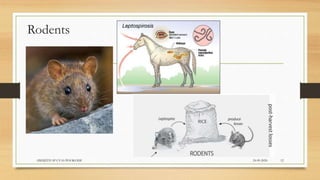
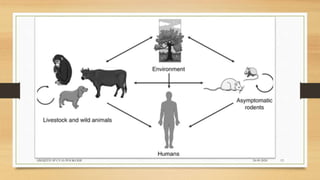
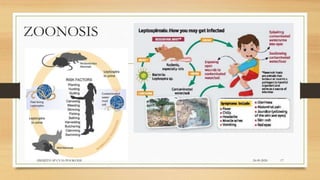
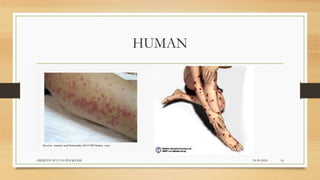
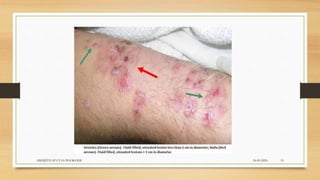
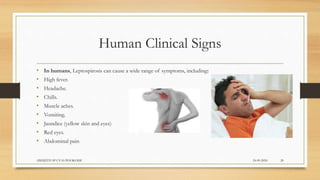
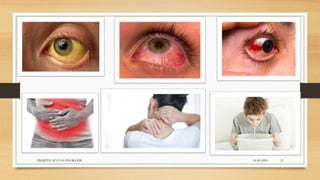
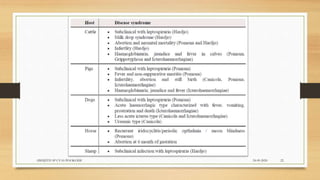
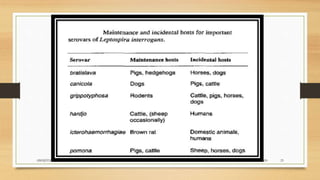
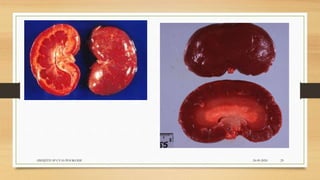
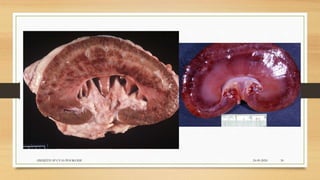
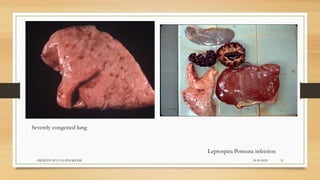
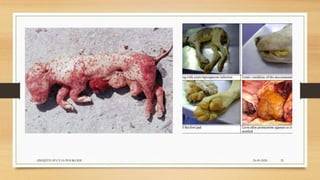
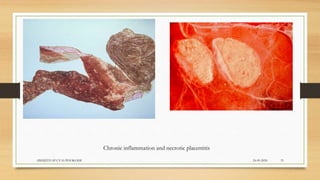
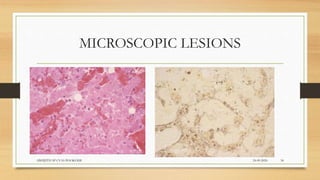
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic bacterial disease caused by Leptospira bacteria. It can infect both humans and animals through contact with infected urine. In humans it causes a range of symptoms from mild to severe. It is transmitted primarily through contact with infected animal urine, especially rodents. The disease affects millions annually worldwide, with symptoms varying between acute and chronic forms depending on the infecting strain. Diagnosis involves microscopy, culture and serological tests while treatment is with antibiotics such as penicillin. Prevention relies on proper hygiene and rodent control.