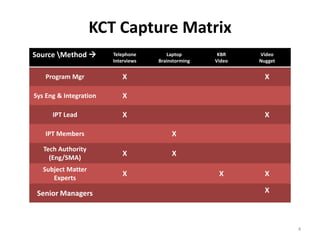
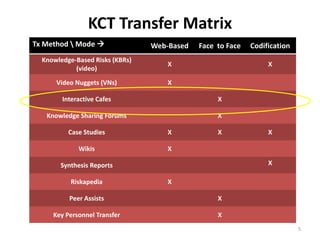
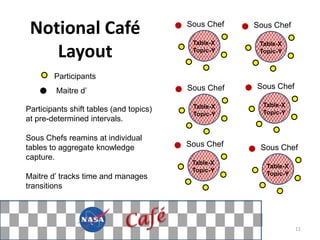
The document describes a knowledge management approach called KCT that was developed and implemented within NASA's Exploration Systems Mission Directorate. It discusses the four parts of the KCT approach: start-up, milestone-based, sustaining, and close-out activities. It also provides details on how knowledge is captured and transferred using various methods, including interviews, brainstorming sessions, videos, forums, and documentation. Finally, it outlines how knowledge cafes are an effective technique for innovation, detailing the process, requirements, documentation, and benefits of using knowledge cafes.