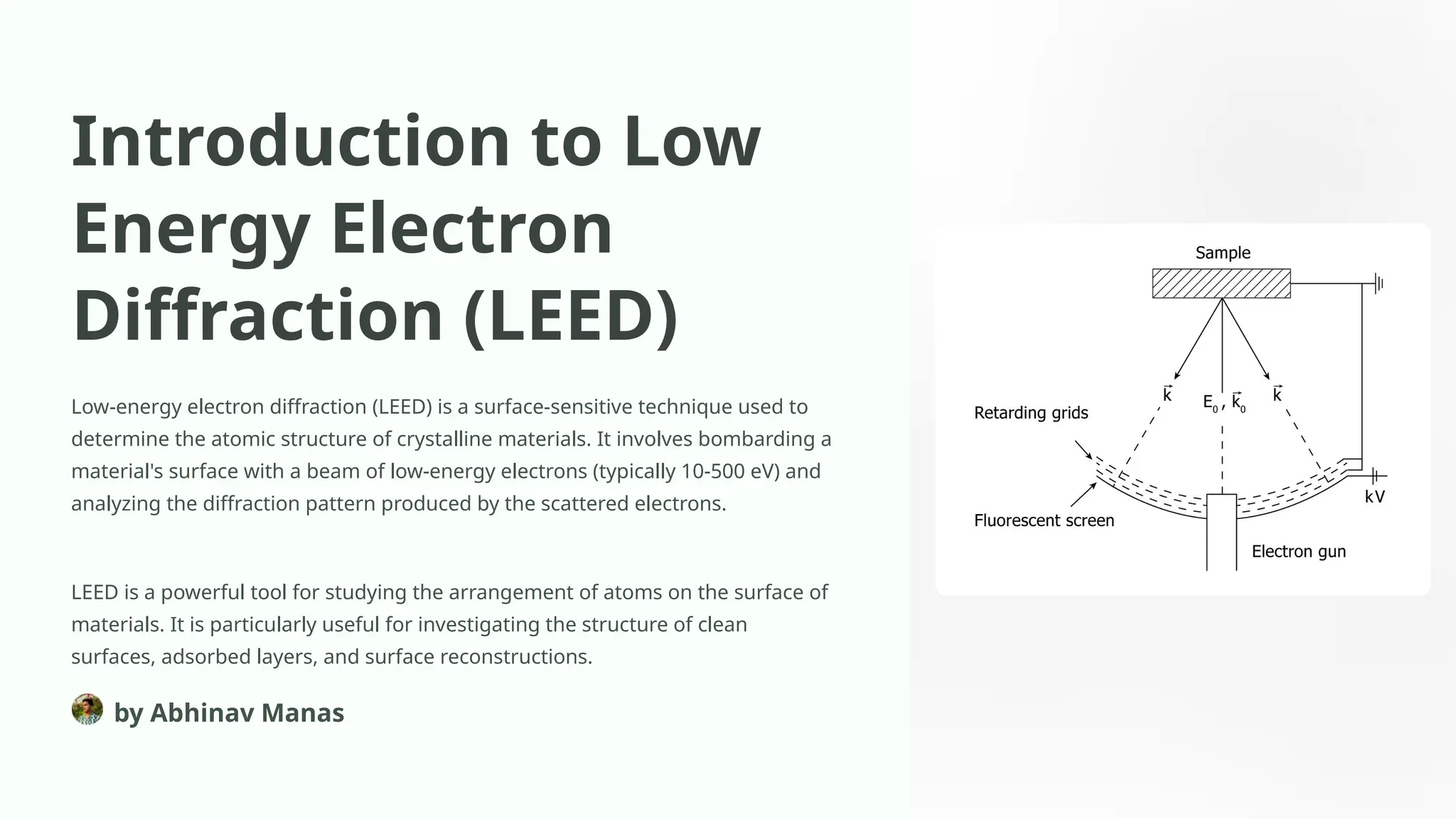
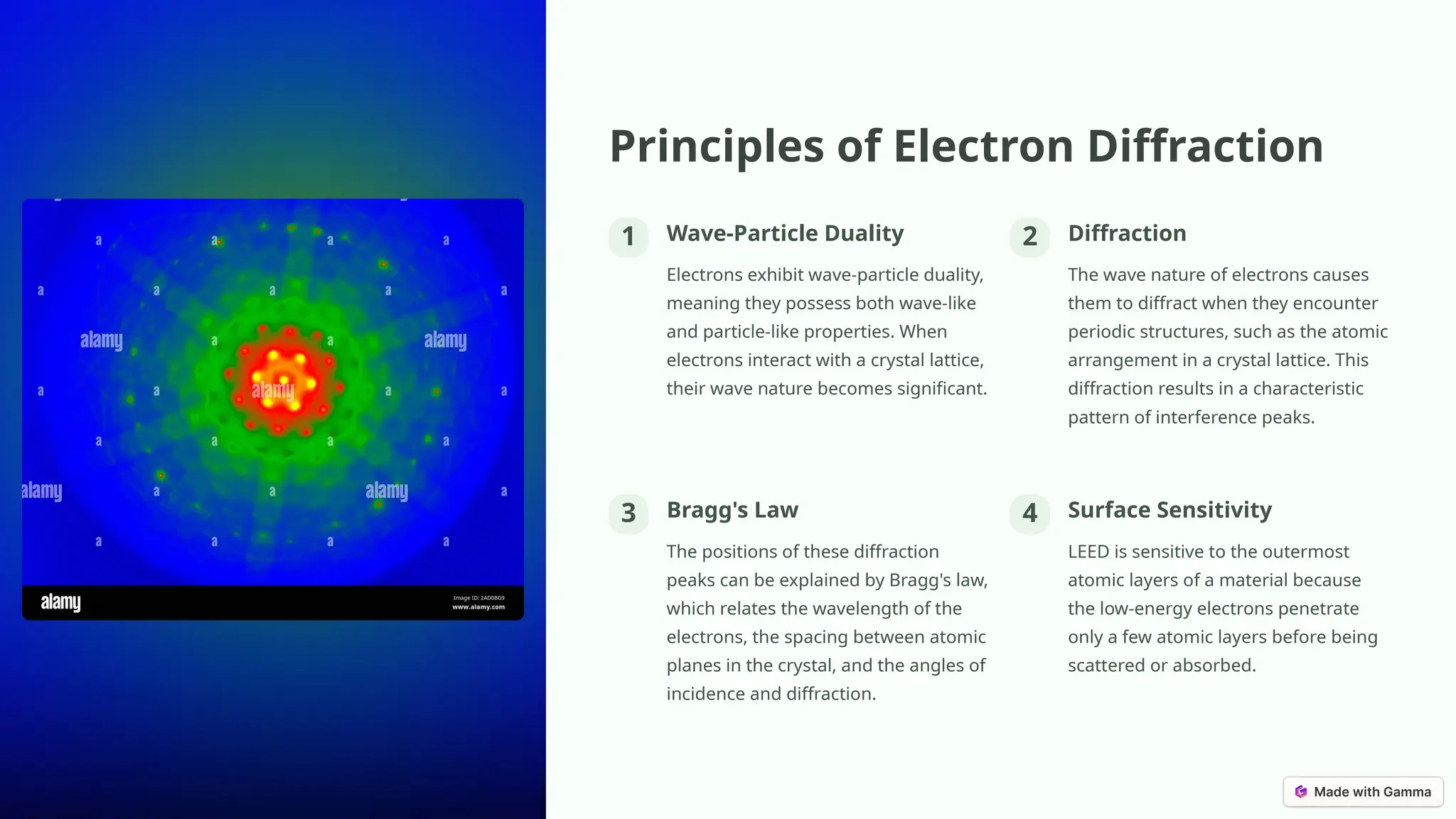
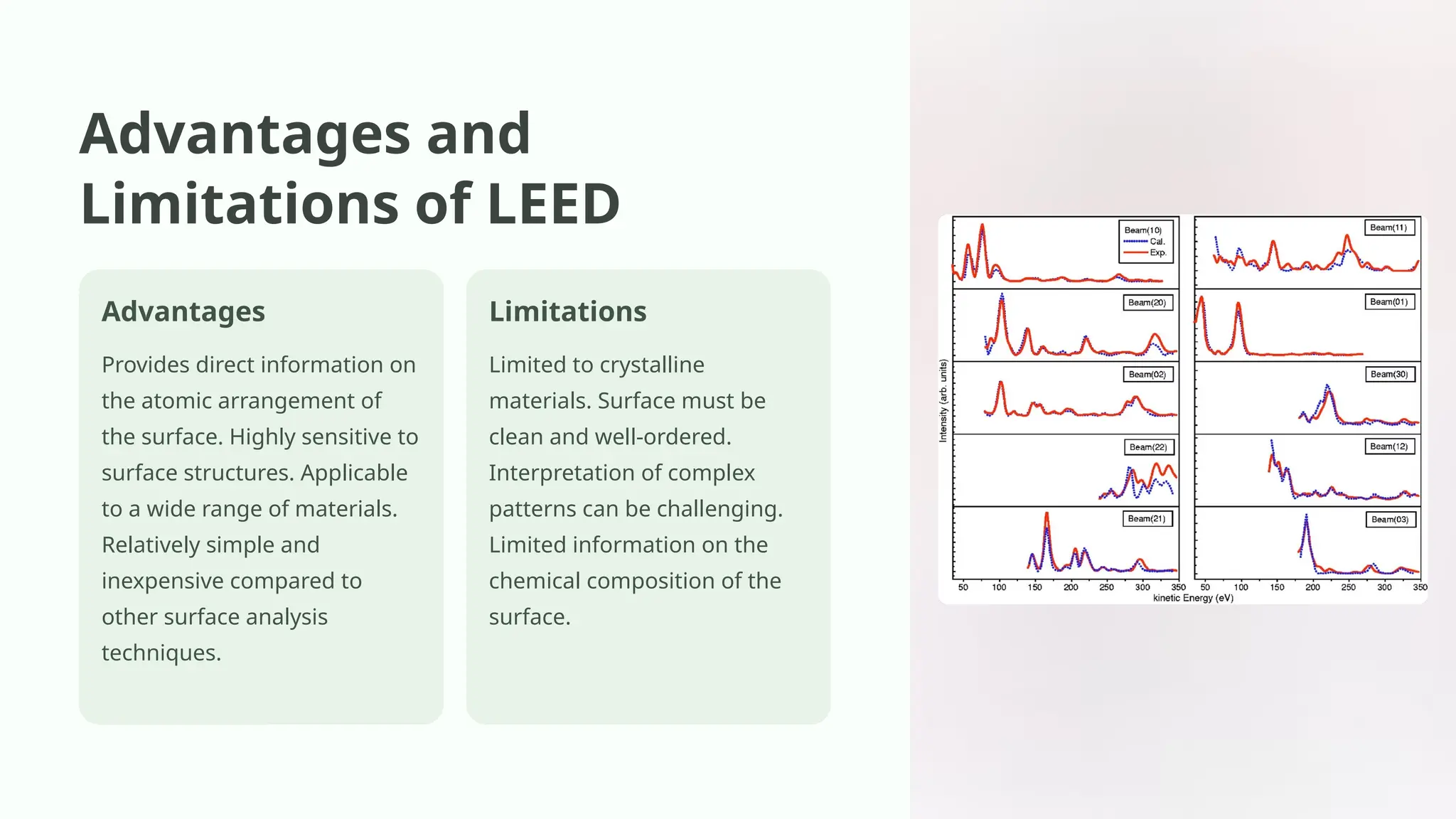
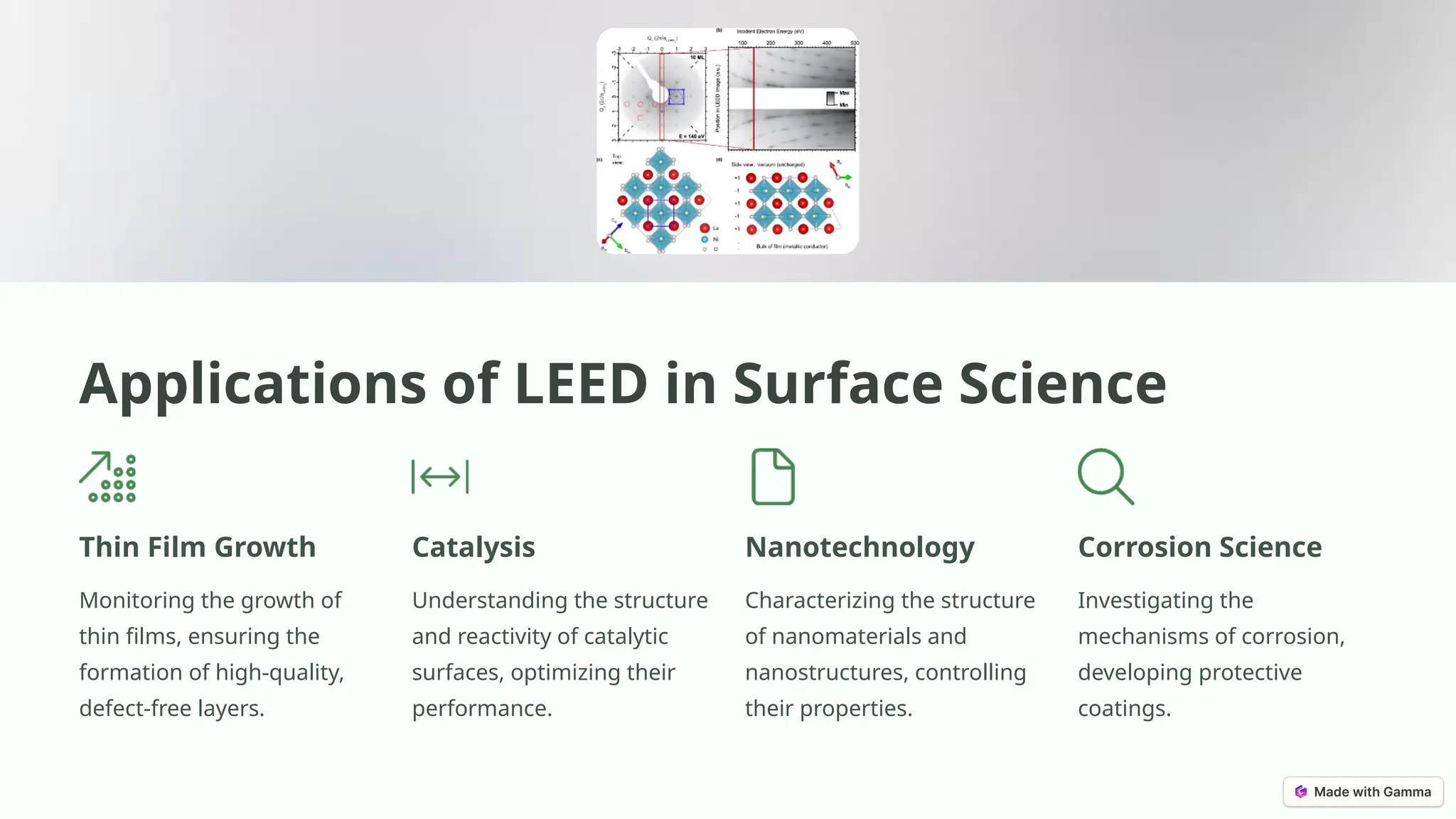
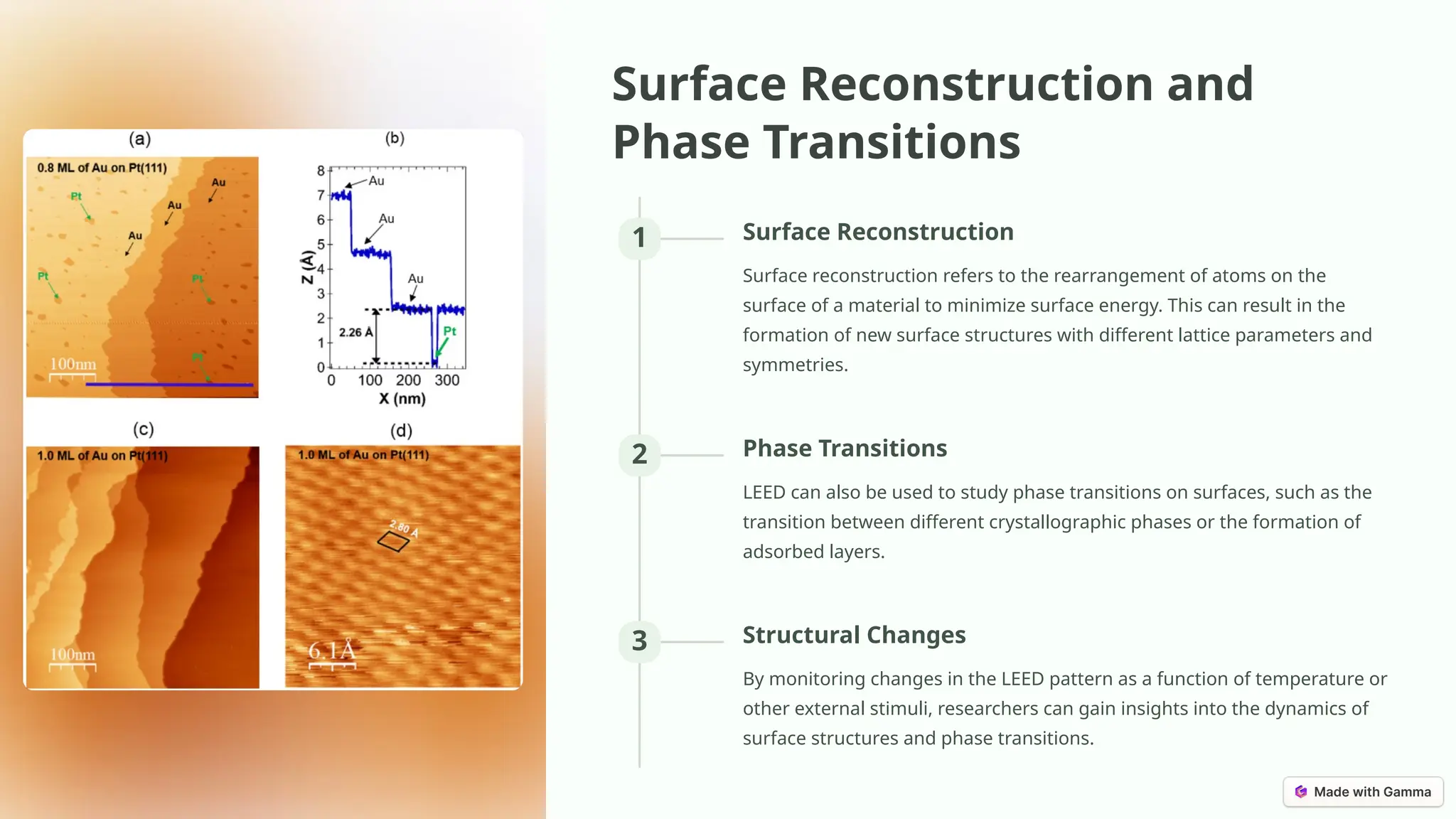
Low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) is a surface-sensitive technique for determining the atomic structure of crystalline materials by analyzing diffraction patterns from low-energy electrons. LEED provides insights into surface structures, including lattice parameters and defects, while being applicable to various materials despite limitations in interpretation and composition analysis. Recent advancements and future prospects focus on high-resolution techniques and the analysis of electronic structure and surface dynamics.