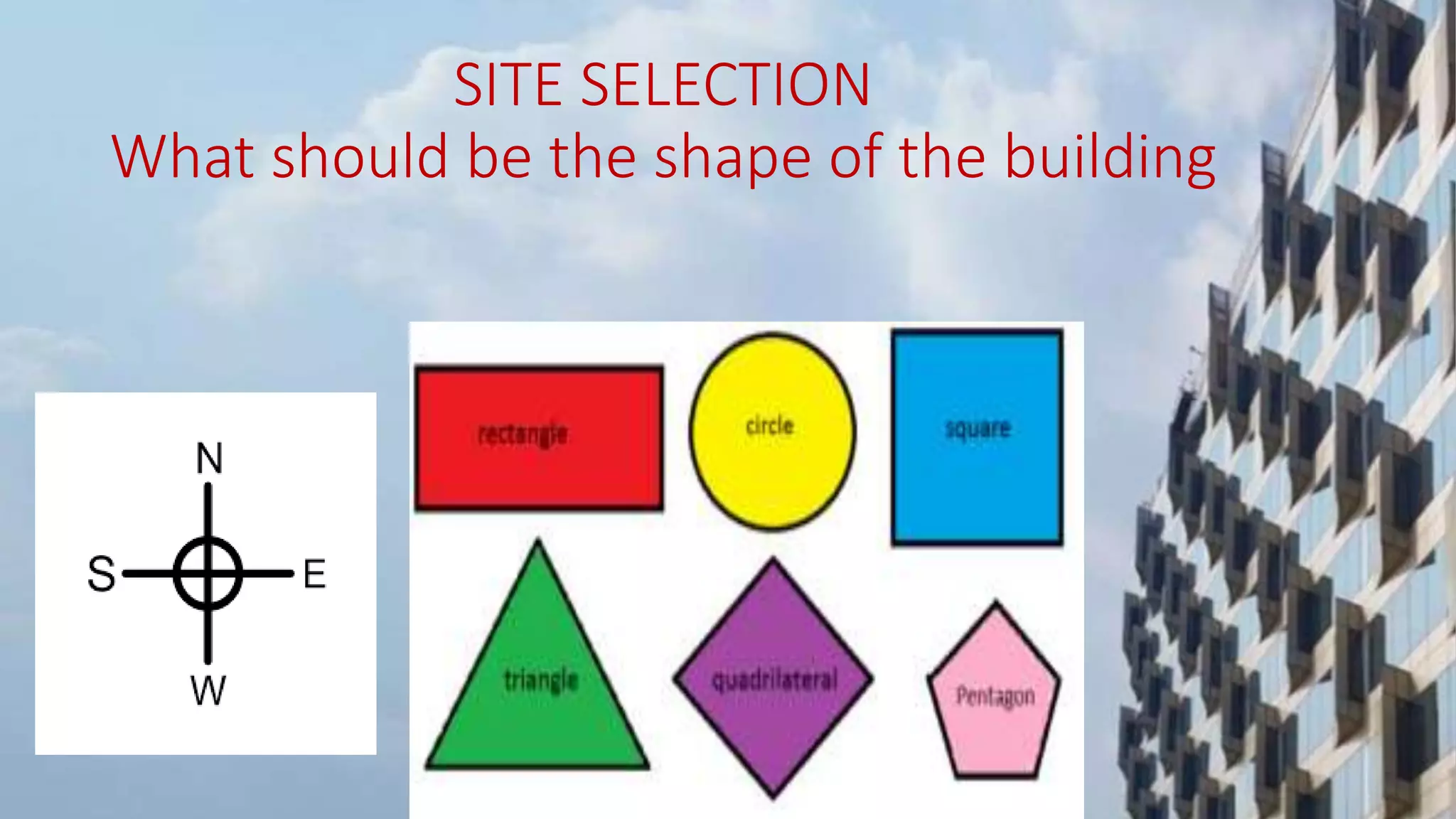
The document discusses sustainable design and construction practices for buildings seeking LEED certification. It covers several key areas: site selection and planning to maximize natural light and reduce energy needs; using sustainable materials like recycled content and rapidly renewable resources; implementing water and energy efficiency strategies like harvesting rainwater, using waterless urinals, and occupancy-sensor lighting; and overall strategies to reduce environmental impact and promote reuse and recycling. The goal is to develop buildings that conserve natural resources and minimize waste.