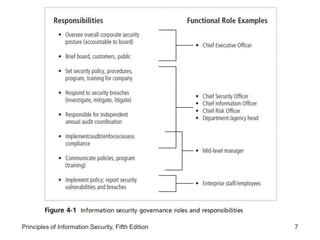
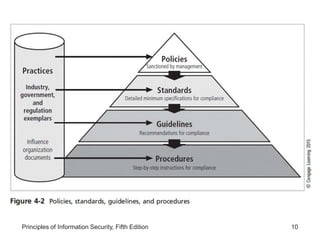
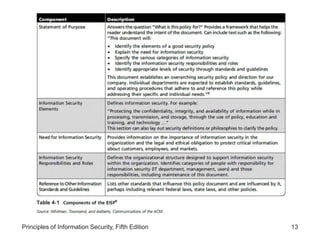
This document discusses information security planning and policy development. It describes management's role in developing, maintaining, and enforcing security policies, standards, procedures and guidelines. It explains that an information security blueprint identifies major components that support the security program. It also discusses how organizations institutionalize policies through education, training and awareness programs. Contingency planning relates to incident response, disaster recovery and business continuity plans. The document provides details on developing an enterprise security policy and issue-specific security policies. It emphasizes that policies must direct acceptable behavior and technologies and never contradict laws.