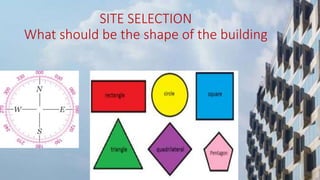
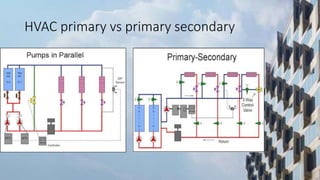
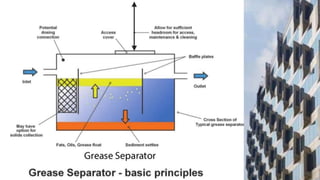
This document discusses sustainable building practices for LEED certification. It covers several main categories: site selection and planning, sustainable architecture and design, water conservation, energy efficiency, building materials, and indoor environmental quality. Specific topics covered include advantages of building orientation, daylighting, water efficiency through harvesting and recycling, energy efficient lighting and HVAC systems, and impacts of volatile organic compounds and fats/oils/grease on drainage systems.