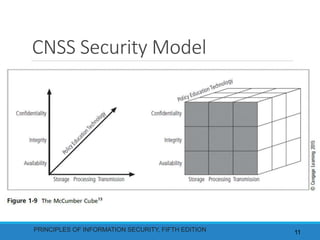
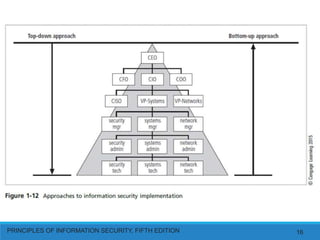
This document discusses the critical characteristics of information from a textbook on information security. It identifies seven key characteristics that provide value to information: availability, accuracy, authenticity, confidentiality, integrity, utility, and possession. Each characteristic is then defined in one or two paragraphs. The document also discusses components of an information system, balancing information security and access, and top-down and bottom-up approaches to implementing information security.