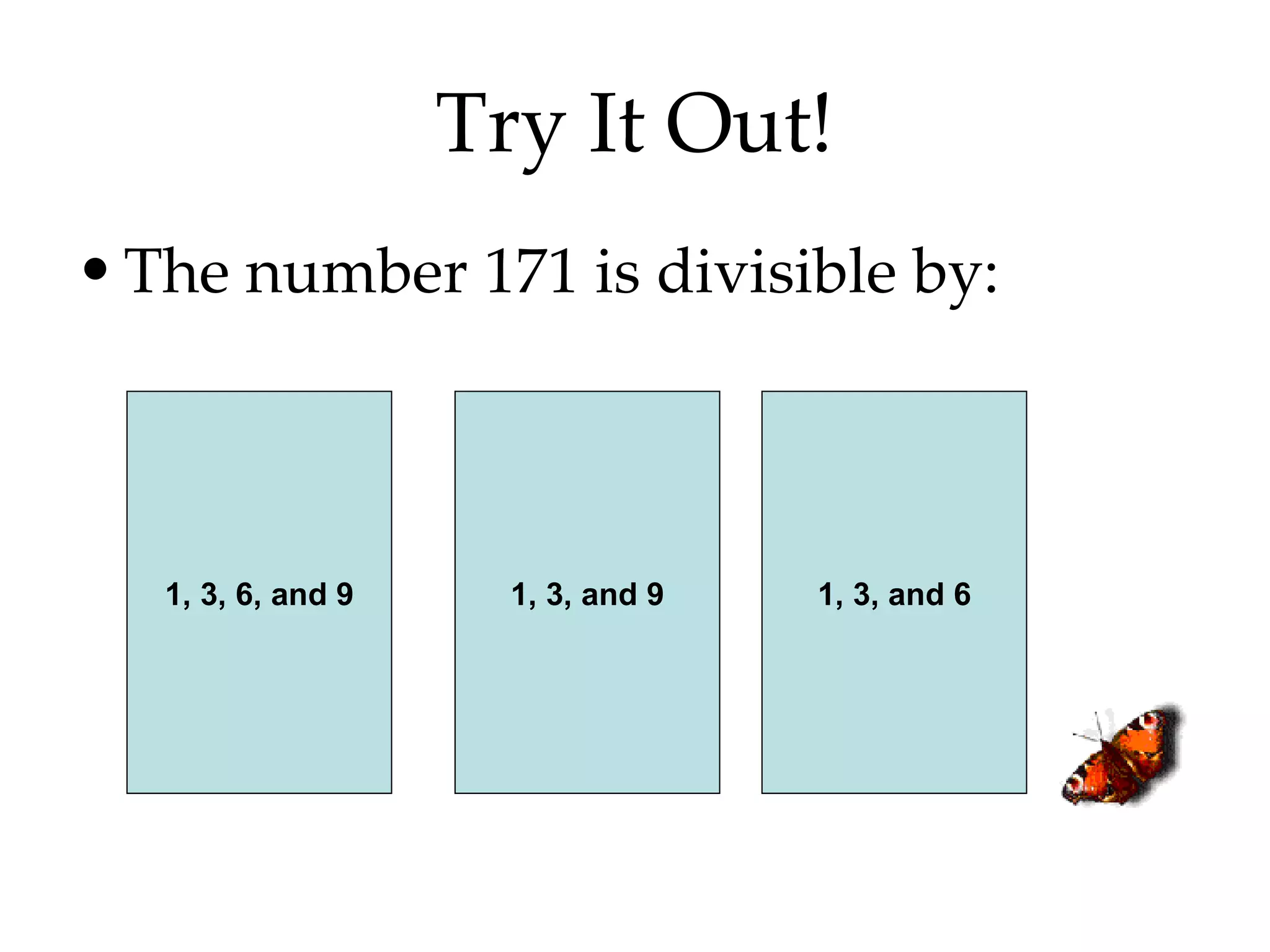
- Using divisibility tests to determine if a number is divisible by another
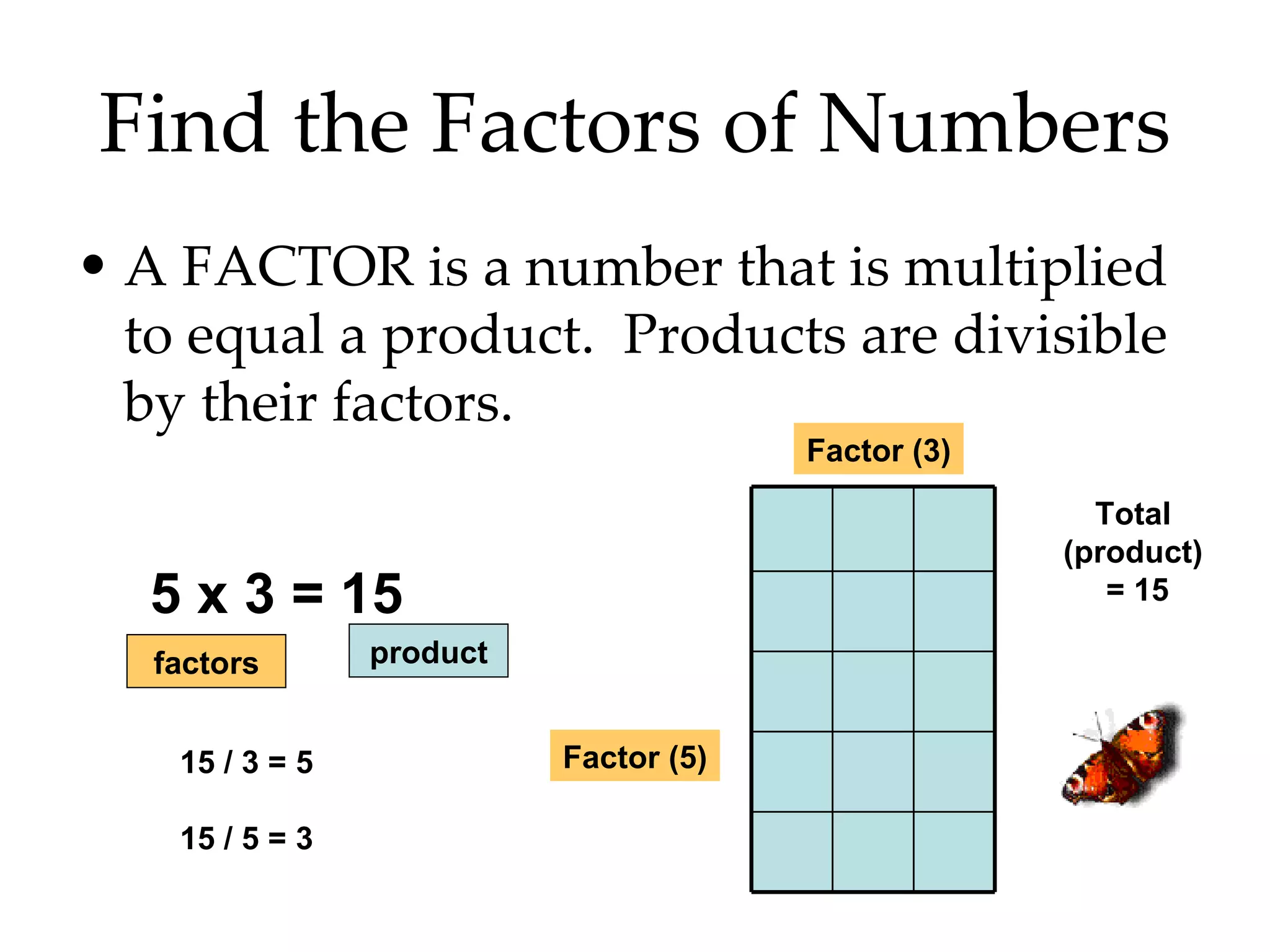
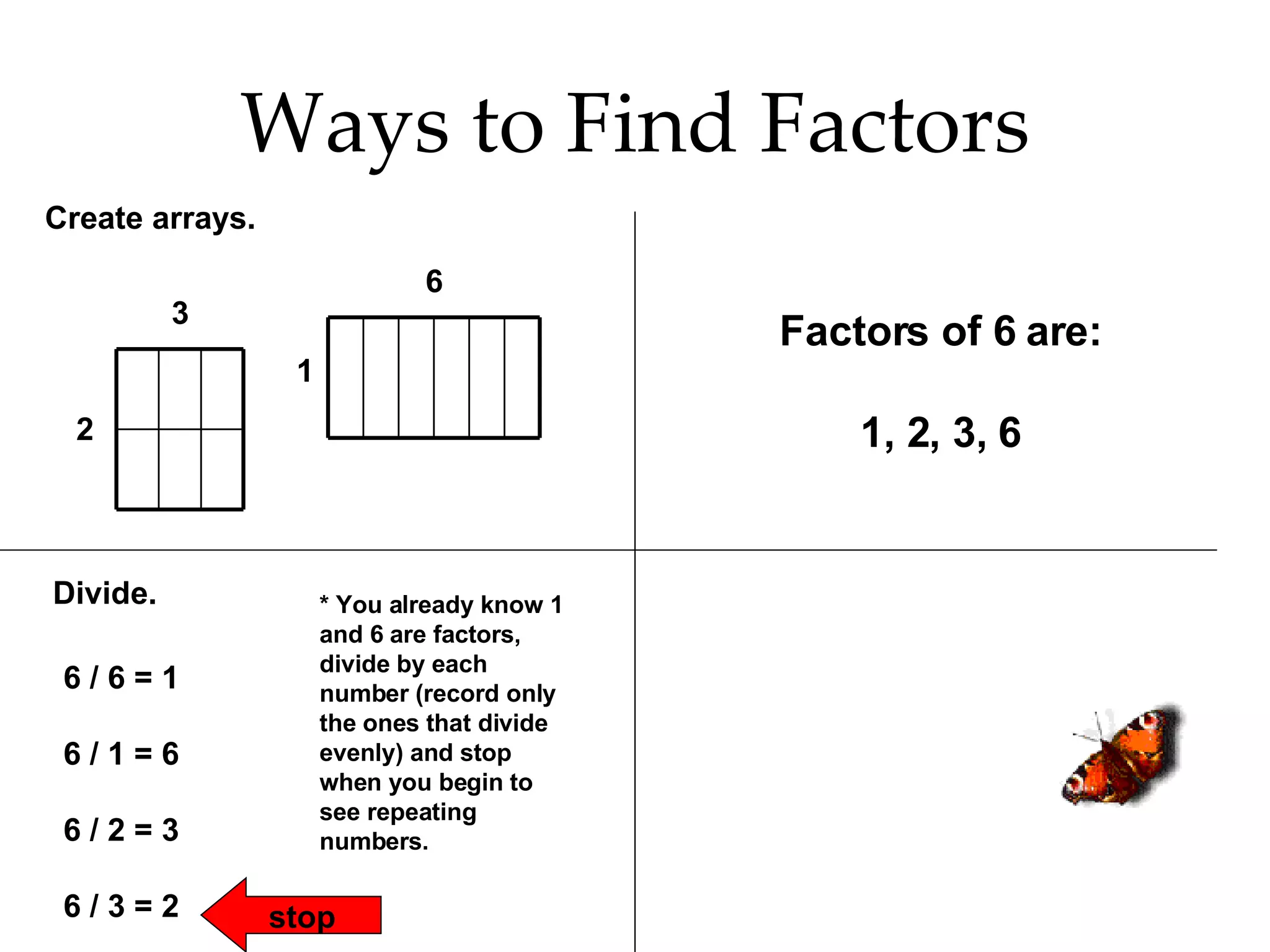
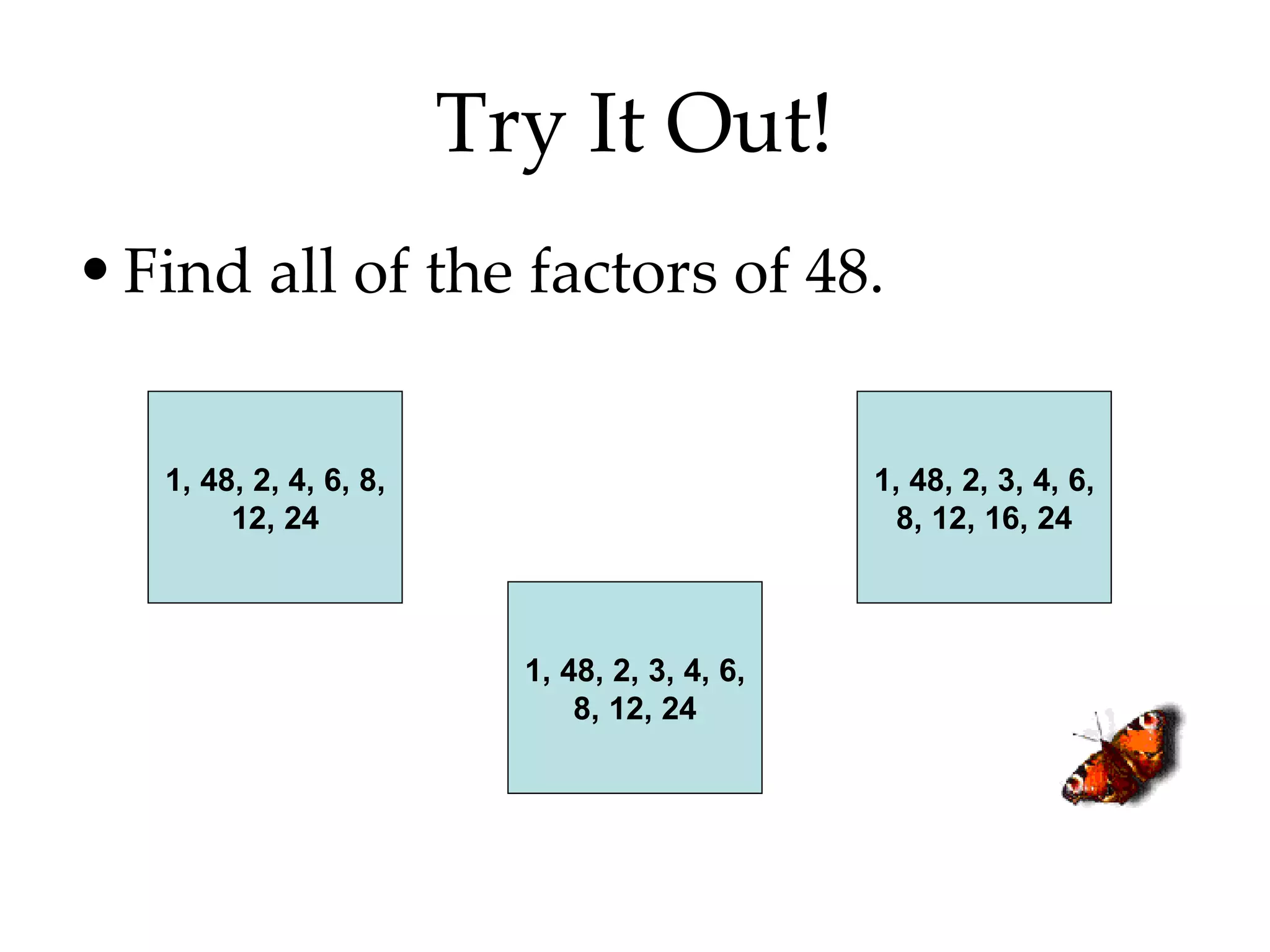
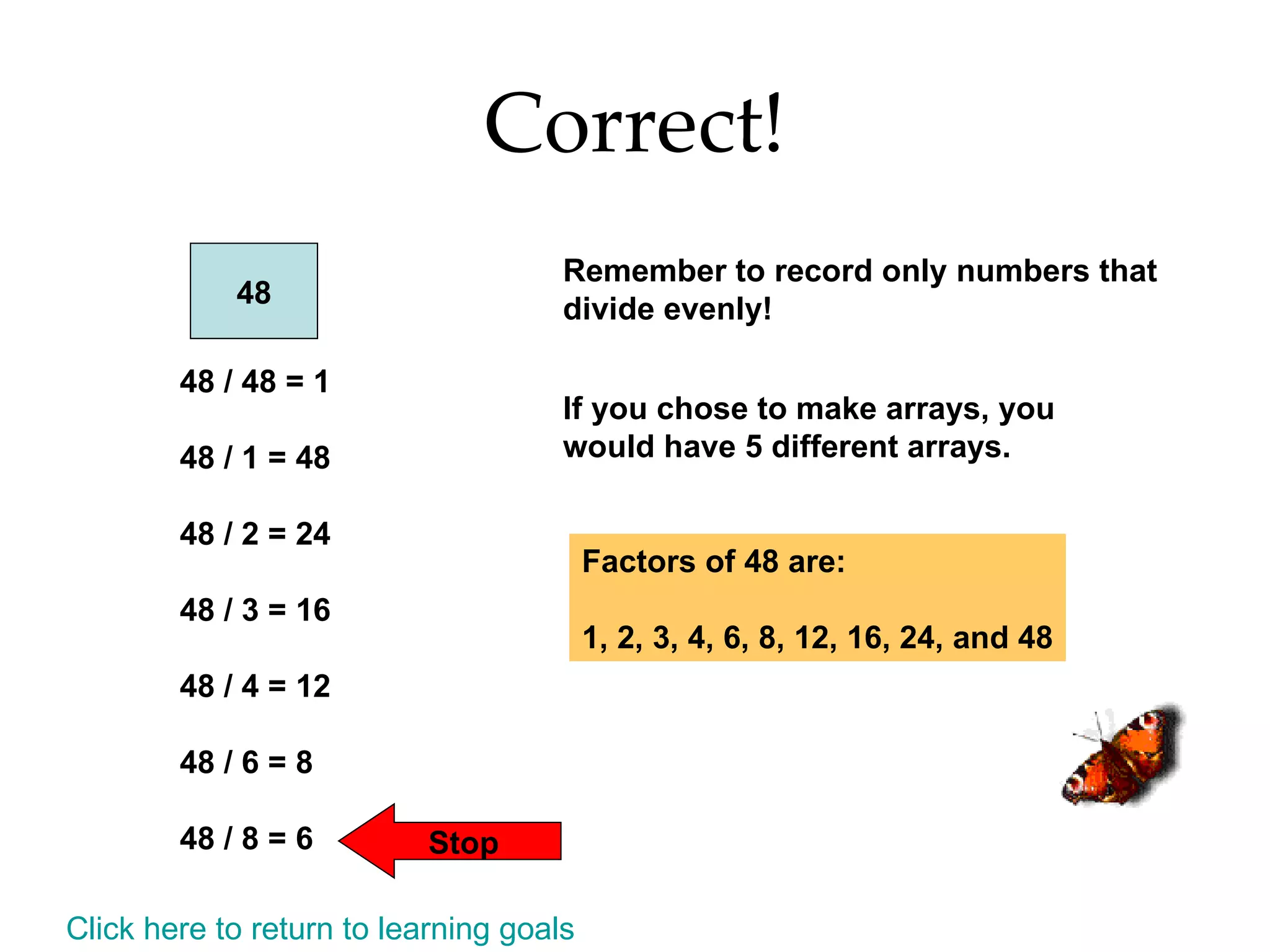
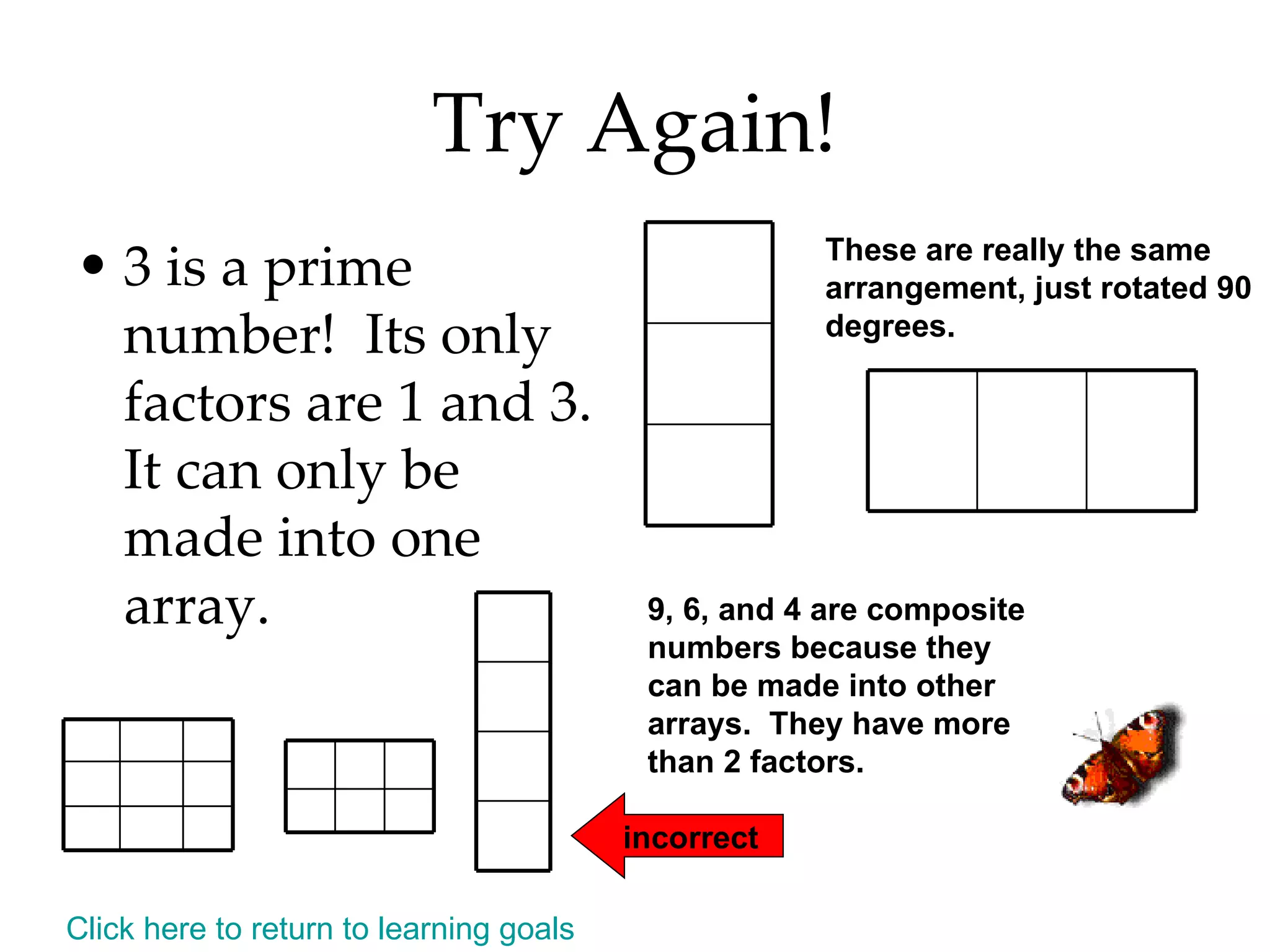
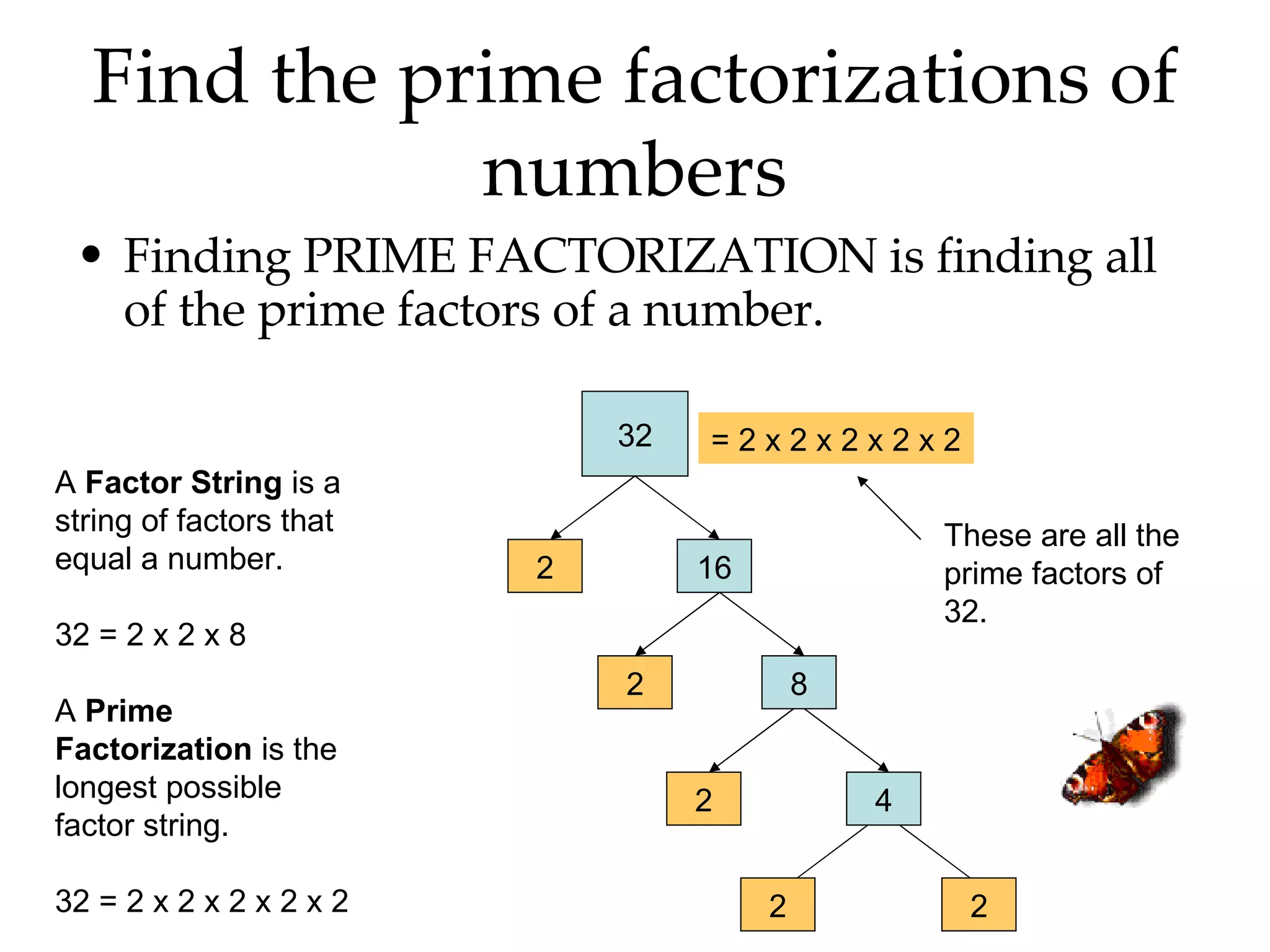
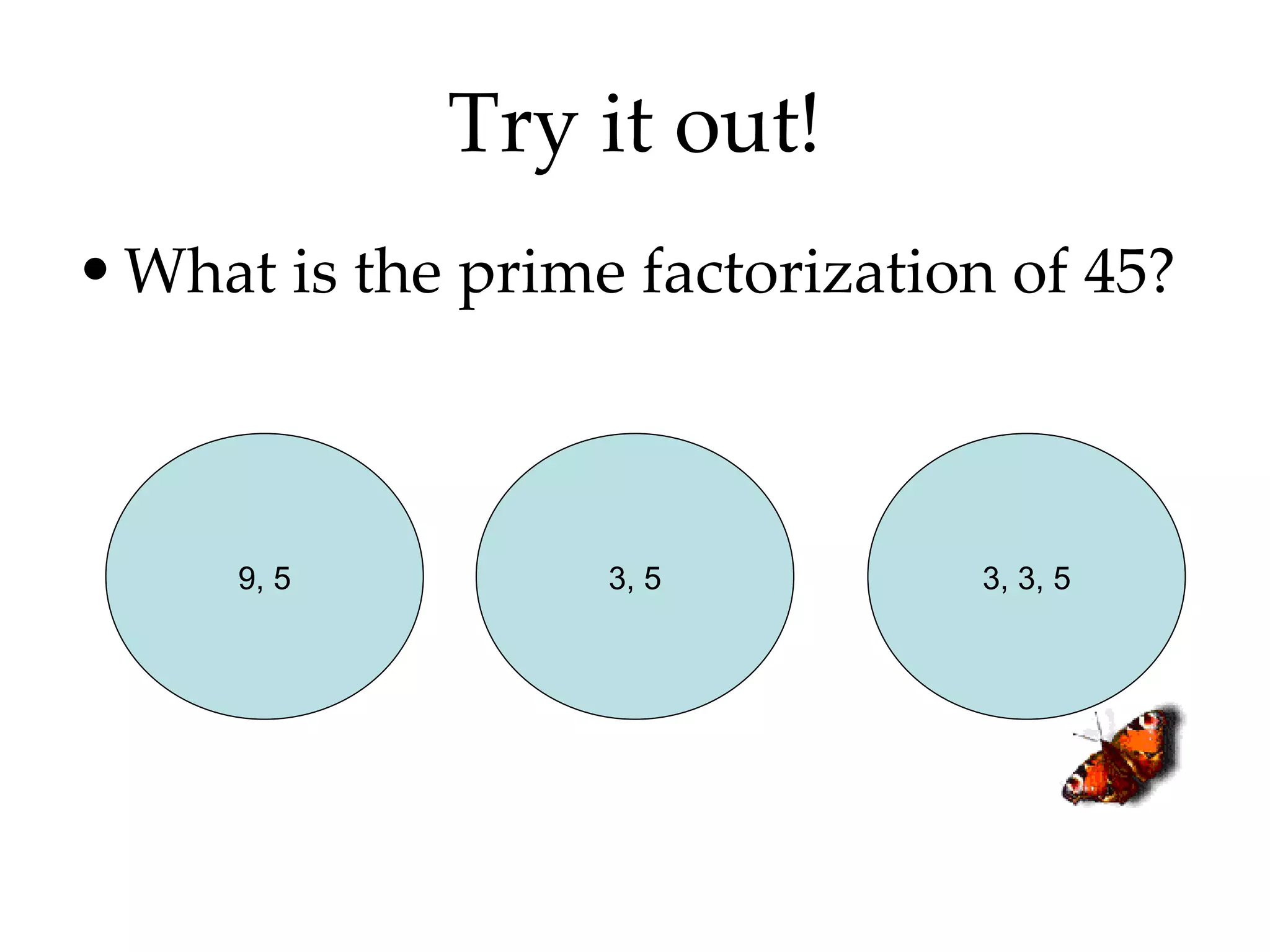
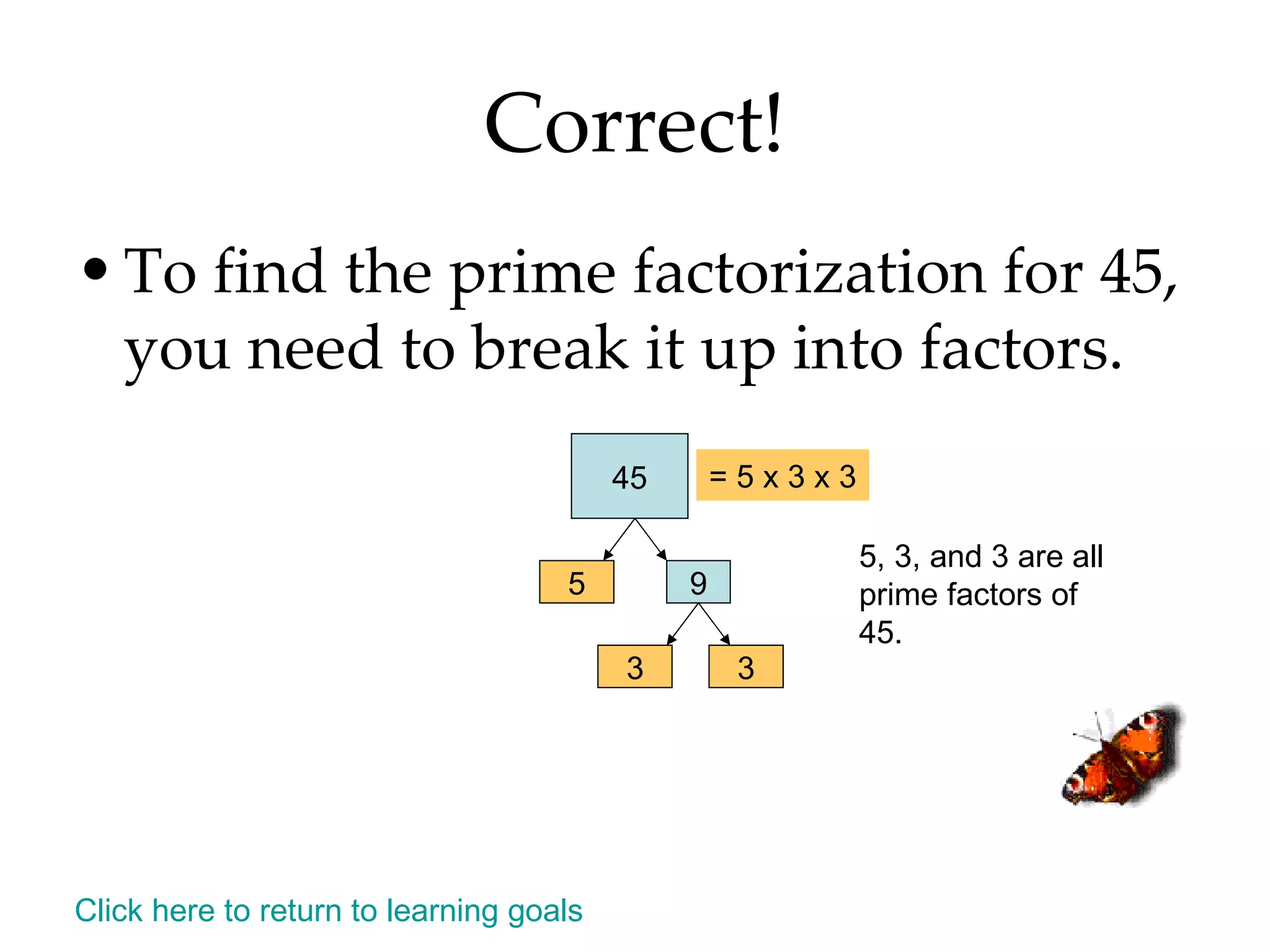
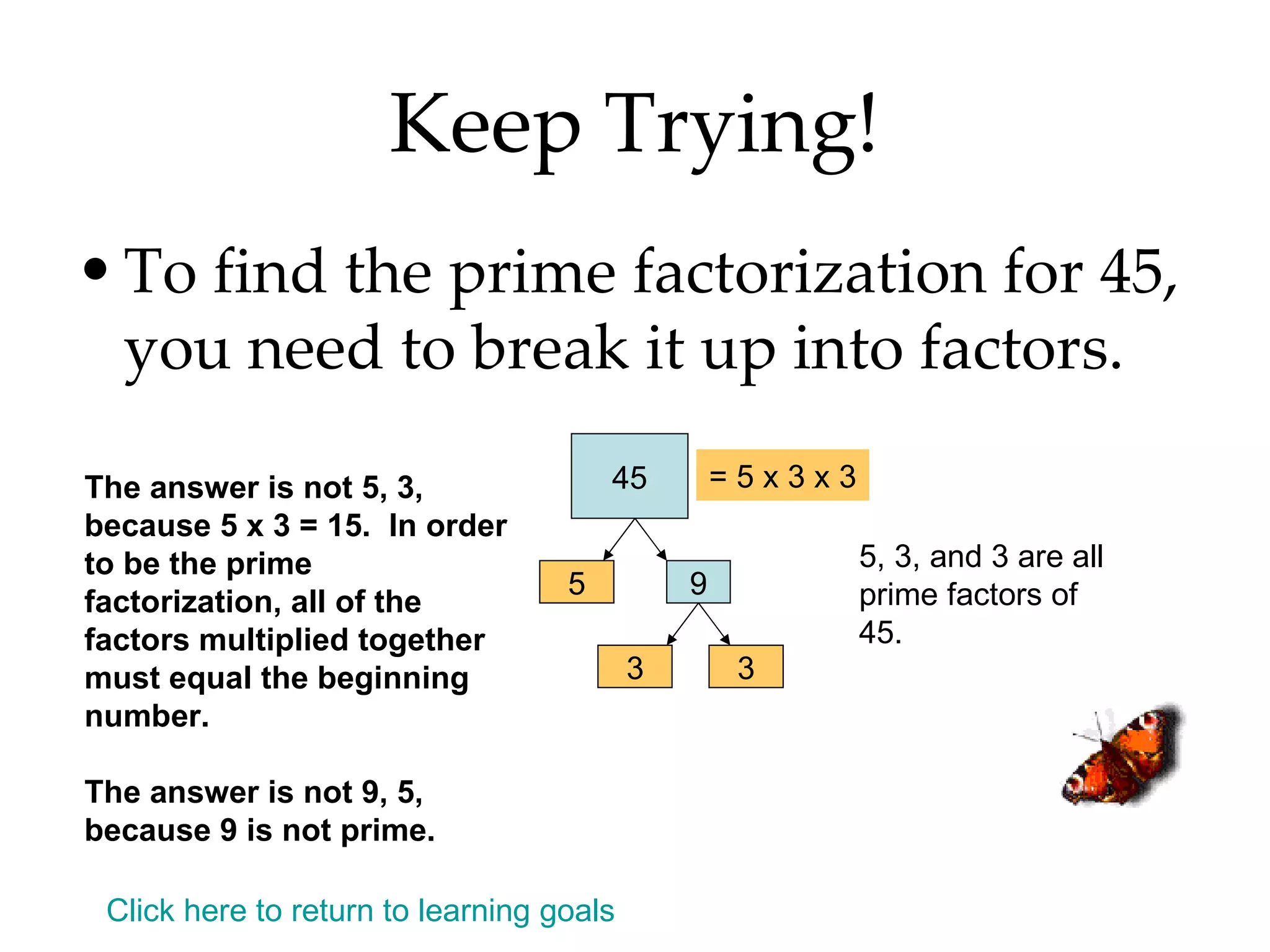
- Finding all the factors of a given number and identifying prime and composite numbers
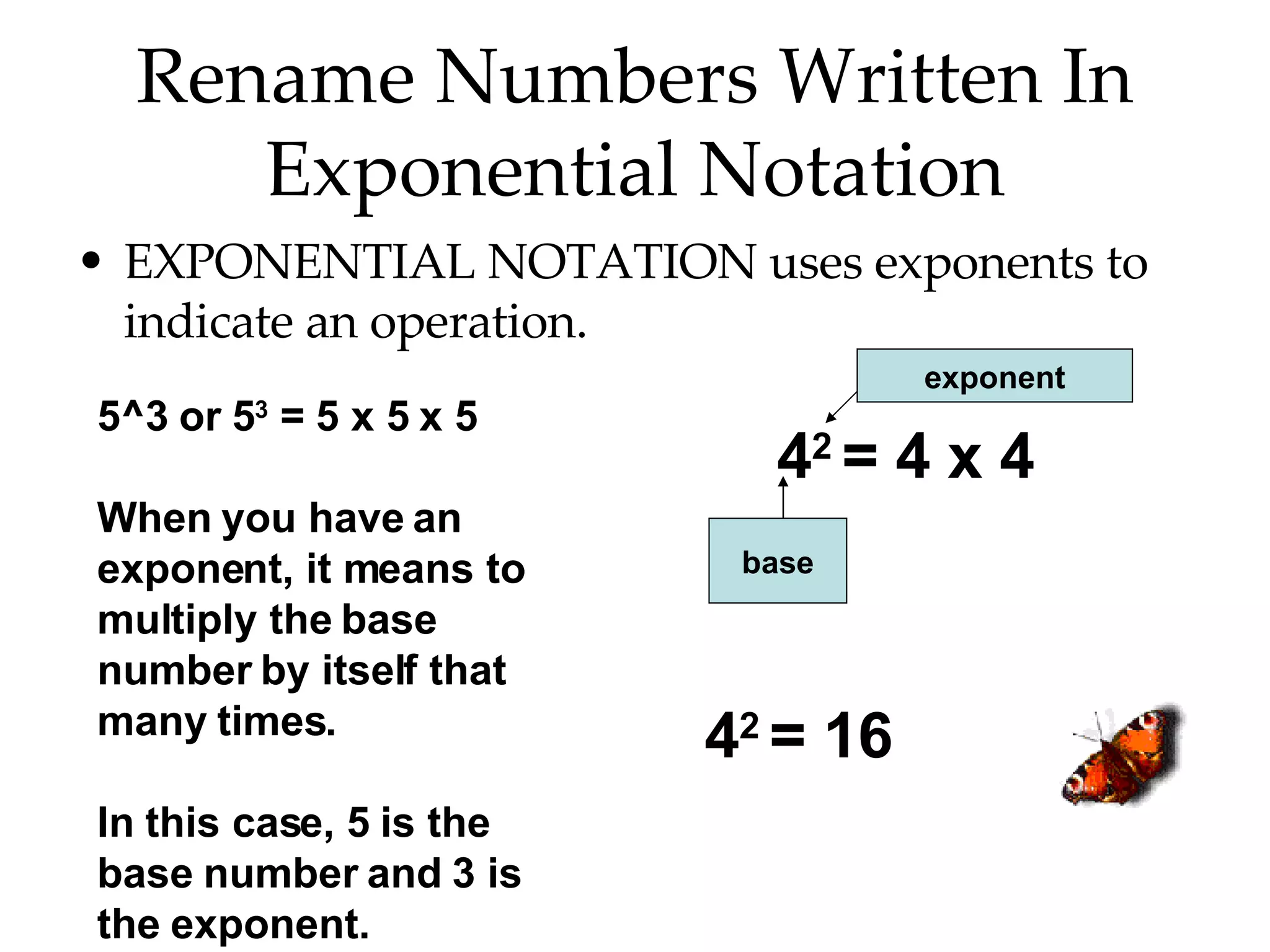
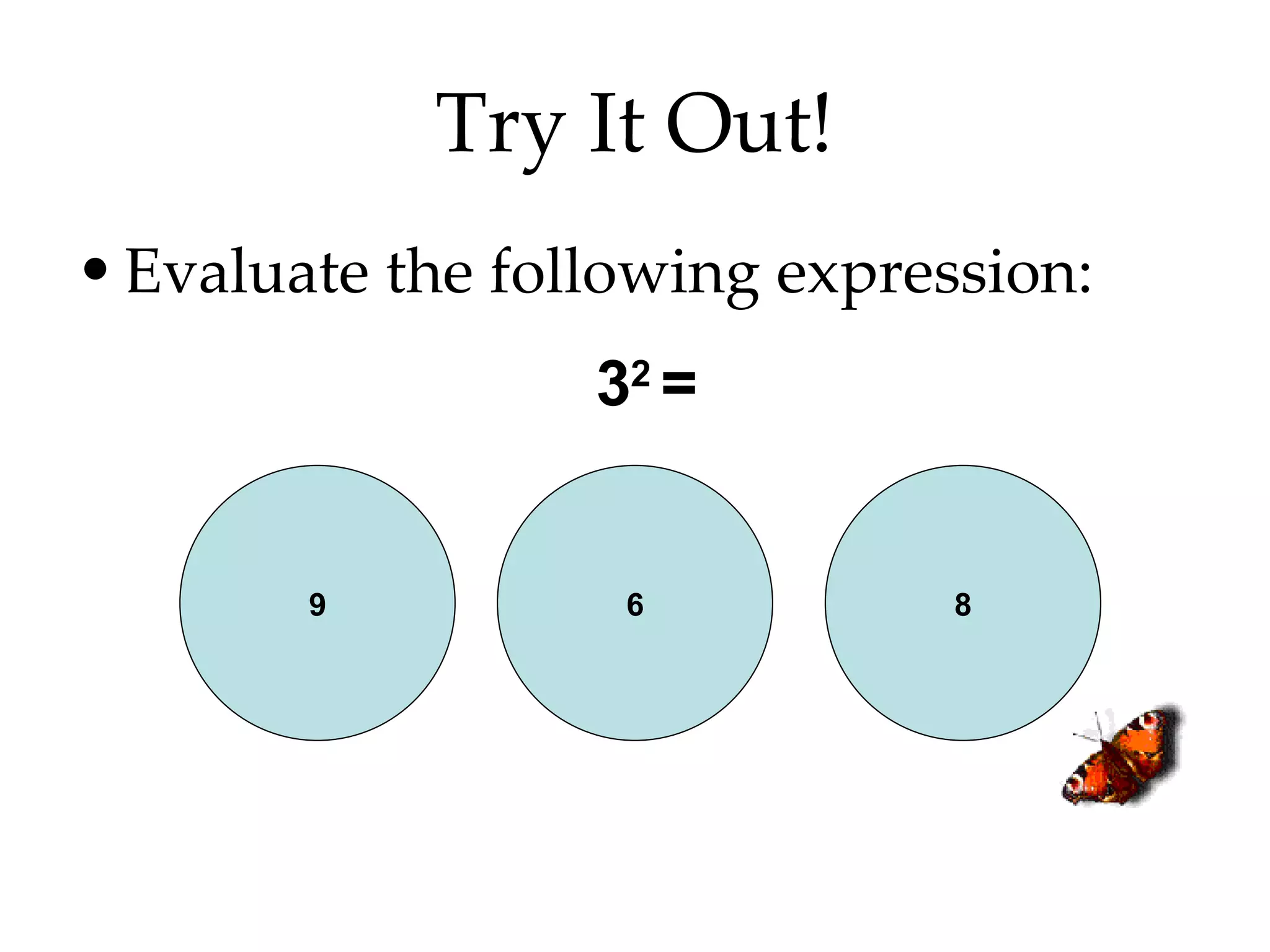
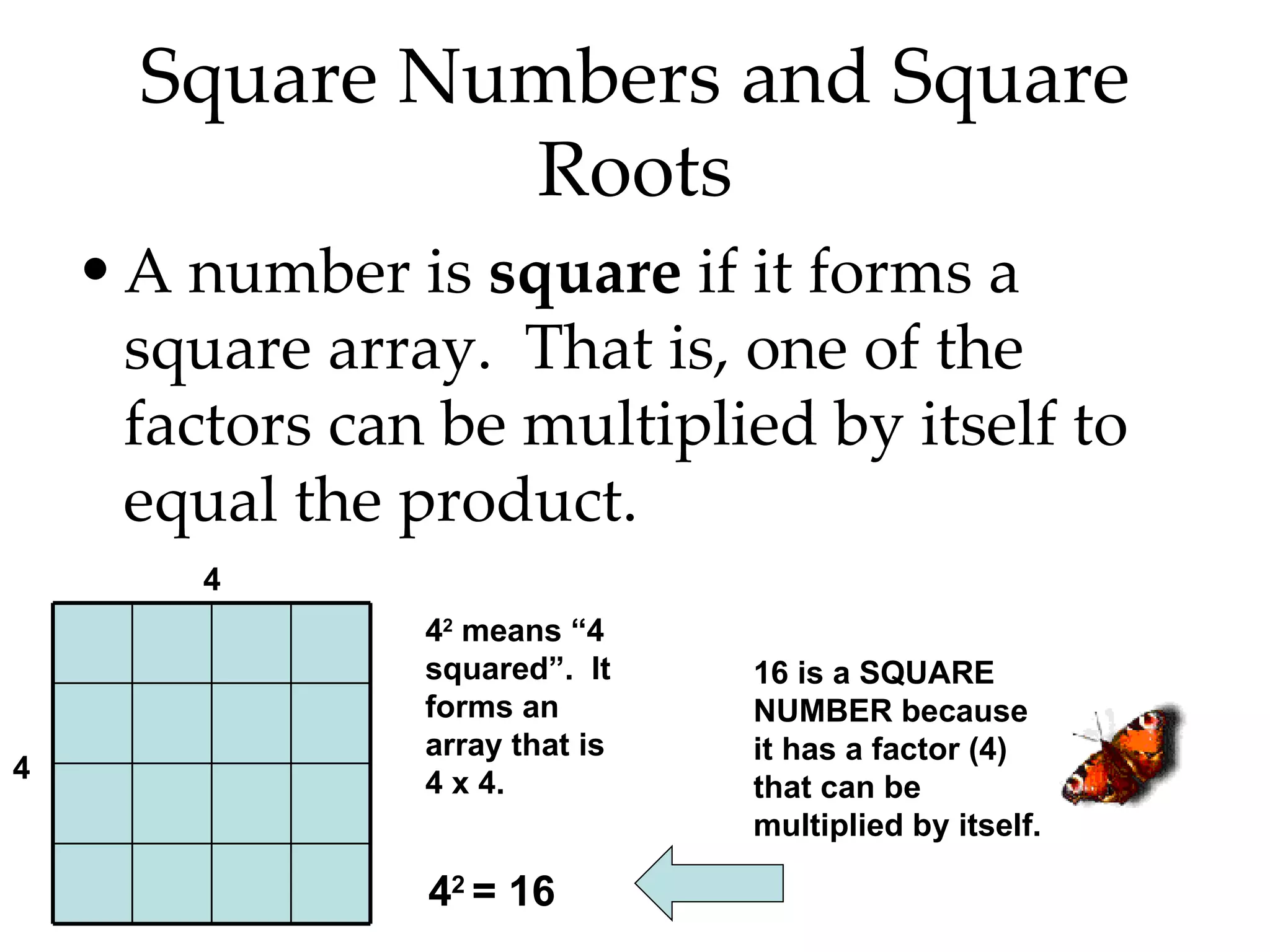
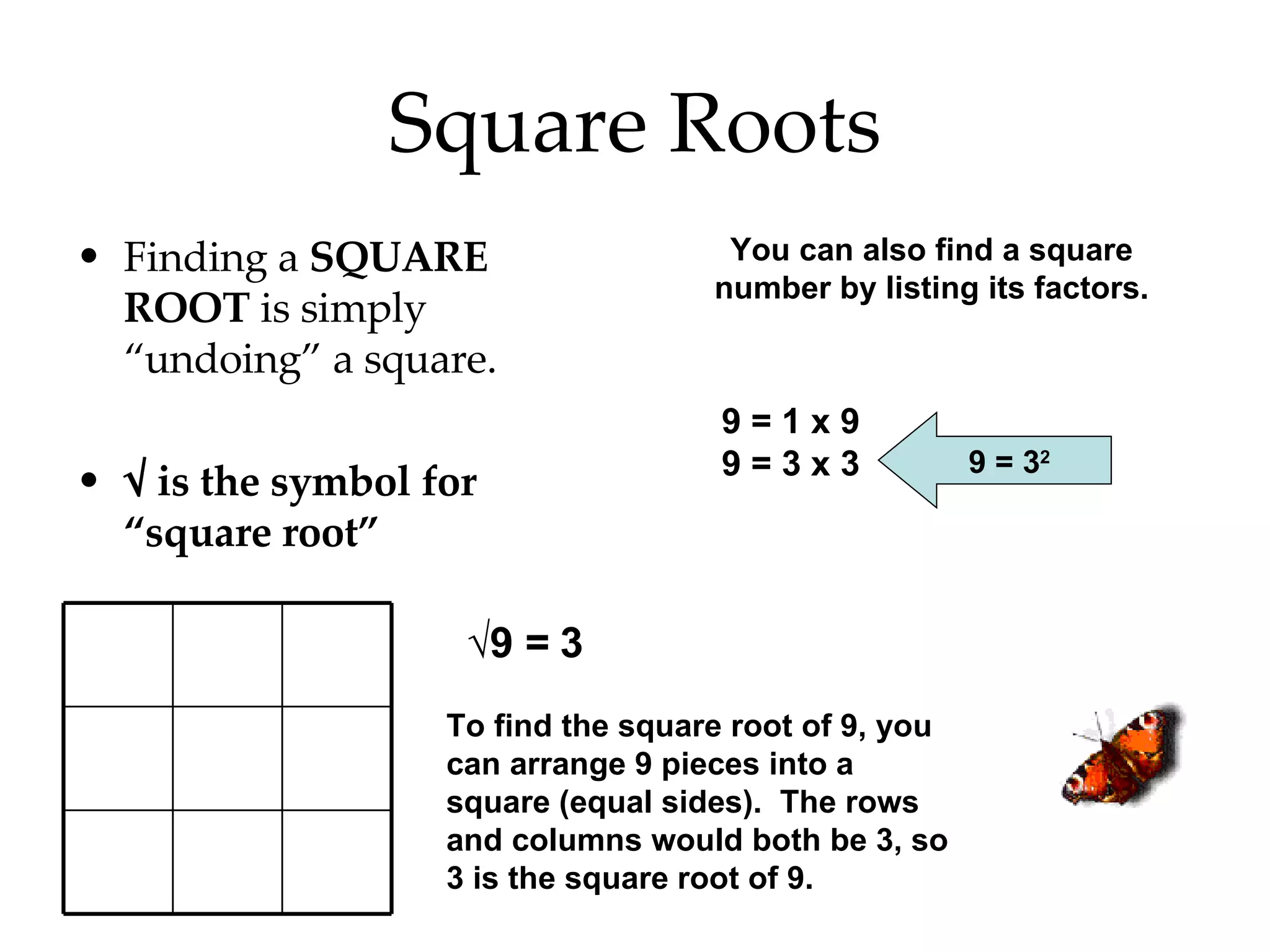
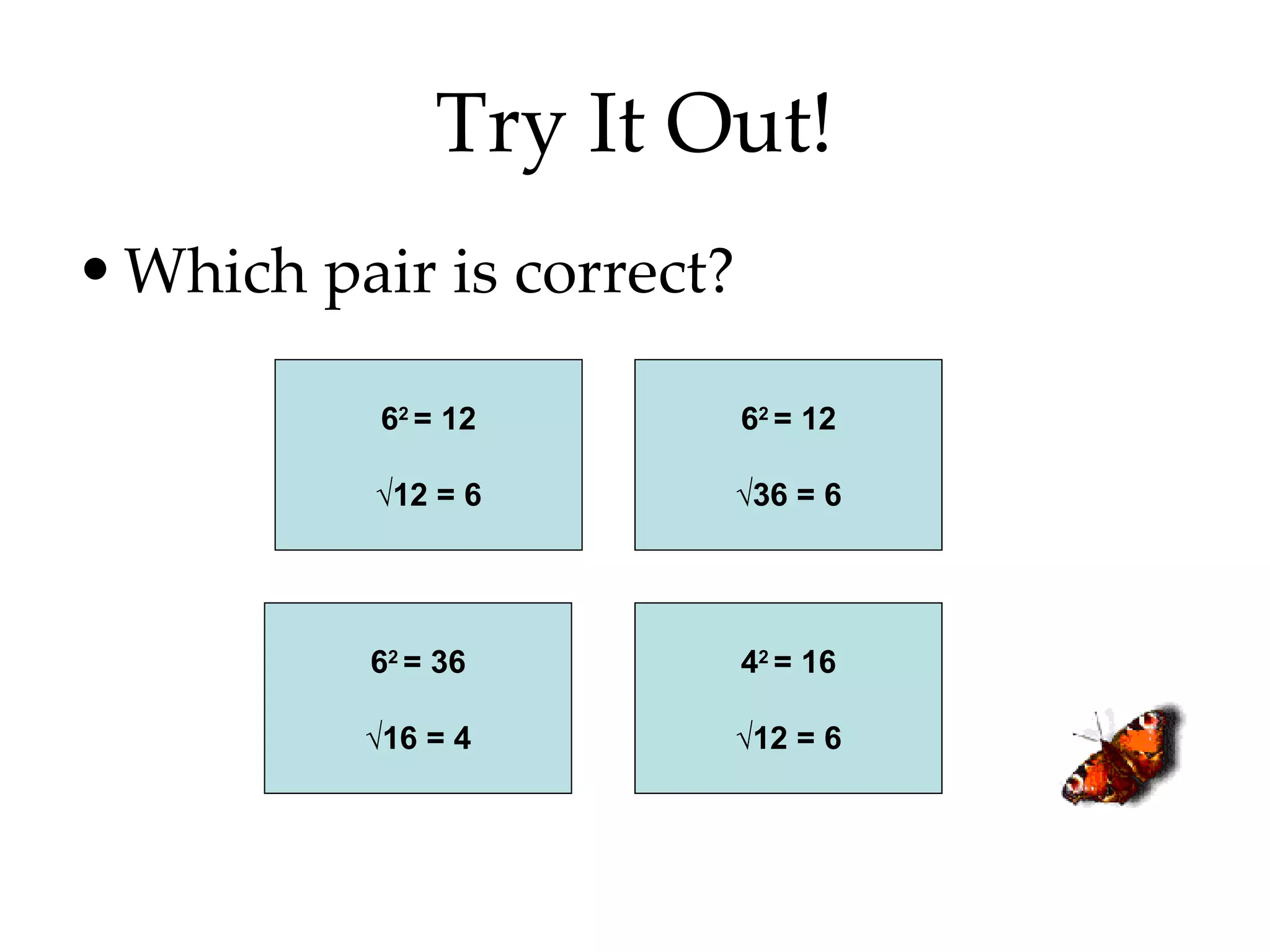
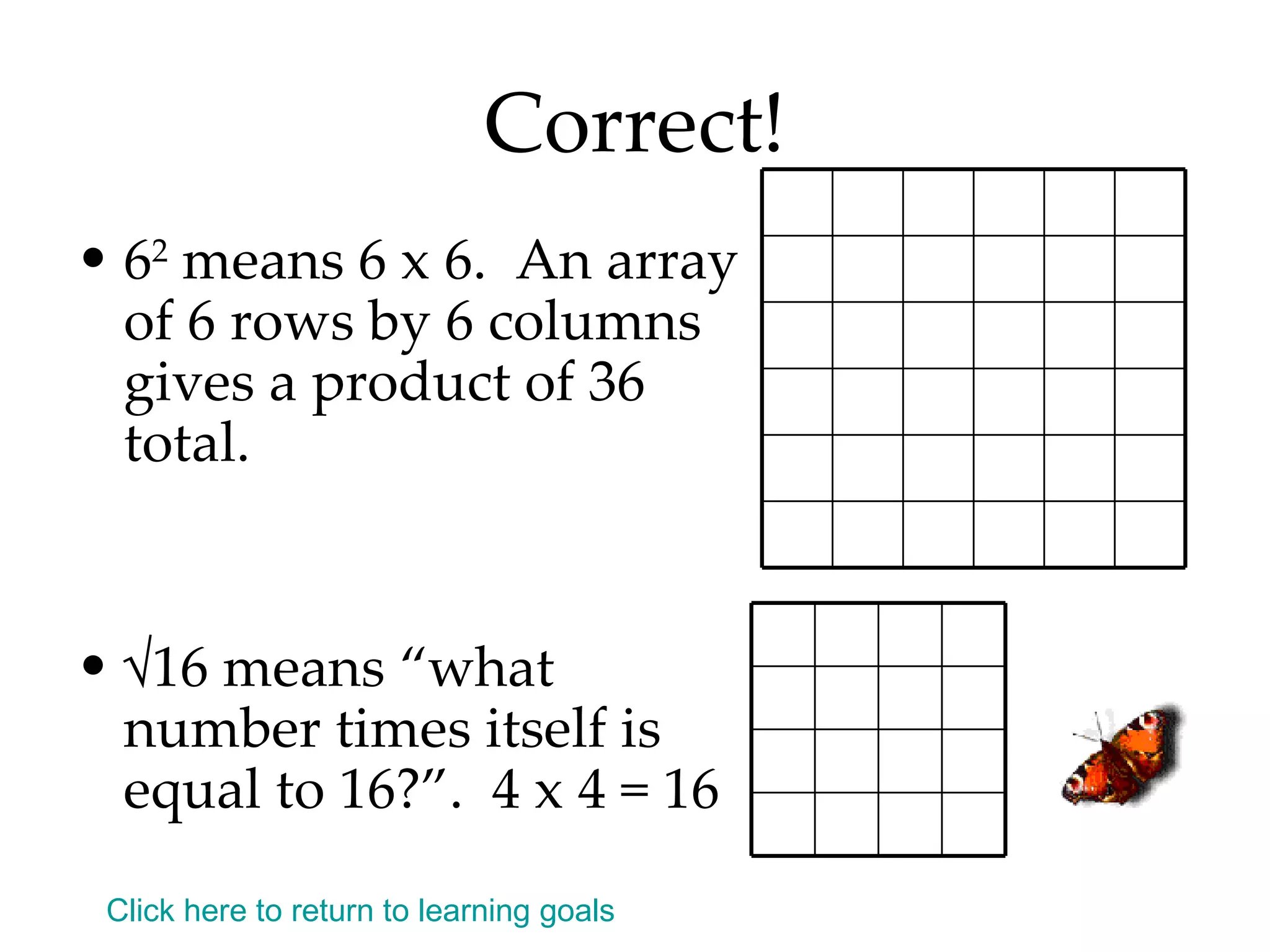
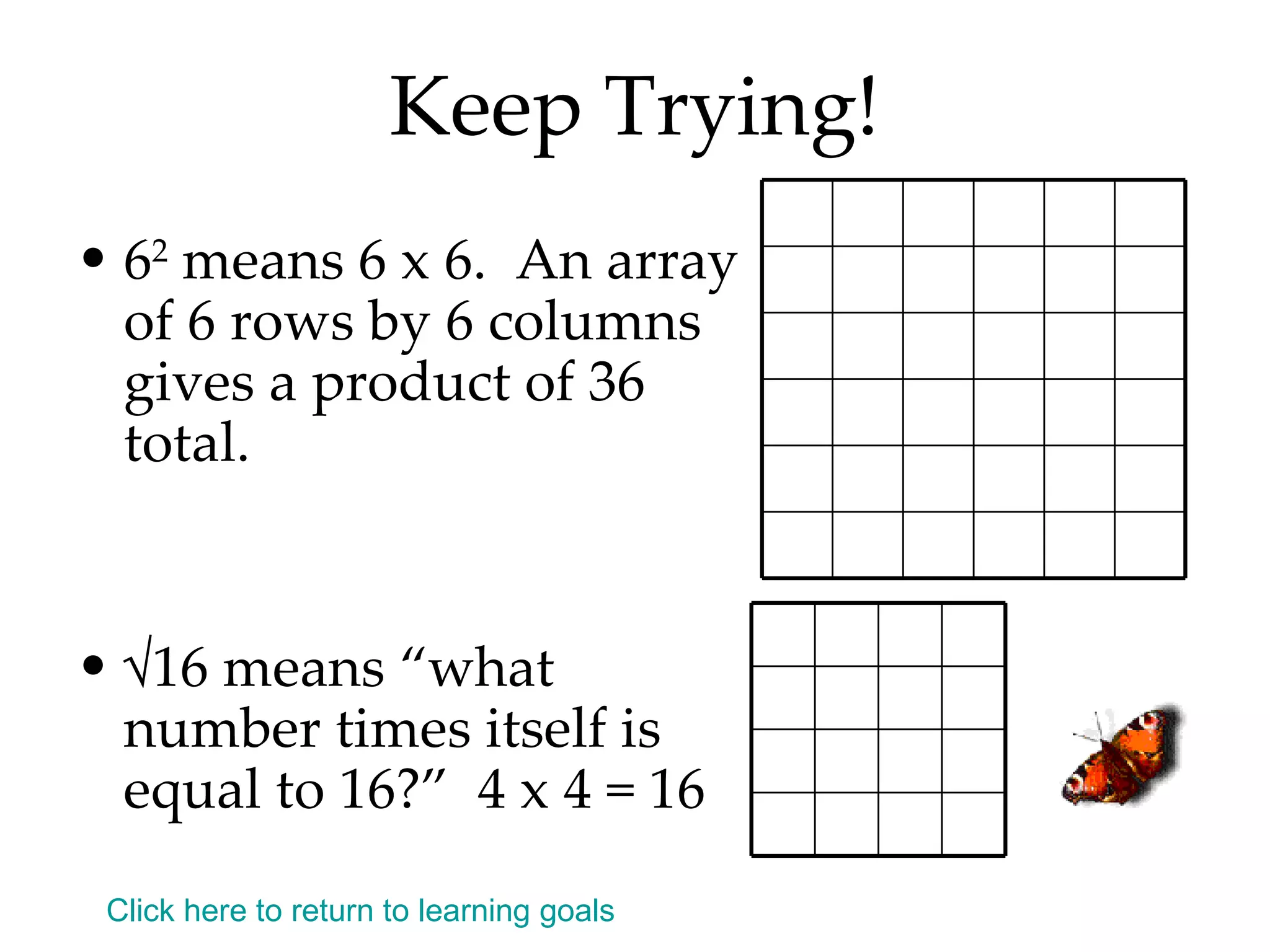
- Writing numbers in exponential notation and relating square numbers to their square roots